Synthetic data offers a scalable and privacy-preserving alternative to traditional user data by generating artificial datasets that mimic real-world patterns without exposing personal information. Unlike user data, which often involves strict compliance with data protection regulations and risks of breaches, synthetic data enhances machine learning model training efficiency while maintaining security. Explore how synthetic data transforms data-driven innovation and safeguards privacy in today's technology landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic data and user data is crucial for ensuring privacy compliance and enhancing data security in technology applications. Synthetic data, generated artificially, eliminates risks associated with handling sensitive user information while enabling effective machine learning model training. User data, containing real personal information, requires stringent protection measures to prevent breaches and maintain user trust. Distinguishing these data types aids in choosing appropriate data management strategies and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
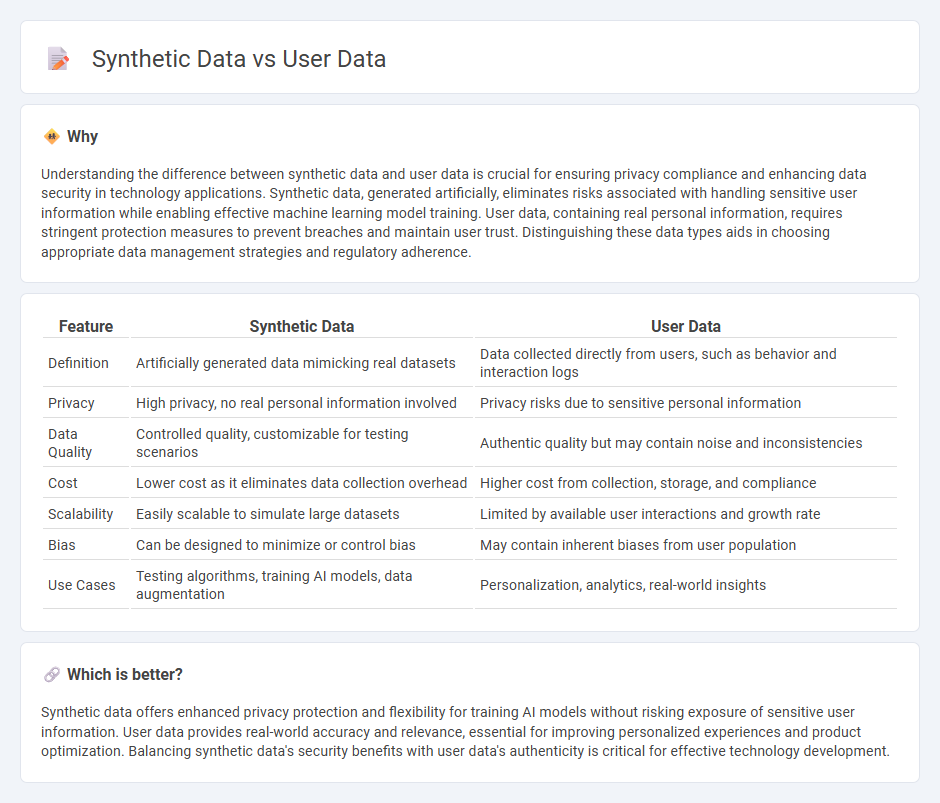
| Feature | Synthetic Data | User Data |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially generated data mimicking real datasets | Data collected directly from users, such as behavior and interaction logs |
| Privacy | High privacy, no real personal information involved | Privacy risks due to sensitive personal information |
| Data Quality | Controlled quality, customizable for testing scenarios | Authentic quality but may contain noise and inconsistencies |
| Cost | Lower cost as it eliminates data collection overhead | Higher cost from collection, storage, and compliance |
| Scalability | Easily scalable to simulate large datasets | Limited by available user interactions and growth rate |
| Bias | Can be designed to minimize or control bias | May contain inherent biases from user population |
| Use Cases | Testing algorithms, training AI models, data augmentation | Personalization, analytics, real-world insights |
Which is better?
Synthetic data offers enhanced privacy protection and flexibility for training AI models without risking exposure of sensitive user information. User data provides real-world accuracy and relevance, essential for improving personalized experiences and product optimization. Balancing synthetic data's security benefits with user data's authenticity is critical for effective technology development.
Connection
Synthetic data is generated to mimic real user data while preserving privacy and enhancing machine learning models. By replicating statistical properties of user data, synthetic data enables scalable testing and training without exposing sensitive information. This connection fosters innovation in technology by balancing data utility with user confidentiality.
Key Terms
Privacy
User data contains personally identifiable information, making it vulnerable to privacy breaches and requiring strict compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Synthetic data, generated algorithmically, minimizes privacy risks by simulating real-world scenarios without exposing actual user details, enabling safer data sharing and analysis. Explore the advantages of synthetic data to enhance your privacy strategy and safeguard sensitive information.
Data Generation
User data consists of real-world information collected from individuals, offering high authenticity but raising privacy concerns and legal restrictions. Synthetic data is artificially generated using algorithms and machine learning models, enabling scalable, privacy-safe data creation that mimics real datasets while overcoming limitations of user data access. Explore the advantages and applications of each data generation method to optimize your data strategy.
Bias
User data often carries inherent biases reflecting historical inequalities and individual behaviors, which can skew machine learning outcomes and perpetuate unfair treatment. Synthetic data, generated algorithmically, enables controlled representation of diverse scenarios, reducing such biases and enhancing model fairness. Explore deeper insights on how synthetic data mitigates bias in AI systems.
Source and External Links
User data: Overview, definition, and example - Cobrief - User data refers to information collected, processed, or stored about individuals during their interaction with digital services, applications, or platforms, encompassing personal, behavioral, and transactional details such as names, emails, browsing history, and purchase behavior.
User Data - Play Console Help - Google Help - User data includes personal and sensitive information like personally identifiable data, financial and payment details, authentication information, contacts, device location, and health data, with strict handling, security, and privacy requirements for apps on Google Play.
User-data formats - cloud-init 25.1.4 documentation - In cloud computing, user-data is configuration data provided by a user at instance launch, used to customize and configure cloud servers, and can be passed in various formats such as cloud-config for tasks like user setup and package installations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com