Quantum dot displays leverage semiconductor nanocrystals to produce vivid colors with higher brightness and energy efficiency compared to traditional plasma screens, which rely on ionized gas to create images. Plasma displays offer deeper blacks and wider viewing angles but consume more power and have shorter lifespans than quantum dot technology. Explore the advancements and benefits of these display technologies to understand which suits your needs best.
Why it is important
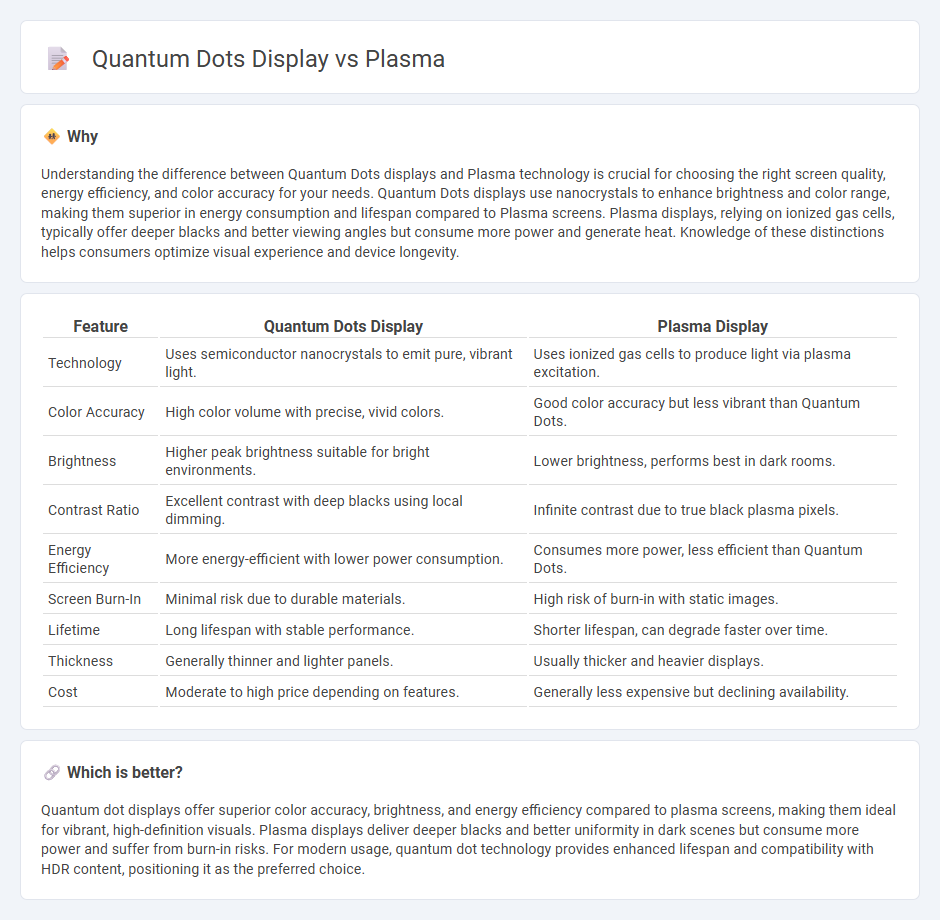
Understanding the difference between Quantum Dots displays and Plasma technology is crucial for choosing the right screen quality, energy efficiency, and color accuracy for your needs. Quantum Dots displays use nanocrystals to enhance brightness and color range, making them superior in energy consumption and lifespan compared to Plasma screens. Plasma displays, relying on ionized gas cells, typically offer deeper blacks and better viewing angles but consume more power and generate heat. Knowledge of these distinctions helps consumers optimize visual experience and device longevity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quantum Dots Display | Plasma Display |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses semiconductor nanocrystals to emit pure, vibrant light. | Uses ionized gas cells to produce light via plasma excitation. |
| Color Accuracy | High color volume with precise, vivid colors. | Good color accuracy but less vibrant than Quantum Dots. |
| Brightness | Higher peak brightness suitable for bright environments. | Lower brightness, performs best in dark rooms. |
| Contrast Ratio | Excellent contrast with deep blacks using local dimming. | Infinite contrast due to true black plasma pixels. |
| Energy Efficiency | More energy-efficient with lower power consumption. | Consumes more power, less efficient than Quantum Dots. |
| Screen Burn-In | Minimal risk due to durable materials. | High risk of burn-in with static images. |
| Lifetime | Long lifespan with stable performance. | Shorter lifespan, can degrade faster over time. |
| Thickness | Generally thinner and lighter panels. | Usually thicker and heavier displays. |
| Cost | Moderate to high price depending on features. | Generally less expensive but declining availability. |
Which is better?
Quantum dot displays offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency compared to plasma screens, making them ideal for vibrant, high-definition visuals. Plasma displays deliver deeper blacks and better uniformity in dark scenes but consume more power and suffer from burn-in risks. For modern usage, quantum dot technology provides enhanced lifespan and compatibility with HDR content, positioning it as the preferred choice.
Connection
Quantum dot displays utilize semiconductor nanocrystals that emit precise colors when exposed to light, enhancing color accuracy and brightness compared to traditional Plasma displays. Plasma technology relies on ionized gas cells to produce images through ultraviolet light exciting phosphors, resulting in rich colors but lower energy efficiency. Both technologies aim to improve visual quality, yet quantum dots offer superior color precision and energy savings in modern display panels.
Key Terms
Emissive vs. Non-emissive
Plasma displays are emissive, generating light through ionized gas cells that produce vibrant colors and deep blacks, ideal for high-contrast viewing. Quantum dot displays, typically non-emissive, rely on an LED backlight combined with semiconductor nanocrystals to enhance color accuracy and brightness while maintaining energy efficiency. Explore the detailed differences in display technologies and their impact on image quality and performance.
Color Gamut
Quantum dots displays offer a wider color gamut compared to plasma screens, reaching up to 90-100% of the DCI-P3 color space, which results in more vibrant and accurate colors. Plasma displays typically cover around 60-70% of the DCI-P3 spectrum, limiting their color richness and saturation. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these technologies impact your viewing experience.
Energy Efficiency
Quantum dot displays outperform plasma in energy efficiency due to their enhanced light emission and precise color control, resulting in lower power consumption for the same brightness level. Plasma screens generally consume more energy because their technology relies on ionized gas cells that emit light less efficiently. Explore detailed comparisons of plasma and quantum dot displays to make an informed energy-saving choice.
Source and External Links
Plasma - Encyclopedia - University of Rochester Medical Center - Plasma is the largest part of blood, making up about 55%, consisting of a light yellow liquid that carries nutrients, hormones, proteins, and waste throughout the body, and contains important components like antibodies and clotting factors used in life-saving treatments.
What Is Plasma? Plasma Donation & Importance - Cleveland Clinic - Plasma is the pale, yellowish liquid portion of blood, about 55% of blood volume, formed by water combined with electrolytes and proteins, and serves as a carrier fluid for blood cells and vital substances.
Plasma Information - Red Cross Blood Donation - Plasma is the liquid component of blood, about 92% water and 7% proteins, which maintains blood pressure, carries electrolytes, supplies clotting and immunity proteins, and supports proper pH balance in the body.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com