Circular electronics emphasize creating devices that minimize waste through reuse, repair, and recycling, promoting sustainability in the tech industry. Design for disassembly focuses on engineering products to be easily taken apart, enhancing recyclability and component recovery. Explore how these innovative approaches revolutionize electronic manufacturing and environmental impact.
Why it is important
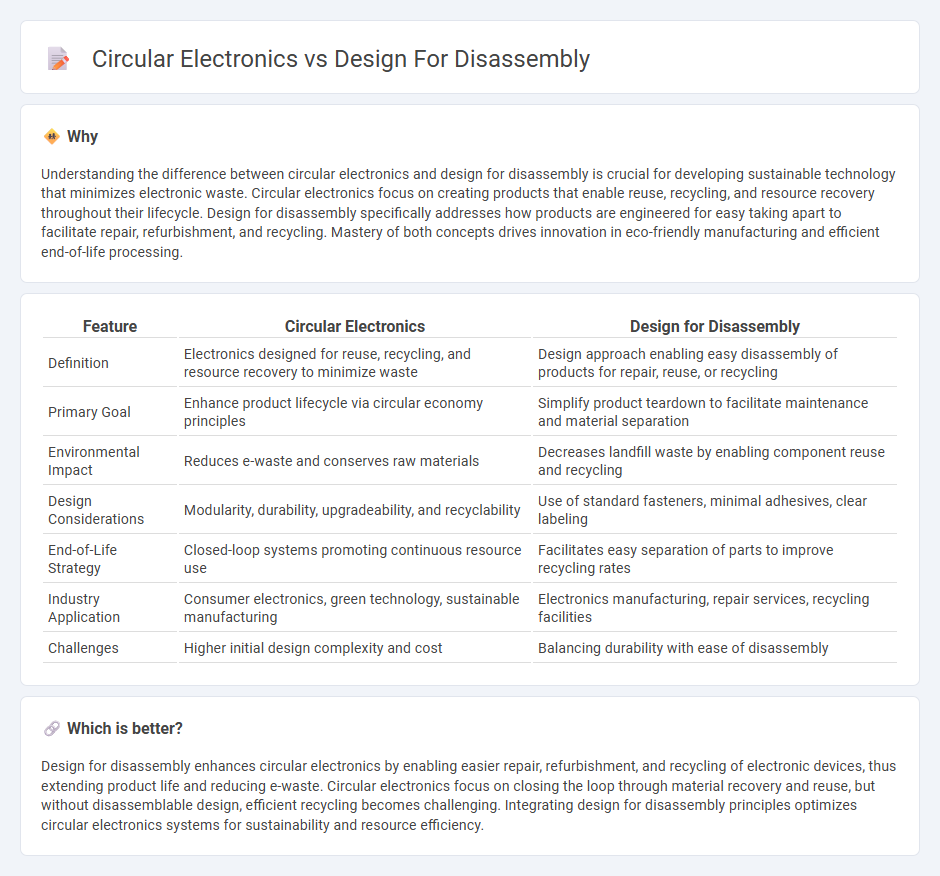
Understanding the difference between circular electronics and design for disassembly is crucial for developing sustainable technology that minimizes electronic waste. Circular electronics focus on creating products that enable reuse, recycling, and resource recovery throughout their lifecycle. Design for disassembly specifically addresses how products are engineered for easy taking apart to facilitate repair, refurbishment, and recycling. Mastery of both concepts drives innovation in eco-friendly manufacturing and efficient end-of-life processing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Circular Electronics | Design for Disassembly |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronics designed for reuse, recycling, and resource recovery to minimize waste | Design approach enabling easy disassembly of products for repair, reuse, or recycling |
| Primary Goal | Enhance product lifecycle via circular economy principles | Simplify product teardown to facilitate maintenance and material separation |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces e-waste and conserves raw materials | Decreases landfill waste by enabling component reuse and recycling |
| Design Considerations | Modularity, durability, upgradeability, and recyclability | Use of standard fasteners, minimal adhesives, clear labeling |
| End-of-Life Strategy | Closed-loop systems promoting continuous resource use | Facilitates easy separation of parts to improve recycling rates |
| Industry Application | Consumer electronics, green technology, sustainable manufacturing | Electronics manufacturing, repair services, recycling facilities |
| Challenges | Higher initial design complexity and cost | Balancing durability with ease of disassembly |
Which is better?
Design for disassembly enhances circular electronics by enabling easier repair, refurbishment, and recycling of electronic devices, thus extending product life and reducing e-waste. Circular electronics focus on closing the loop through material recovery and reuse, but without disassemblable design, efficient recycling becomes challenging. Integrating design for disassembly principles optimizes circular electronics systems for sustainability and resource efficiency.
Connection
Circular electronics focus on sustainable product life cycles by integrating design for disassembly principles, which enable easy separation of components for repair, reuse, and recycling. This approach reduces electronic waste and conserves valuable materials by facilitating efficient recovery processes. Emphasizing modular designs and standardized parts enhances the effectiveness of circular electronics in promoting environmental sustainability.
Key Terms
Modularity
Design for disassembly emphasizes creating electronics with modular components that can be easily separated and replaced, enhancing repairability and end-of-life recycling. Circular electronics prioritize modularity to extend product lifespan, reduce waste, and support sustainable material recovery through efficient component reuse. Explore how modular design principles drive circular economy initiatives in electronic device manufacturing.
E-waste Management
Design for disassembly emphasizes creating electronic products that can be easily taken apart, facilitating efficient recycling and component reuse to reduce e-waste. Circular electronics integrate this approach by promoting material recovery, modularity, and product lifecycle extension, which align with sustainable manufacturing and waste minimization. Explore how combining design for disassembly with circular electronics principles revolutionizes e-waste management and contributes to environmental sustainability.
Material Recovery
Design for disassembly enhances circular electronics by enabling efficient material recovery through standardized connectors and modular components. This approach minimizes waste and maximizes reuse of critical materials like rare earth metals and high-grade plastics. Discover more about how design innovations drive sustainable electronics and resource efficiency.
Source and External Links
Design for Disassembly in the Age of Circularity - Design for Disassembly (DfD) promotes products and structures that can be easily taken apart for reuse, recycling, or repurposing by using reversible connections, modular designs, and recyclable materials to support circular economy principles and reduce environmental impact.
What Is Design For Disassembly (DfD)? - LightNOW - DfD involves selecting materials and fasteners that allow easy, damage-free disassembly of products or systems, enabling efficient recycling and maintenance to reduce waste and environmental footprint across various industries like electronics and construction.
A Guide to Design for Disassembly - This method prioritizes mechanical, reversible connections and non-toxic, high-quality materials to ease dismantlement, support adaptability, and extend lifespan, while facilitating selective removal and reuse of building components via modular and standardized design.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com