Spatial computing integrates real-world environments with digital interfaces using advanced sensors and AI to create interactive, immersive experiences. Digital twins replicate physical assets or systems digitally to simulate, analyze, and optimize their real-time performance using IoT data and machine learning. Explore how these cutting-edge technologies revolutionize industries and enhance decision-making processes.
Why it is important
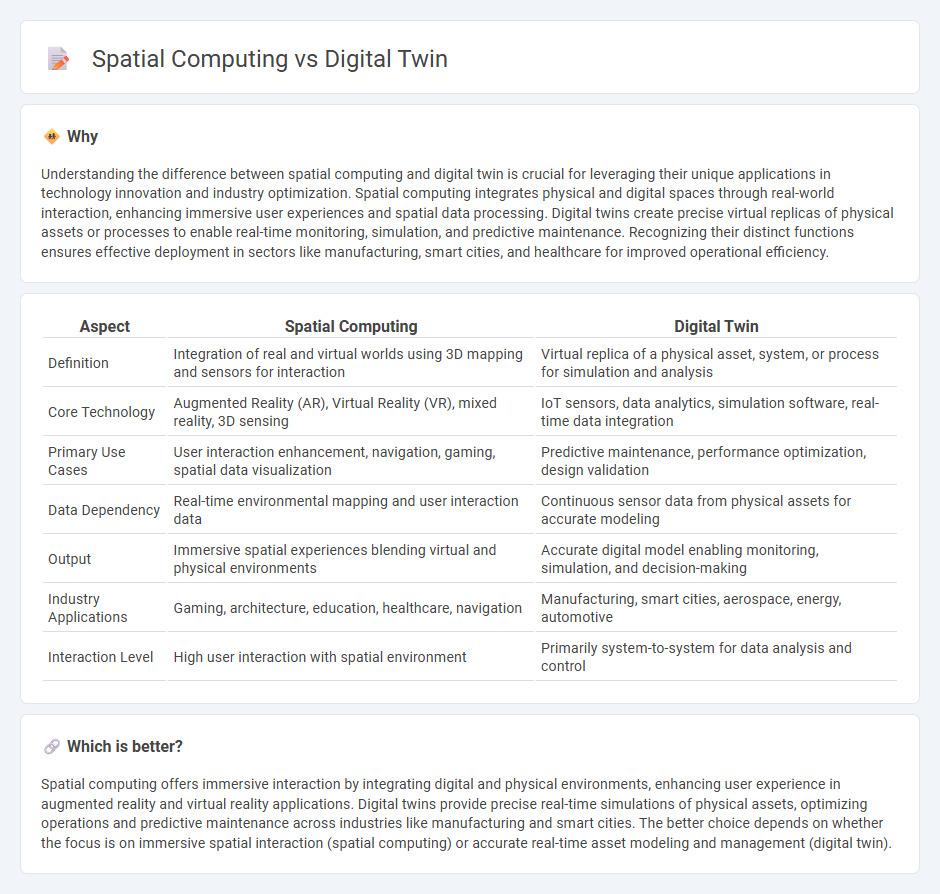
Understanding the difference between spatial computing and digital twin is crucial for leveraging their unique applications in technology innovation and industry optimization. Spatial computing integrates physical and digital spaces through real-world interaction, enhancing immersive user experiences and spatial data processing. Digital twins create precise virtual replicas of physical assets or processes to enable real-time monitoring, simulation, and predictive maintenance. Recognizing their distinct functions ensures effective deployment in sectors like manufacturing, smart cities, and healthcare for improved operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Spatial Computing | Digital Twin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of real and virtual worlds using 3D mapping and sensors for interaction | Virtual replica of a physical asset, system, or process for simulation and analysis |
| Core Technology | Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), mixed reality, 3D sensing | IoT sensors, data analytics, simulation software, real-time data integration |
| Primary Use Cases | User interaction enhancement, navigation, gaming, spatial data visualization | Predictive maintenance, performance optimization, design validation |
| Data Dependency | Real-time environmental mapping and user interaction data | Continuous sensor data from physical assets for accurate modeling |
| Output | Immersive spatial experiences blending virtual and physical environments | Accurate digital model enabling monitoring, simulation, and decision-making |
| Industry Applications | Gaming, architecture, education, healthcare, navigation | Manufacturing, smart cities, aerospace, energy, automotive |
| Interaction Level | High user interaction with spatial environment | Primarily system-to-system for data analysis and control |
Which is better?
Spatial computing offers immersive interaction by integrating digital and physical environments, enhancing user experience in augmented reality and virtual reality applications. Digital twins provide precise real-time simulations of physical assets, optimizing operations and predictive maintenance across industries like manufacturing and smart cities. The better choice depends on whether the focus is on immersive spatial interaction (spatial computing) or accurate real-time asset modeling and management (digital twin).
Connection
Spatial computing integrates real-world data with digital environments, enabling precise mapping and interaction within physical spaces. Digital twins leverage spatial computing by creating real-time, virtual replicas of physical assets or environments for simulation and analysis. This connection enhances predictive maintenance, operational efficiency, and immersive user experiences across industries like manufacturing, urban planning, and healthcare.
Key Terms
Simulation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of physical assets or systems for real-time simulation and monitoring, enabling precise performance optimization and predictive maintenance. Spatial computing integrates 3D environments with interactive simulations, enhancing user experience through immersive visualization and contextual data interaction. Explore how these technologies transform simulation by bridging physical and digital realities with unprecedented accuracy and engagement.
Virtual Environment
Digital twins create highly detailed virtual replicas of physical environments, enabling real-time monitoring and simulation of assets and processes. Spatial computing enhances these virtual environments by integrating 3D mapping, sensor data, and augmented reality to provide immersive and interactive experiences. Explore how combining digital twins with spatial computing can revolutionize virtual environment design and operation.
Real-time Data
Digital twin technology leverages real-time data streams to create dynamic virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance. Spatial computing integrates real-time data with 3D environments to facilitate immersive interactions and context-aware experiences across physical and digital spaces. Explore more to understand how these technologies enhance real-time data utilization and operational insights.
Source and External Links
Definition of a Digital Twin - A digital twin is an integrated data-driven virtual representation of real-world entities and processes, synchronized with the physical counterpart in real-time to enable continuous improvement, decision-making, and simulation of predicted futures.
What Is a Digital Twin? - A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object or system updated with real-time data from sensors, used to simulate, analyze, and optimize the object's performance across its lifecycle.
Digital twin - A digital twin is a digital model that replicates a real-world physical product, system, or process to enable simulation, monitoring, maintenance and optimization by continuously updating itself with real-time data throughout its lifecycle.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com