Passkeys offer a modern, password-free authentication method using cryptographic keys stored on devices, enhancing security against phishing attacks. Digital signatures, on the other hand, provide document and transaction authenticity by using asymmetric encryption to verify the sender's identity and ensure data integrity. Explore the key differences and applications of passkeys versus digital signatures to better protect your digital environment.
Why it is important
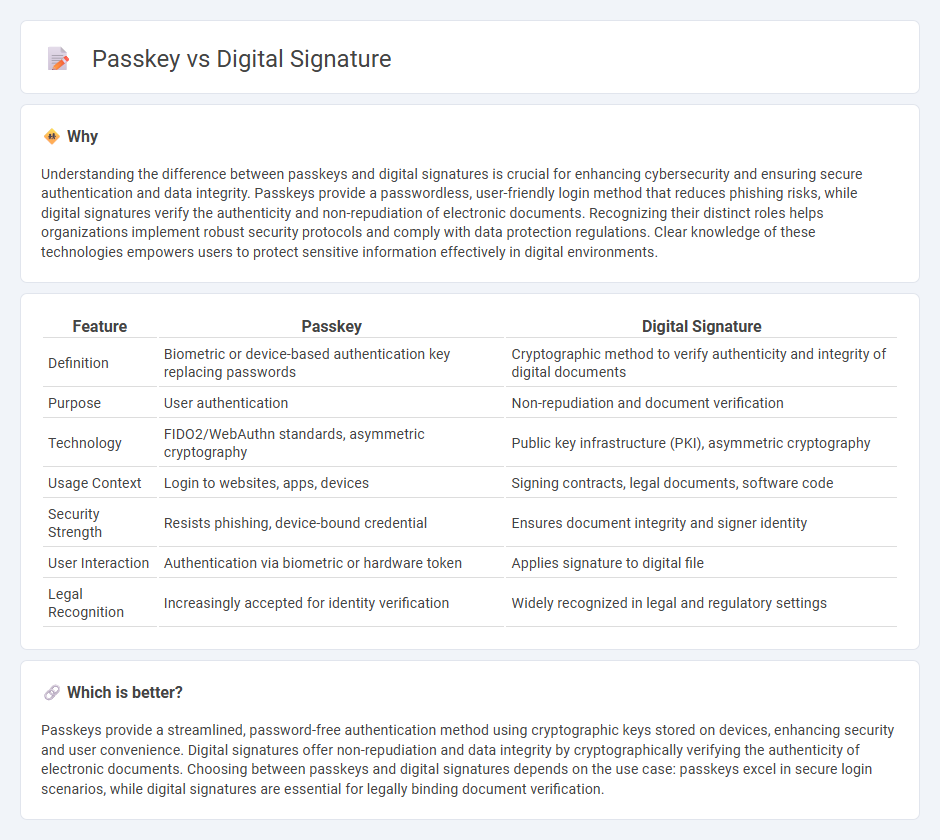
Understanding the difference between passkeys and digital signatures is crucial for enhancing cybersecurity and ensuring secure authentication and data integrity. Passkeys provide a passwordless, user-friendly login method that reduces phishing risks, while digital signatures verify the authenticity and non-repudiation of electronic documents. Recognizing their distinct roles helps organizations implement robust security protocols and comply with data protection regulations. Clear knowledge of these technologies empowers users to protect sensitive information effectively in digital environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Passkey | Digital Signature |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biometric or device-based authentication key replacing passwords | Cryptographic method to verify authenticity and integrity of digital documents |
| Purpose | User authentication | Non-repudiation and document verification |
| Technology | FIDO2/WebAuthn standards, asymmetric cryptography | Public key infrastructure (PKI), asymmetric cryptography |
| Usage Context | Login to websites, apps, devices | Signing contracts, legal documents, software code |
| Security Strength | Resists phishing, device-bound credential | Ensures document integrity and signer identity |
| User Interaction | Authentication via biometric or hardware token | Applies signature to digital file |
| Legal Recognition | Increasingly accepted for identity verification | Widely recognized in legal and regulatory settings |
Which is better?
Passkeys provide a streamlined, password-free authentication method using cryptographic keys stored on devices, enhancing security and user convenience. Digital signatures offer non-repudiation and data integrity by cryptographically verifying the authenticity of electronic documents. Choosing between passkeys and digital signatures depends on the use case: passkeys excel in secure login scenarios, while digital signatures are essential for legally binding document verification.
Connection
Passkeys utilize cryptographic keys that are fundamentally linked to digital signatures, enabling secure and passwordless authentication. Digital signatures authenticate the integrity and origin of data by using private keys, which are integral to the passkey mechanism in verifying user identity. This connection ensures enhanced security through asymmetric encryption, reducing the risk of phishing and credential theft.
Key Terms
Authentication
Digital signatures rely on cryptographic algorithms to verify the authenticity and integrity of documents by linking the signer's identity to the data. Passkeys, on the other hand, serve as a secure, passwordless authentication method using asymmetric key pairs stored on devices, enhancing user access control. Explore the differences in security applications and user experience by learning more about digital signatures and passkeys.
Cryptography
Digital signatures leverage asymmetric cryptography, using a private key to create a unique signature that validates the authenticity and integrity of a message or document, while passkeys employ cryptographic principles such as public-key cryptography to replace traditional passwords with secure, phishing-resistant authentication methods. Digital signatures ensure message non-repudiation and verification using algorithms like RSA or ECDSA, whereas passkeys utilize protocols such as FIDO2 and WebAuthn for seamless access. Explore the cryptographic distinctions and applications of digital signatures and passkeys to understand their evolving roles in secure communication.
Identity Verification
Digital signatures provide robust identity verification by using cryptographic algorithms to authenticate the signer's identity and ensure document integrity. Passkeys utilize biometric data or device-based credentials to simplify user authentication while maintaining strong protection against identity theft. Explore how these technologies can enhance your security framework and streamline identity verification processes.
Source and External Links
Understanding digital signatures - Digital signatures use a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) with public and private keys to uniquely and securely sign documents, ensuring authenticity and integrity by invalidating the signature if the document is altered after signing.
Digital signature: doc signing at scale - Acrobat - A digital signature is an e-signature backed by a trusted digital certificate, providing strong identity verification, regulatory compliance, and cryptographic proof that the document is unaltered and the signer is authentic.
Digital signature - Wikipedia - A digital signature is a mathematical scheme that verifies the authenticity of digital messages or documents using asymmetric cryptography, offering non-repudiation and tamper detection across numerous applications like contracts and financial transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com