Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on a central authority, leveraging blockchain technology to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Decentralized identity empowers users with control over their personal information by using cryptographic methods to verify identities without intermediaries. Explore how these innovations transform digital security and privacy in the evolving technology landscape.
Why it is important
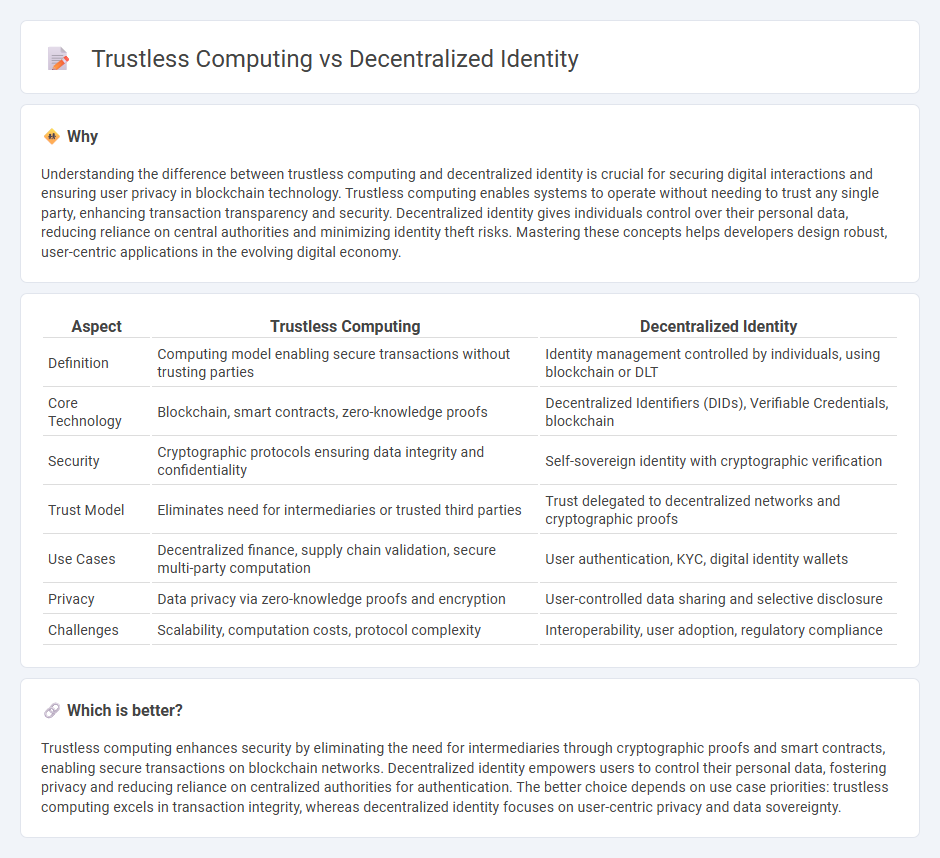
Understanding the difference between trustless computing and decentralized identity is crucial for securing digital interactions and ensuring user privacy in blockchain technology. Trustless computing enables systems to operate without needing to trust any single party, enhancing transaction transparency and security. Decentralized identity gives individuals control over their personal data, reducing reliance on central authorities and minimizing identity theft risks. Mastering these concepts helps developers design robust, user-centric applications in the evolving digital economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Trustless Computing | Decentralized Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Computing model enabling secure transactions without trusting parties | Identity management controlled by individuals, using blockchain or DLT |
| Core Technology | Blockchain, smart contracts, zero-knowledge proofs | Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), Verifiable Credentials, blockchain |
| Security | Cryptographic protocols ensuring data integrity and confidentiality | Self-sovereign identity with cryptographic verification |
| Trust Model | Eliminates need for intermediaries or trusted third parties | Trust delegated to decentralized networks and cryptographic proofs |
| Use Cases | Decentralized finance, supply chain validation, secure multi-party computation | User authentication, KYC, digital identity wallets |
| Privacy | Data privacy via zero-knowledge proofs and encryption | User-controlled data sharing and selective disclosure |
| Challenges | Scalability, computation costs, protocol complexity | Interoperability, user adoption, regulatory compliance |
Which is better?
Trustless computing enhances security by eliminating the need for intermediaries through cryptographic proofs and smart contracts, enabling secure transactions on blockchain networks. Decentralized identity empowers users to control their personal data, fostering privacy and reducing reliance on centralized authorities for authentication. The better choice depends on use case priorities: trustless computing excels in transaction integrity, whereas decentralized identity focuses on user-centric privacy and data sovereignty.
Connection
Trustless computing enables secure transactions without relying on centralized authorities, which is fundamental to decentralized identity systems that empower users to control their own digital identities. Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to create immutable, verifiable credentials, enhancing privacy and reducing identity fraud. The synergy between trustless computing and decentralized identity fosters a more secure, transparent, and user-centric digital ecosystem.
Key Terms
Blockchain
Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to enable users to control their own digital identities without reliance on centralized authorities, enhancing privacy and security. Trustless computing uses blockchain's consensus mechanisms to perform computations and transactions without needing to trust a single party, ensuring data integrity and transparency. Explore how these blockchain innovations transform digital interactions and security by learning more about their unique applications.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) empowers individuals with full control over their digital identities, eliminating reliance on centralized authorities by leveraging decentralized identity frameworks built on blockchain technology. Trustless computing enhances SSI by enabling secure and verifiable interactions without the need for intermediaries, ensuring privacy, data integrity, and user autonomy through cryptographic proofs and distributed ledger consensus. Explore the evolving landscape of SSI and trustless computing to understand how they revolutionize identity management and secure digital trust.
Cryptographic Protocols
Decentralized identity leverages cryptographic protocols like zero-knowledge proofs and self-sovereign identity frameworks to enable users to control their digital credentials without centralized authorities. Trustless computing utilizes secure multi-party computation and blockchain consensus mechanisms to perform computations without requiring mutual trust among participants. Explore the latest advancements in cryptographic protocols to understand their impact on digital security and privacy.
Source and External Links
What Is Decentralized Identity? A Comprehensive Guide - Provides an overview of decentralized identity, focusing on its core concepts like decentralization, self-sovereign identity, decentralized identifiers, and verifiable credentials.
What is Decentralized Identity? - Explains how decentralized identity works through components like credentials, digital wallets, issuers, verifiers, and blockchain technology.
Overview of Decentralized Identities - Discusses decentralized identities as a means to avoid storing personal data and empower users with control over their digital identities via verifiable credentials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com