Ambient intelligence integrates artificial intelligence into everyday environments to create responsive, context-aware spaces that enhance user experience seamlessly. Unlike traditional artificial intelligence, ambient intelligence emphasizes invisibility and adaptability in smart homes, workplaces, and cities. Explore this evolving intersection to understand how these technologies are shaping the future of interaction and automation.
Why it is important
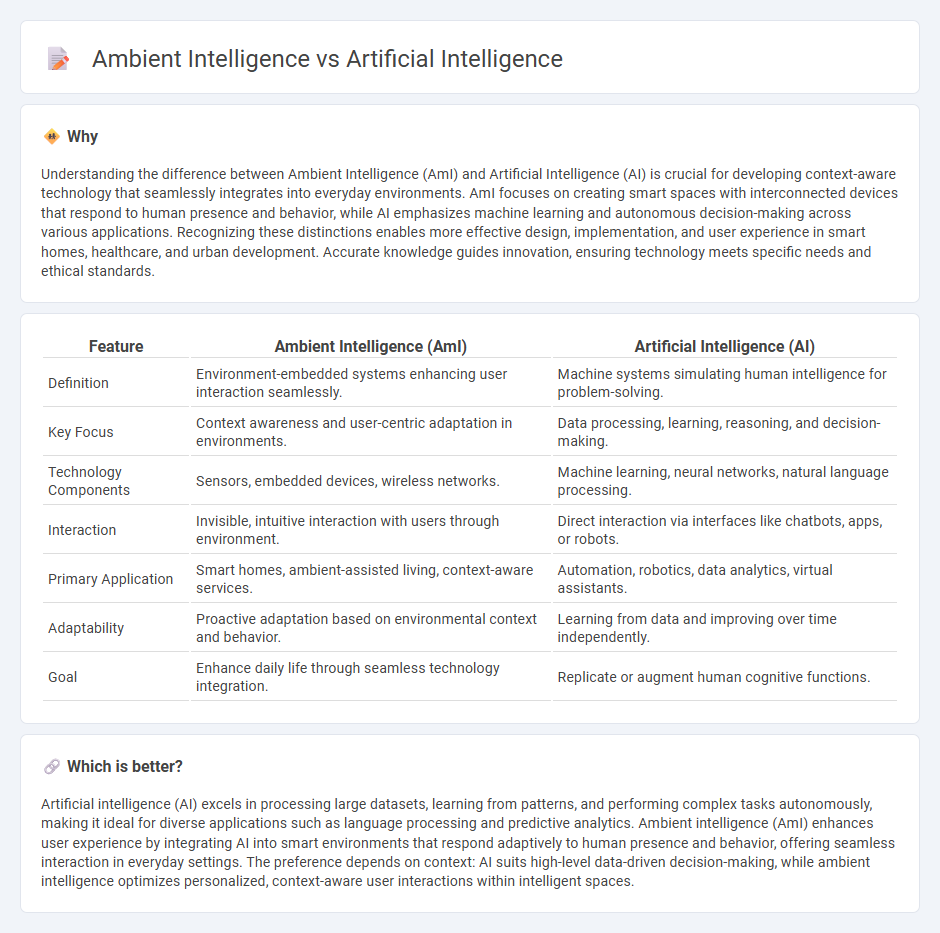
Understanding the difference between Ambient Intelligence (AmI) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is crucial for developing context-aware technology that seamlessly integrates into everyday environments. AmI focuses on creating smart spaces with interconnected devices that respond to human presence and behavior, while AI emphasizes machine learning and autonomous decision-making across various applications. Recognizing these distinctions enables more effective design, implementation, and user experience in smart homes, healthcare, and urban development. Accurate knowledge guides innovation, ensuring technology meets specific needs and ethical standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ambient Intelligence (AmI) | Artificial Intelligence (AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Environment-embedded systems enhancing user interaction seamlessly. | Machine systems simulating human intelligence for problem-solving. |
| Key Focus | Context awareness and user-centric adaptation in environments. | Data processing, learning, reasoning, and decision-making. |
| Technology Components | Sensors, embedded devices, wireless networks. | Machine learning, neural networks, natural language processing. |
| Interaction | Invisible, intuitive interaction with users through environment. | Direct interaction via interfaces like chatbots, apps, or robots. |
| Primary Application | Smart homes, ambient-assisted living, context-aware services. | Automation, robotics, data analytics, virtual assistants. |
| Adaptability | Proactive adaptation based on environmental context and behavior. | Learning from data and improving over time independently. |
| Goal | Enhance daily life through seamless technology integration. | Replicate or augment human cognitive functions. |
Which is better?
Artificial intelligence (AI) excels in processing large datasets, learning from patterns, and performing complex tasks autonomously, making it ideal for diverse applications such as language processing and predictive analytics. Ambient intelligence (AmI) enhances user experience by integrating AI into smart environments that respond adaptively to human presence and behavior, offering seamless interaction in everyday settings. The preference depends on context: AI suits high-level data-driven decision-making, while ambient intelligence optimizes personalized, context-aware user interactions within intelligent spaces.
Connection
Ambient intelligence (AmI) integrates artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to create environments responsive to human presence and behavior. AI algorithms process data collected from sensors and devices, enabling AmI systems to adapt contextually in real-time. This synergy enhances user experience by providing intelligent automation and personalized interactions within smart homes, cities, and workplaces.
Key Terms
Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses machine learning algorithms that enable systems to analyze data, recognize patterns, and make predictions, driving autonomous decision-making in diverse applications. Ambient intelligence (AmI) integrates AI with sensor networks and context-aware computing to create environments that adapt intelligently to user needs and behaviors in real time. Explore deeper insights into how machine learning differentiates and unites AI and AmI in transforming technology experiences.
Context Awareness
Artificial intelligence (AI) excels in processing large datasets and learning patterns to make decisions, while ambient intelligence (AmI) emphasizes seamless, context-aware interactions within smart environments. Context awareness in AmI involves real-time sensing and adaptation to users' behaviors, preferences, and environmental changes, creating personalized and intuitive experiences. Discover how context-aware technologies in AI and AmI are revolutionizing smart living and user-centric applications.
Ubiquitous Computing
Artificial intelligence (AI) enables machines to perform tasks requiring human intelligence, while ambient intelligence (AmI) integrates AI into environments to create context-aware, adaptive systems in ubiquitous computing. Ubiquitous computing embeds computational capability into everyday objects, allowing AmI to enhance user experience seamlessly by responding to real-time data and user behavior. Discover more about the intersection of AI, AmI, and ubiquitous computing for future smart environments.
Source and External Links
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? | Google Cloud - Artificial intelligence is a set of technologies enabling computers to perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, including image analysis, speech recognition, and data analytics, largely based on machine learning and deep learning techniques applied to vast data sets.
Artificial intelligence - Wikipedia - Artificial intelligence (AI) is the computational capability to perform human intelligence tasks such as learning, reasoning, perception, and decision-making, used in advanced web searches, virtual assistants, autonomous vehicles, and more, with foundations in computer science and related disciplines.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): What it is and why it matters - SAS - AI enables machines to learn from experience and adjust to new inputs using algorithms and large data, covering fields like machine learning, neural networks, deep learning, computer vision, and natural language processing to perform tasks such as image and speech recognition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com