Spatial computing integrates digital information with physical space through technologies like augmented reality and 3D mapping, enabling immersive user experiences. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects everyday objects via the internet, allowing real-time data exchange and automation across devices such as smart home systems and industrial sensors. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies intersect and transform various industries.
Why it is important
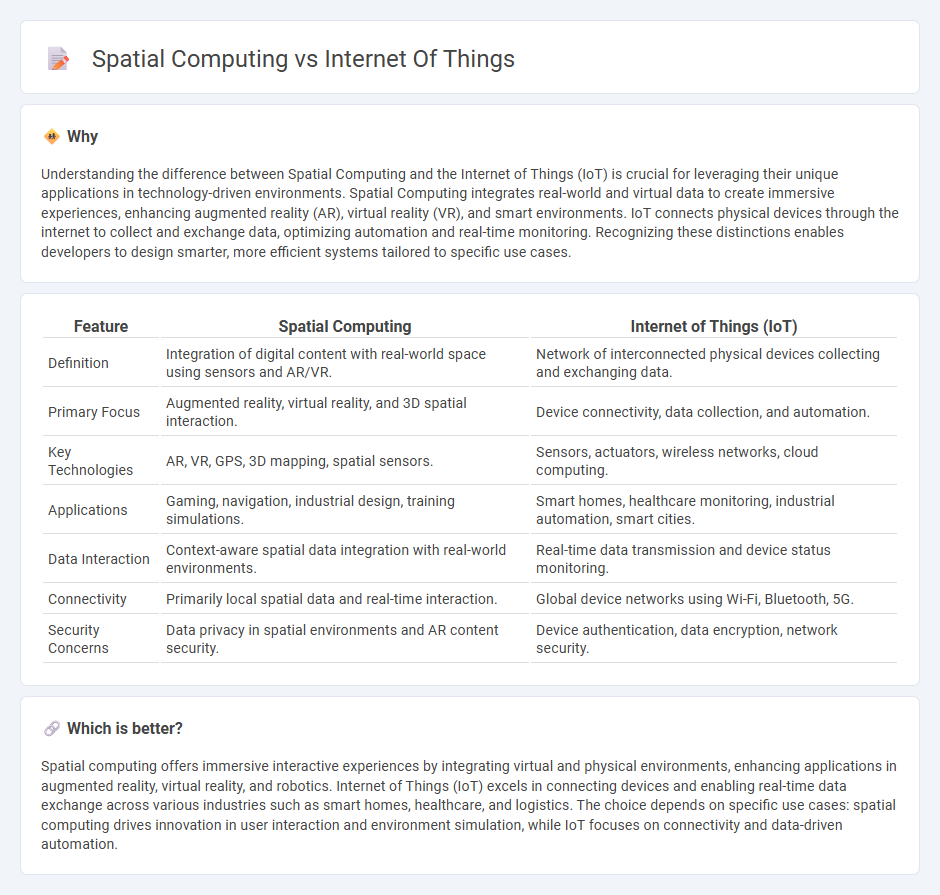
Understanding the difference between Spatial Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) is crucial for leveraging their unique applications in technology-driven environments. Spatial Computing integrates real-world and virtual data to create immersive experiences, enhancing augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and smart environments. IoT connects physical devices through the internet to collect and exchange data, optimizing automation and real-time monitoring. Recognizing these distinctions enables developers to design smarter, more efficient systems tailored to specific use cases.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Spatial Computing | Internet of Things (IoT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of digital content with real-world space using sensors and AR/VR. | Network of interconnected physical devices collecting and exchanging data. |
| Primary Focus | Augmented reality, virtual reality, and 3D spatial interaction. | Device connectivity, data collection, and automation. |
| Key Technologies | AR, VR, GPS, 3D mapping, spatial sensors. | Sensors, actuators, wireless networks, cloud computing. |
| Applications | Gaming, navigation, industrial design, training simulations. | Smart homes, healthcare monitoring, industrial automation, smart cities. |
| Data Interaction | Context-aware spatial data integration with real-world environments. | Real-time data transmission and device status monitoring. |
| Connectivity | Primarily local spatial data and real-time interaction. | Global device networks using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G. |
| Security Concerns | Data privacy in spatial environments and AR content security. | Device authentication, data encryption, network security. |
Which is better?
Spatial computing offers immersive interactive experiences by integrating virtual and physical environments, enhancing applications in augmented reality, virtual reality, and robotics. Internet of Things (IoT) excels in connecting devices and enabling real-time data exchange across various industries such as smart homes, healthcare, and logistics. The choice depends on specific use cases: spatial computing drives innovation in user interaction and environment simulation, while IoT focuses on connectivity and data-driven automation.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates digital and physical environments by utilizing sensors, cameras, and 3D mapping technologies, thereby enhancing the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem through precise location tracking and context-aware applications. IoT devices generate vast amounts of real-time data from connected objects, which spatial computing processes to enable immersive augmented reality, smart city infrastructure, and advanced automation. The synergy between spatial computing and IoT fosters intelligent environments that improve decision-making, resource management, and user experience across industries.
Key Terms
Connectivity vs. Spatial Awareness
Internet of Things (IoT) emphasizes seamless connectivity by linking devices through networks to enable data exchange and remote control, enhancing automation and efficiency across industries. Spatial computing prioritizes spatial awareness by integrating sensors, 3D mapping, and augmented reality to understand and interact with physical environments dynamically. Explore how these technologies converge and impact future innovations by learning more about their distinct functionalities and applications.
Sensors vs. 3D Mapping
Sensors in the Internet of Things (IoT) capture real-time data from physical environments, enabling smart devices to monitor temperature, motion, and other variables for enhanced automation and connectivity. Spatial computing leverages 3D mapping to create immersive digital representations of physical spaces, allowing precise interaction and analysis within augmented and virtual environments. Explore how integrating IoT sensors with spatial computing technologies revolutionizes industry applications and user experiences.
Data Exchange vs. Real-Time Interaction
The Internet of Things (IoT) primarily emphasizes seamless data exchange among interconnected devices, enabling efficient monitoring and automation across industries such as smart cities, healthcare, and manufacturing. In contrast, spatial computing focuses on real-time interaction within 3D environments, integrating augmented reality, virtual reality, and advanced sensors to create immersive and context-aware user experiences. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies reshape digital ecosystems by learning more about their distinct applications and future potential.
Source and External Links
What Is the Internet of Things? - Oracle - The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects embedded with sensors and software that connect and exchange data over the internet, enabling seamless interaction between people, processes, and things, including applications in industry known as Industrial IoT or Industry 4.0.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)? - IBM - IoT refers to connected physical devices with sensors and network connectivity, ranging from smart home gadgets to industrial machinery, which collect and share data to enable autonomous operations and have applications across multiple industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities.
What is IoT? - Internet of Things Explained - AWS - IoT is the network of connected devices and technology that enables communication between devices and the cloud, made practical by advances in small, inexpensive computing chips, allowing everyday objects to sense, collect data, and respond intelligently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com