Vector databases specialize in storing and querying high-dimensional vectors, making them ideal for applications like image recognition, natural language processing, and recommendation systems. Key-value stores excel in fast, scalable retrieval of simple data pairs, frequently used in caching, session management, and real-time analytics. Explore the differences and use cases to determine which technology best suits your data management needs.
Why it is important
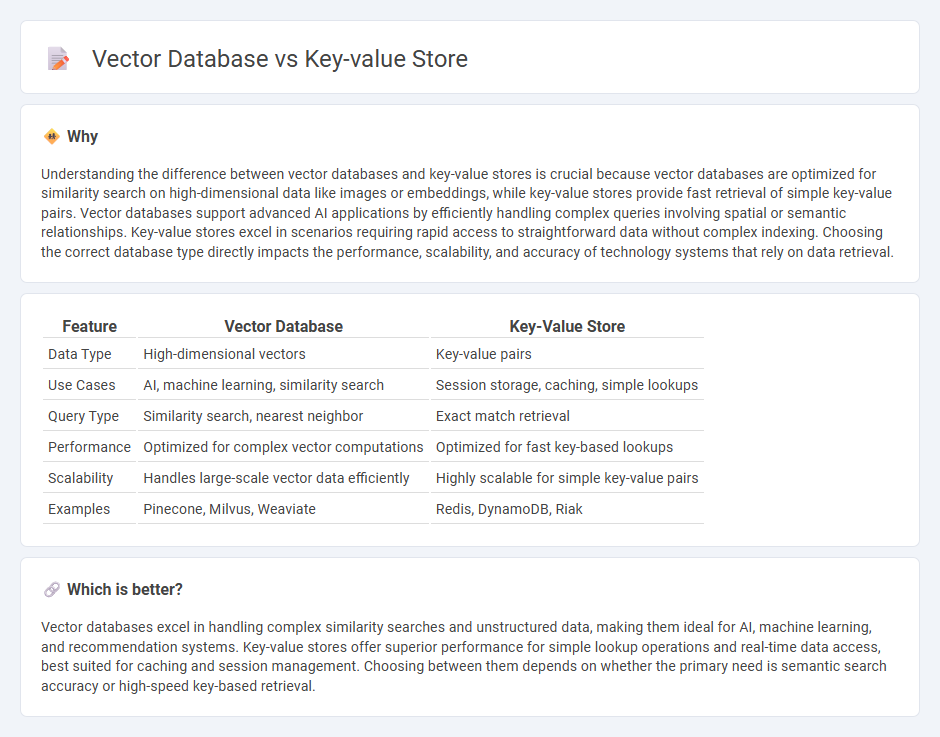
Understanding the difference between vector databases and key-value stores is crucial because vector databases are optimized for similarity search on high-dimensional data like images or embeddings, while key-value stores provide fast retrieval of simple key-value pairs. Vector databases support advanced AI applications by efficiently handling complex queries involving spatial or semantic relationships. Key-value stores excel in scenarios requiring rapid access to straightforward data without complex indexing. Choosing the correct database type directly impacts the performance, scalability, and accuracy of technology systems that rely on data retrieval.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Database | Key-Value Store |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | High-dimensional vectors | Key-value pairs |
| Use Cases | AI, machine learning, similarity search | Session storage, caching, simple lookups |
| Query Type | Similarity search, nearest neighbor | Exact match retrieval |
| Performance | Optimized for complex vector computations | Optimized for fast key-based lookups |
| Scalability | Handles large-scale vector data efficiently | Highly scalable for simple key-value pairs |
| Examples | Pinecone, Milvus, Weaviate | Redis, DynamoDB, Riak |
Which is better?
Vector databases excel in handling complex similarity searches and unstructured data, making them ideal for AI, machine learning, and recommendation systems. Key-value stores offer superior performance for simple lookup operations and real-time data access, best suited for caching and session management. Choosing between them depends on whether the primary need is semantic search accuracy or high-speed key-based retrieval.
Connection
Vector databases store high-dimensional vectors to enable efficient similarity search and machine learning applications, while key-value stores provide fast retrieval of data using unique keys. Vector databases often use key-value store principles to index and organize vectors, allowing rapid lookups by associating vector IDs (keys) with their corresponding data (values). This connection enhances performance in handling large-scale vector data, optimizing search capabilities in AI and recommendation systems.
Key Terms
Data Model
Key-value stores use a simple data model consisting of unique keys associated with corresponding values, optimized for fast retrieval of exact matches, ideal for caching and session management. Vector databases employ a high-dimensional vector space data model, enabling similarity search and machine learning applications by organizing data as mathematical vectors. Explore the detailed differences to understand which data model suits your specific application needs best.
Query Capability
Key-value stores excel in simple, high-speed retrieval where data is accessed using unique keys, supporting basic queries but lacking complex search functionalities. Vector databases optimize handling of high-dimensional data, enabling advanced similarity searches, nearest neighbor queries, and semantic search capability crucial for AI and machine learning applications. Explore the distinctions in query capabilities further to determine the best fit for your data retrieval needs.
Scalability
Key-value stores excel in horizontal scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes with simple key-based retrieval, supporting high-throughput applications. Vector databases maintain scalability while handling complex similarity searches on high-dimensional data by leveraging approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) algorithms and optimized indexing structures. Explore detailed scalability comparisons and use cases to understand which system best fits your large-scale data needs.
Source and External Links
What is a Key-Value Database? - Redis - A key-value store is a NoSQL database that uses unique keys and associated arbitrary values in a simple key-value pair format, optimized for high performance and scalability, differing from relational databases by not supporting complex queries on values, only on keys.
Key-value database - Wikipedia - A key-value store manages associative arrays or dictionaries by storing records as opaque data accessible solely via unique keys, offering flexibility and performance advantages over relational databases but limited querying capability.
What is a Key Value Database? - AWS - Key-value databases organize data as key-value pairs with each key uniquely identifying a value, providing flexible schemas and enabling efficient retrieval by key without requiring predefined relationships or complex queries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com