Circular electronics focus on designing devices for easy repair, reuse, and recycling to minimize electronic waste and conserve resources. Sustainable electronics emphasize reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle, including energy-efficient manufacturing and responsible material sourcing. Explore how these innovative approaches are transforming the electronics industry for a greener future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and sustainable electronics is vital for informed decision-making in environmental impact mitigation. Circular electronics emphasize product lifecycle extension through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling, reducing electronic waste significantly. Sustainable electronics focus on minimizing environmental harm during production, use, and disposal by incorporating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient processes. Distinguishing these concepts helps drive innovation and policies tailored to both reduce waste and promote green manufacturing technologies.
Comparison Table
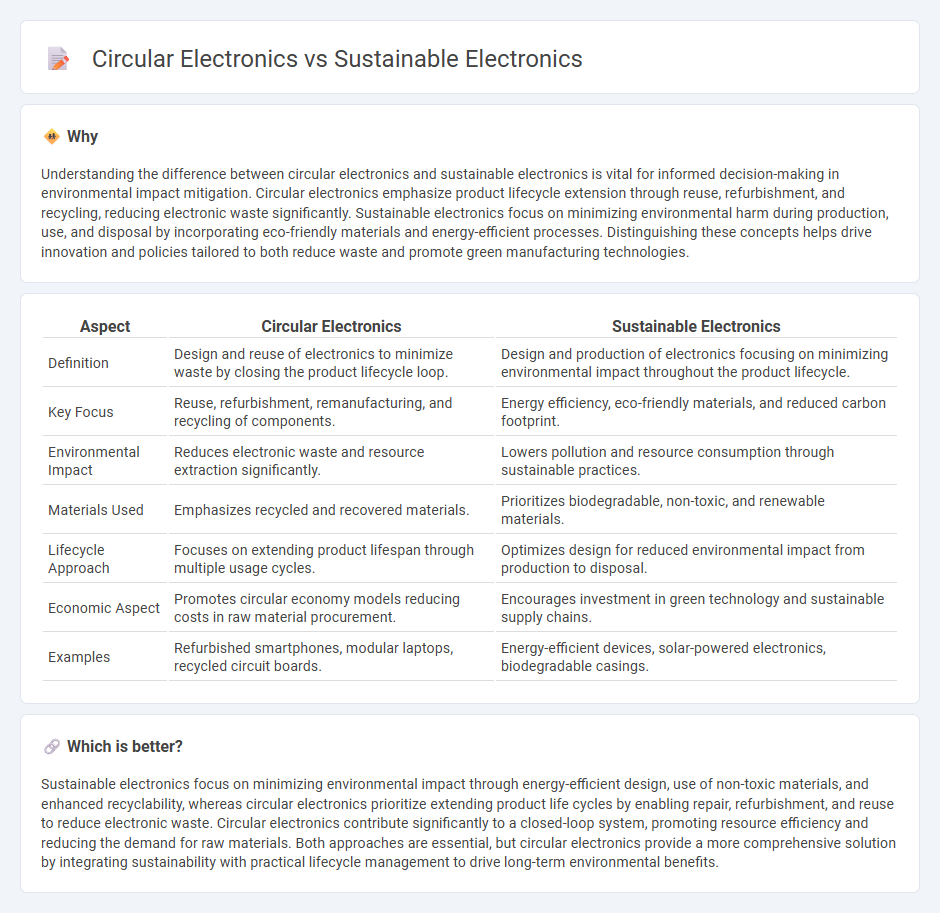
| Aspect | Circular Electronics | Sustainable Electronics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Design and reuse of electronics to minimize waste by closing the product lifecycle loop. | Design and production of electronics focusing on minimizing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. |
| Key Focus | Reuse, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling of components. | Energy efficiency, eco-friendly materials, and reduced carbon footprint. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces electronic waste and resource extraction significantly. | Lowers pollution and resource consumption through sustainable practices. |
| Materials Used | Emphasizes recycled and recovered materials. | Prioritizes biodegradable, non-toxic, and renewable materials. |
| Lifecycle Approach | Focuses on extending product lifespan through multiple usage cycles. | Optimizes design for reduced environmental impact from production to disposal. |
| Economic Aspect | Promotes circular economy models reducing costs in raw material procurement. | Encourages investment in green technology and sustainable supply chains. |
| Examples | Refurbished smartphones, modular laptops, recycled circuit boards. | Energy-efficient devices, solar-powered electronics, biodegradable casings. |
Which is better?
Sustainable electronics focus on minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient design, use of non-toxic materials, and enhanced recyclability, whereas circular electronics prioritize extending product life cycles by enabling repair, refurbishment, and reuse to reduce electronic waste. Circular electronics contribute significantly to a closed-loop system, promoting resource efficiency and reducing the demand for raw materials. Both approaches are essential, but circular electronics provide a more comprehensive solution by integrating sustainability with practical lifecycle management to drive long-term environmental benefits.
Connection
Circular electronics focus on designing devices for reuse, repair, and recycling to minimize waste, aligning closely with sustainable electronics principles that emphasize reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Both approaches prioritize resource efficiency by promoting the recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste and reducing the extraction of virgin resources. Implementing circular electronics strategies enhances sustainability by extending product lifespan and closing material loops, contributing significantly to reducing e-waste and greenhouse gas emissions in the technology sector.
Key Terms
Eco-design
Sustainable electronics emphasize reducing environmental impact through energy efficiency and resource conservation, while circular electronics prioritize designing products for reuse, repair, and recycling to extend their lifecycle. Eco-design in circular electronics integrates modular components and biodegradable materials to minimize e-waste and promote a closed-loop system. Explore more about innovative eco-design strategies driving the future of sustainable and circular electronics.
E-waste management
Sustainable electronics emphasize reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle by using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs, while circular electronics prioritize resource recovery and reuse to minimize e-waste generation. Effective e-waste management in circular electronics involves refurbishing, remanufacturing, and recycling to extend product life and recover valuable components. Explore more about how these approaches transform electronic waste strategies for a greener future.
Resource recovery
Sustainable electronics emphasize minimizing environmental impact through energy efficiency, use of eco-friendly materials, and reducing e-waste generation. Circular electronics prioritize resource recovery by designing products for easy disassembly, refurbishment, and recycling to keep materials in use longer and reduce raw material extraction. Explore how innovative approaches in resource recovery are transforming the electronics industry.
Source and External Links
Sustainable Electronics - INEMI Roadmap - The electronics industry is shifting toward modular, repairable, and recyclable design, integrating sustainability into every lifecycle stage to reduce waste and resource use while advancing recycling technologies and circular supply chains.
9 Sustainable Electronics Brands Putting The 'E' In Eco-Friendly - Brands like Anker and Nimble are leading with eco-friendly products--such as chargers made from recycled plastics and solar panels--that minimize environmental impact through responsible materials, carbon-neutral certification, and ethical manufacturing practices.
Sage Sustainable Electronics - Sage specializes in refurbishing and ethically recycling used electronics, helping companies reduce e-waste by extending device lifespans, securely clearing data, and offering certified, sustainable IT asset disposition services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com