Synthetic media detection involves identifying AI-generated content by analyzing patterns and inconsistencies in audio, video, or images, enhancing digital authenticity verification. Digital watermarking embeds invisible information into media files to securely track ownership and prevent unauthorized use, providing a robust layer of content protection. Explore more about how these technologies safeguard digital media integrity and combat misinformation.
Why it is important
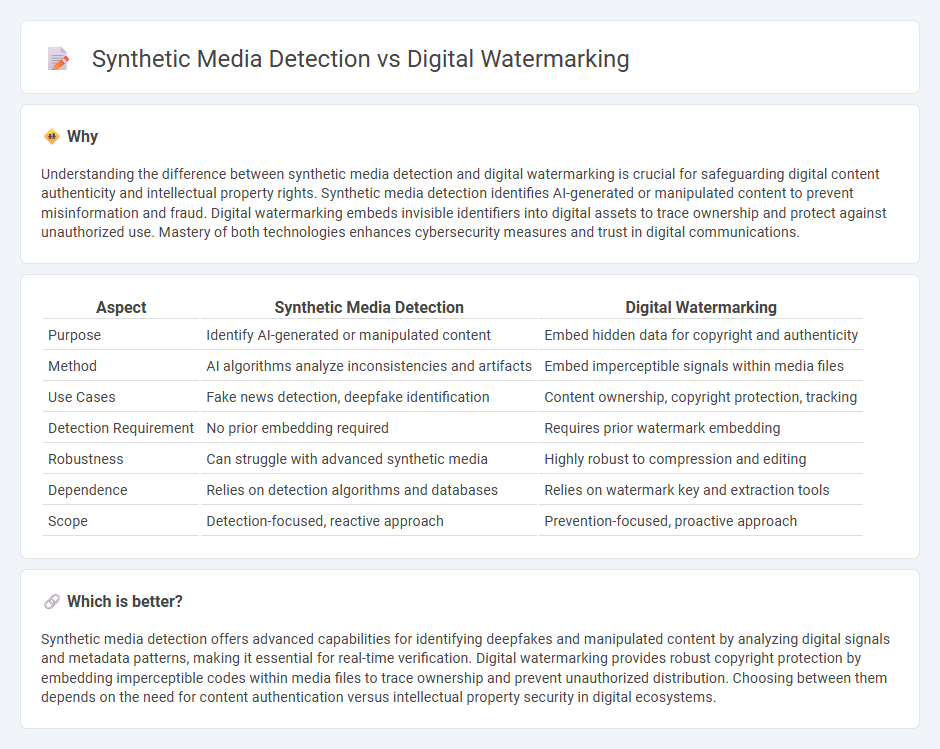
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and digital watermarking is crucial for safeguarding digital content authenticity and intellectual property rights. Synthetic media detection identifies AI-generated or manipulated content to prevent misinformation and fraud. Digital watermarking embeds invisible identifiers into digital assets to trace ownership and protect against unauthorized use. Mastery of both technologies enhances cybersecurity measures and trust in digital communications.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Media Detection | Digital Watermarking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify AI-generated or manipulated content | Embed hidden data for copyright and authenticity |
| Method | AI algorithms analyze inconsistencies and artifacts | Embed imperceptible signals within media files |
| Use Cases | Fake news detection, deepfake identification | Content ownership, copyright protection, tracking |
| Detection Requirement | No prior embedding required | Requires prior watermark embedding |
| Robustness | Can struggle with advanced synthetic media | Highly robust to compression and editing |
| Dependence | Relies on detection algorithms and databases | Relies on watermark key and extraction tools |
| Scope | Detection-focused, reactive approach | Prevention-focused, proactive approach |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection offers advanced capabilities for identifying deepfakes and manipulated content by analyzing digital signals and metadata patterns, making it essential for real-time verification. Digital watermarking provides robust copyright protection by embedding imperceptible codes within media files to trace ownership and prevent unauthorized distribution. Choosing between them depends on the need for content authentication versus intellectual property security in digital ecosystems.
Connection
Synthetic media detection relies on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content, often using digital watermarking techniques embedded directly into media files to verify authenticity. Digital watermarking provides a covert marker that helps trace the origin and detect tampering, enhancing the reliability of synthetic media detection systems. This connection strengthens digital content verification, combating misinformation and ensuring intellectual property protection in the age of AI-generated media.
Key Terms
Robustness
Digital watermarking embeds imperceptible information into media files to ensure content authenticity, relying heavily on robustness to resist tampering and degradation across diverse platforms. Synthetic media detection leverages advanced algorithms and AI to identify generated or manipulated content, emphasizing resilience against sophisticated forgery techniques. Explore the latest advancements in robustness strategies to understand how these technologies combat digital manipulation effectively.
Deepfake Identification
Digital watermarking embeds imperceptible signals into media files to verify authenticity, providing a straightforward tool for deepfake identification by tracing original content. Synthetic media detection employs advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze inconsistencies in facial features, voice patterns, and temporal artifacts characteristic of deepfakes. Explore this rapidly evolving field to understand how these techniques safeguard media integrity against sophisticated synthetic manipulations.
Signal Processing
Digital watermarking embeds imperceptible signals into media content using signal processing techniques to verify authenticity and track ownership. Synthetic media detection employs advanced signal processing algorithms to identify artifacts, inconsistencies, or manipulation signatures within audio, images, or video generated by AI models. Explore the nuances of these signal processing methods to better understand their applications in media security.
Source and External Links
Digital Watermarking and its Types - GeeksforGeeks - Digital watermarking is a technique where a marker is covertly embedded in digital media like images, audio, or video to identify copyright ownership and detect infringement, with types including visible, invisible, public, and fragile watermarks and a life cycle involving embedding, attack, and protection phases.
What is a digital watermark? - Box - A digital watermark is a unique identifier embedded into digital content that can be visible or invisible and designed to be fragile or robust depending on the need, used for branding, tamper detection, and copyright protection.
What Is Digital Watermarking? | Fortra's Digital Guardian - Digital watermarking is a security method embedding codes or images in multimedia content to protect intellectual property, trace copyright infringement, and verify ownership, including use in sensitive business and legal documents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com