Vector databases excel in handling complex, high-dimensional data such as images and natural language, enabling advanced similarity searches and AI-driven applications. Key-value stores provide efficient, scalable solutions for simple data retrieval using unique keys, making them ideal for caching and session management. Explore how each technology suits different use cases to optimize your data strategy effectively.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vector databases and key-value stores is crucial for optimizing data retrieval methods in AI applications and big data analytics. Vector databases excel in handling high-dimensional data for similarity search, enhancing performance in recommendation systems and image recognition tasks. Key-value stores provide rapid access to simple, discrete data pairs, ideal for caching and session management. Choosing the right database type directly impacts system efficiency and scalability in technology-driven environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vector Databases | Key-Value Stores |
|---|---|---|
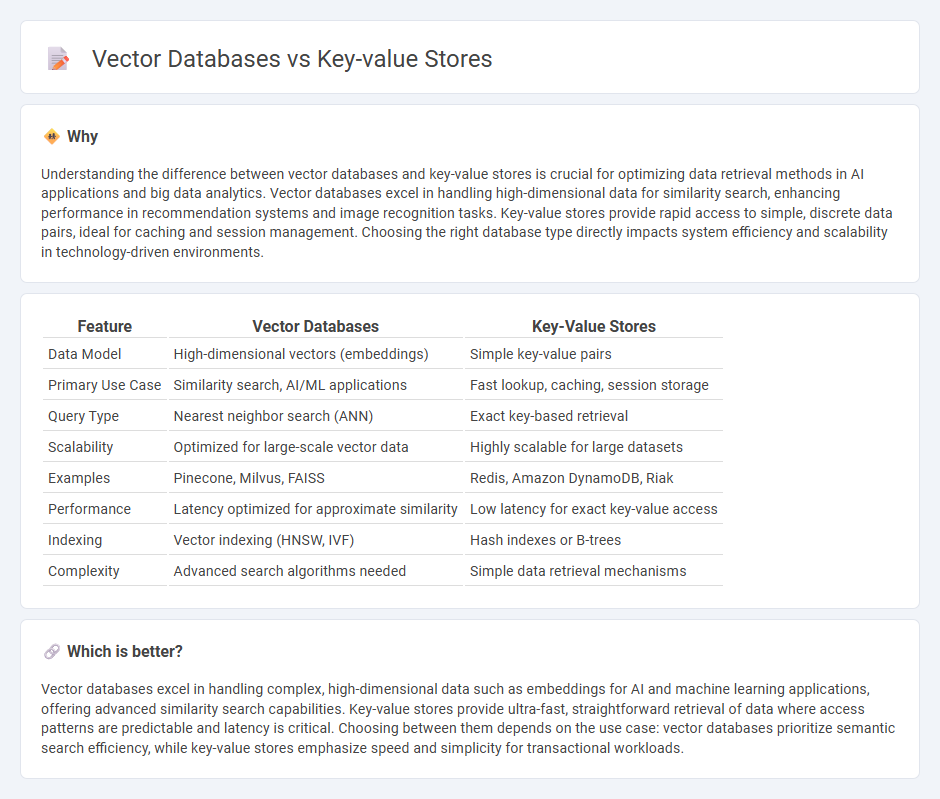
| Data Model | High-dimensional vectors (embeddings) | Simple key-value pairs |
| Primary Use Case | Similarity search, AI/ML applications | Fast lookup, caching, session storage |
| Query Type | Nearest neighbor search (ANN) | Exact key-based retrieval |
| Scalability | Optimized for large-scale vector data | Highly scalable for large datasets |
| Examples | Pinecone, Milvus, FAISS | Redis, Amazon DynamoDB, Riak |
| Performance | Latency optimized for approximate similarity | Low latency for exact key-value access |
| Indexing | Vector indexing (HNSW, IVF) | Hash indexes or B-trees |
| Complexity | Advanced search algorithms needed | Simple data retrieval mechanisms |
Which is better?
Vector databases excel in handling complex, high-dimensional data such as embeddings for AI and machine learning applications, offering advanced similarity search capabilities. Key-value stores provide ultra-fast, straightforward retrieval of data where access patterns are predictable and latency is critical. Choosing between them depends on the use case: vector databases prioritize semantic search efficiency, while key-value stores emphasize speed and simplicity for transactional workloads.
Connection
Vector databases and key-value stores share a foundational concept of storing data as key-value pairs, enabling efficient retrieval and indexing. Vector databases extend this model by using high-dimensional vectors as values to represent complex data like images or text embeddings, facilitating similarity searches. This connection allows vector databases to leverage the scalability and speed of key-value frameworks while supporting advanced neural search capabilities.
Key Terms
Data Model
Key-value stores organize data as simple pairs where each unique key maps directly to a corresponding value, making them highly efficient for lookup operations and suitable for caching or session management. Vector databases store complex data representations like vectors generated from multimedia, text, or other high-dimensional data, enabling similarity searches and machine learning applications. Explore how these differing data models impact performance and use cases to choose the right solution for your storage needs.
Query Mechanism
Key-value stores use simple lookup queries based on unique keys, enabling fast retrieval of exact matches but lacking support for complex or similarity-based searches. Vector databases employ advanced query mechanisms such as approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search, facilitating efficient similarity comparisons in high-dimensional vector spaces crucial for AI and machine learning applications. Explore deeper insights into how these distinct query mechanisms impact performance and use cases.
Scalability
Key-value stores excel in scalability by distributing data across multiple nodes, enabling fast read and write operations through simple key-based retrieval. Vector databases are optimized to handle high-dimensional vector data, scaling through techniques like indexing, partitioning, and approximate nearest neighbor search to efficiently manage large volumes of embeddings. Explore more to understand how each database type supports scalability in complex data environments.
Source and External Links
What is a Key-Value Database? - A key-value database uses a simple key-value pair method to store data, offering excellent performance and flexibility compared to relational databases.
Key-Value Stores Explained - Key-value stores are databases that efficiently store data as unique identifiers paired with their associated values, providing fast read and write operations.
What is a Key Value Database? - Key-value databases organize data as key-value pairs, allowing for rapid access and storage with support for various data types and flexible schema designs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com