Spatial computing integrates digital content directly into the physical environment, enabling interaction through natural gestures and spatial awareness. Virtual reality immerses users in a completely simulated environment, often requiring headsets and controllers to navigate. Explore the key differences and applications of spatial computing and virtual reality to understand their impact on future technology.
Why it is important
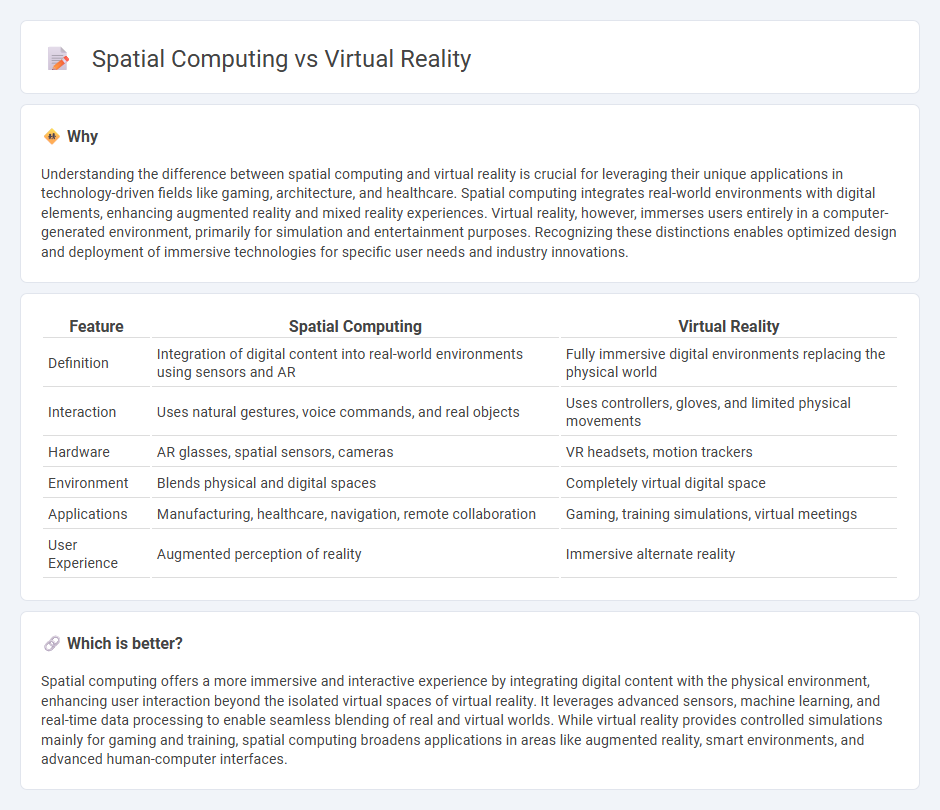
Understanding the difference between spatial computing and virtual reality is crucial for leveraging their unique applications in technology-driven fields like gaming, architecture, and healthcare. Spatial computing integrates real-world environments with digital elements, enhancing augmented reality and mixed reality experiences. Virtual reality, however, immerses users entirely in a computer-generated environment, primarily for simulation and entertainment purposes. Recognizing these distinctions enables optimized design and deployment of immersive technologies for specific user needs and industry innovations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Spatial Computing | Virtual Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of digital content into real-world environments using sensors and AR | Fully immersive digital environments replacing the physical world |
| Interaction | Uses natural gestures, voice commands, and real objects | Uses controllers, gloves, and limited physical movements |
| Hardware | AR glasses, spatial sensors, cameras | VR headsets, motion trackers |
| Environment | Blends physical and digital spaces | Completely virtual digital space |
| Applications | Manufacturing, healthcare, navigation, remote collaboration | Gaming, training simulations, virtual meetings |
| User Experience | Augmented perception of reality | Immersive alternate reality |
Which is better?
Spatial computing offers a more immersive and interactive experience by integrating digital content with the physical environment, enhancing user interaction beyond the isolated virtual spaces of virtual reality. It leverages advanced sensors, machine learning, and real-time data processing to enable seamless blending of real and virtual worlds. While virtual reality provides controlled simulations mainly for gaming and training, spatial computing broadens applications in areas like augmented reality, smart environments, and advanced human-computer interfaces.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates digital objects into the real world through precise mapping, enabling immersive environments powered by virtual reality. Virtual reality leverages spatial computing technologies such as 3D sensors, environmental tracking, and gesture recognition to create interactive simulations. This connection drives advancements in gaming, training, architecture, and healthcare by offering realistic user experiences and spatially-aware interactions.
Key Terms
Immersion
Virtual reality delivers full immersion by completely replacing the physical environment with a digital one, utilizing headsets like Oculus Quest or HTC Vive to engage users in a fully controlled sensory experience. Spatial computing integrates digital content with the real world through augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) devices such as Microsoft HoloLens, enabling interaction with both virtual and physical spaces simultaneously. Explore the nuances of immersion in these technologies to understand their unique applications and advantages.
Interaction
Virtual reality (VR) immerses users in a fully digital environment, emphasizing interaction through handheld controllers and motion sensors for precise input. Spatial computing integrates digital elements into the physical world, enabling natural interaction via gestures, voice commands, and eye tracking within augmented reality (AR) settings. Explore how these technologies redefine user experiences by blending or replacing reality through advanced interaction methods.
Environmental Mapping
Environmental mapping in virtual reality (VR) relies on pre-defined digital environments, creating immersive experiences through 3D modeling and sensor data integration. Spatial computing enhances this by dynamically scanning and understanding real-world surroundings using LIDAR, depth sensors, and AI-driven algorithms to enable precise interaction between virtual and physical spaces. Explore the advancements in environmental mapping to discover how these technologies redefine immersive experiences.
Source and External Links
What is virtual reality (VR) and how does it work? - Virtual reality is a technology that immerses users in an artificial 3D environment using hardware like headsets and motion controllers combined with software that simulates realistic sensory experiences in real-time.
Immerse Yourself in Virtual Reality - The Future Now - VR creates a sense of presence by simulating a three-dimensional environment that users can explore and interact with using specialized electronic devices such as headsets and controllers, with applications across gaming, education, and healthcare.
Virtual reality (VR) | Definition, Development, Technology ... - VR enables interaction with a computer-generated 3-D environment through devices like goggles and gloves, providing immersive experiences by adjusting visuals in real-time based on user movements to simulate presence.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com