Decentralized identity leverages blockchain and cryptographic methods to give users sovereign control over their personal data, enhancing privacy and security without relying on centralized authorities. OAuth, a widely adopted authorization framework, enables third-party access to user information via centralized identity providers, often compromising data ownership and increasing vulnerability to breaches. Explore the intricacies of both to understand which model best aligns with your security and privacy needs.
Why it is important
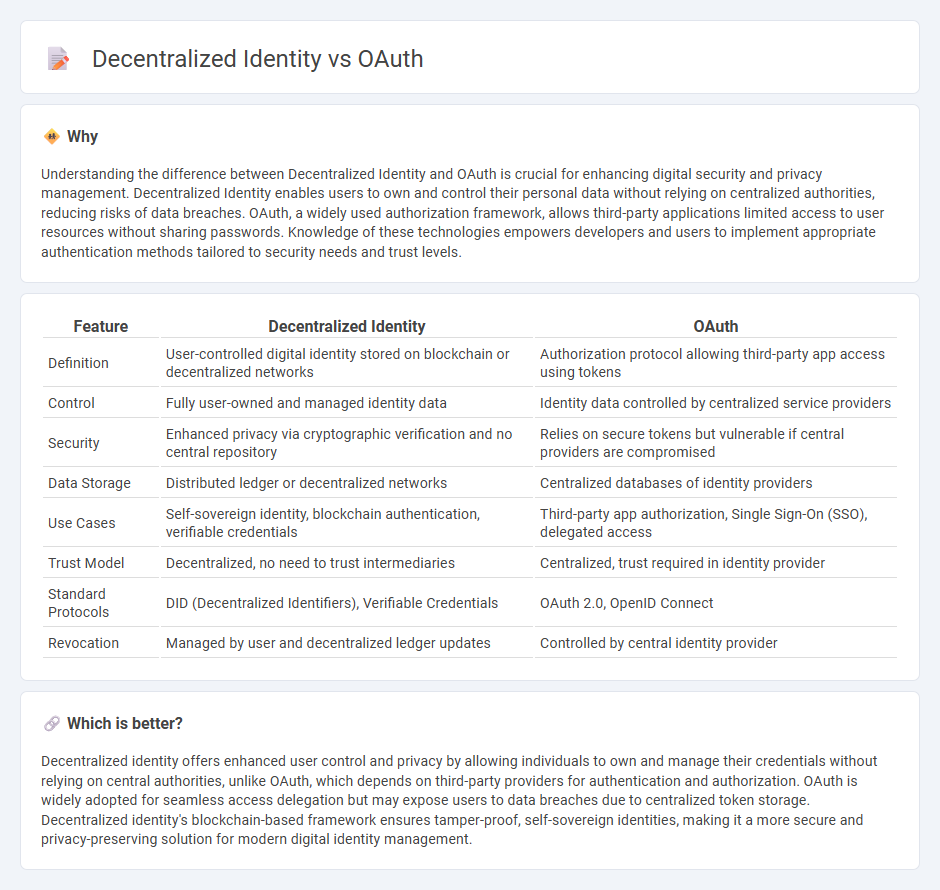
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Identity and OAuth is crucial for enhancing digital security and privacy management. Decentralized Identity enables users to own and control their personal data without relying on centralized authorities, reducing risks of data breaches. OAuth, a widely used authorization framework, allows third-party applications limited access to user resources without sharing passwords. Knowledge of these technologies empowers developers and users to implement appropriate authentication methods tailored to security needs and trust levels.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Identity | OAuth |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | User-controlled digital identity stored on blockchain or decentralized networks | Authorization protocol allowing third-party app access using tokens |
| Control | Fully user-owned and managed identity data | Identity data controlled by centralized service providers |
| Security | Enhanced privacy via cryptographic verification and no central repository | Relies on secure tokens but vulnerable if central providers are compromised |
| Data Storage | Distributed ledger or decentralized networks | Centralized databases of identity providers |
| Use Cases | Self-sovereign identity, blockchain authentication, verifiable credentials | Third-party app authorization, Single Sign-On (SSO), delegated access |
| Trust Model | Decentralized, no need to trust intermediaries | Centralized, trust required in identity provider |
| Standard Protocols | DID (Decentralized Identifiers), Verifiable Credentials | OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect |
| Revocation | Managed by user and decentralized ledger updates | Controlled by central identity provider |
Which is better?
Decentralized identity offers enhanced user control and privacy by allowing individuals to own and manage their credentials without relying on central authorities, unlike OAuth, which depends on third-party providers for authentication and authorization. OAuth is widely adopted for seamless access delegation but may expose users to data breaches due to centralized token storage. Decentralized identity's blockchain-based framework ensures tamper-proof, self-sovereign identities, making it a more secure and privacy-preserving solution for modern digital identity management.
Connection
Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to give users control over their personal data, while OAuth is an authorization protocol that enables secure access delegation between applications. These technologies are connected as decentralized identity frameworks integrate OAuth mechanisms to facilitate user authentication and permission management without relying on centralized authorities. This combination enhances security, privacy, and user sovereignty in digital identity management systems.
Key Terms
Authorization
OAuth is a widely adopted authorization framework that enables third-party applications to access user resources without sharing credentials, relying on centralized identity providers like Google or Facebook. In contrast, decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology and verifiable credentials to give users control over their data, eliminating the need for centralized authorities for authorization decisions. Explore the key differences and benefits of OAuth and decentralized identity in managing secure and user-centric authorization.
Self-sovereign identity
OAuth serves as an authorization framework enabling secure access delegation without exposing user credentials, while decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to empower individuals with self-sovereign identity (SSI), granting full control over their digital identities. SSI eliminates reliance on centralized authorities by allowing users to manage, share, and verify personal data through cryptographically secured verifiable credentials. Discover how SSI transforms digital trust and privacy by exploring its principles and applications in modern identity management.
Federated authentication
OAuth facilitates federated authentication by enabling users to grant third-party applications access without sharing credentials, relying on centralized identity providers like Google or Facebook. Decentralized identity, in contrast, allows users to control their credentials via blockchain-based or distributed ledger technologies, eliminating centralized authorities and enhancing privacy and security. Explore further to understand the impact of these models on future digital identity management.
Source and External Links
OAuth - OAuth is an open standard for access delegation, allowing users to grant applications access to their account information without sharing credentials.
What Is OAuth? - OAuth enables users to sign in to one app or service using another without revealing private information like passwords.
OAuth 2.0 - OAuth 2.0 is the industry-standard protocol for authorization, focusing on client developer simplicity and providing specific authorization flows for various applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com