Ambient intelligence integrates advanced sensors and artificial intelligence into environments to create responsive, context-aware systems enhancing daily life. Wearable technology focuses on personal devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers that monitor health metrics and provide seamless connectivity. Explore how these innovative technologies are transforming human interaction and lifestyle efficiency.
Why it is important
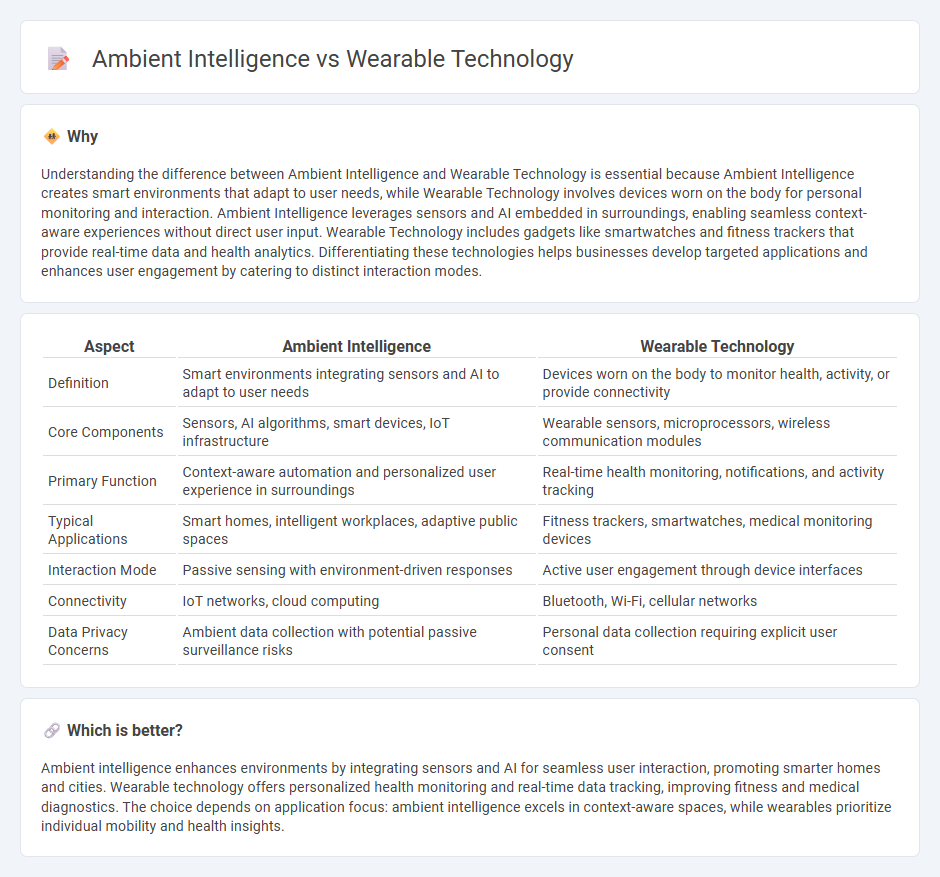
Understanding the difference between Ambient Intelligence and Wearable Technology is essential because Ambient Intelligence creates smart environments that adapt to user needs, while Wearable Technology involves devices worn on the body for personal monitoring and interaction. Ambient Intelligence leverages sensors and AI embedded in surroundings, enabling seamless context-aware experiences without direct user input. Wearable Technology includes gadgets like smartwatches and fitness trackers that provide real-time data and health analytics. Differentiating these technologies helps businesses develop targeted applications and enhances user engagement by catering to distinct interaction modes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ambient Intelligence | Wearable Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smart environments integrating sensors and AI to adapt to user needs | Devices worn on the body to monitor health, activity, or provide connectivity |
| Core Components | Sensors, AI algorithms, smart devices, IoT infrastructure | Wearable sensors, microprocessors, wireless communication modules |
| Primary Function | Context-aware automation and personalized user experience in surroundings | Real-time health monitoring, notifications, and activity tracking |
| Typical Applications | Smart homes, intelligent workplaces, adaptive public spaces | Fitness trackers, smartwatches, medical monitoring devices |
| Interaction Mode | Passive sensing with environment-driven responses | Active user engagement through device interfaces |
| Connectivity | IoT networks, cloud computing | Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, cellular networks |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Ambient data collection with potential passive surveillance risks | Personal data collection requiring explicit user consent |
Which is better?
Ambient intelligence enhances environments by integrating sensors and AI for seamless user interaction, promoting smarter homes and cities. Wearable technology offers personalized health monitoring and real-time data tracking, improving fitness and medical diagnostics. The choice depends on application focus: ambient intelligence excels in context-aware spaces, while wearables prioritize individual mobility and health insights.
Connection
Ambient intelligence integrates sensors and devices within environments to create adaptive, context-aware systems that respond to user needs seamlessly. Wearable technology acts as a key component by continuously collecting real-time biometric and behavioral data, enabling ambient intelligence systems to personalize interactions and enhance user experiences. This synergy enhances smart environments in healthcare, fitness, and daily living through proactive monitoring and responsive adjustments.
Key Terms
Sensors
Wearable technology integrates advanced sensors directly on the body, enabling real-time monitoring of physiological signals such as heart rate, temperature, and movement patterns. Ambient intelligence relies on an array of interconnected environmental sensors embedded in living spaces to detect and interpret contextual data for adaptive responses. Explore how these sensor systems redefine human-environment interaction and health monitoring by learning more about their distinct capabilities and applications.
Context-awareness
Wearable technology offers personalized context-awareness by continuously monitoring physiological and environmental data through sensors embedded in smartwatches and fitness trackers, enabling real-time health analytics and adaptive user interfaces. Ambient intelligence integrates context-aware computing into environments using interconnected devices, such as smart homes equipped with sensors and AI, to proactively respond to occupants' needs without direct user intervention. Explore further to understand how these technologies reshape human-computer interaction through context-aware innovation.
Ubiquitous computing
Wearable technology integrates computational devices directly onto the body, enabling real-time data collection and personalized user interaction through sensors, smart fabrics, and embedded processors. Ambient intelligence, through ubiquitous computing frameworks, leverages environments embedded with interconnected devices and context-aware systems to seamlessly respond to human presence and activities. Explore more to understand how these paradigms shape the future of human-computer interaction and ambient experiences.
Source and External Links
Wearable technology - Wearable technology refers to electronic devices designed to be worn on the body, like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smartglasses, which collect data such as vital signs and activity levels, often providing real-time biofeedback and connectivity through the Internet of Things for uses ranging from health monitoring to communication.
What is Wearable Technology? Definition, Uses and Examples - Wearable technology includes a range of devices such as smartwatches, VR headsets, medical sensors, and smart jewelry, equipped with microprocessors and connectivity that enable tracking of bodily movements, biometric data, and environmental information to support health, fitness, and entertainment applications.
7 ways wearable technology can help you reach your health goals - Wearable technology helps improve health by encouraging physical activity, monitoring heart health, aiding healthy eating through food and hydration tracking, and allowing remote management of chronic health conditions through data collection and personalized feedback.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com