Edge mesh networks distribute processing and data storage closer to devices, reducing latency and improving real-time responsiveness compared to centralized networks that rely on a single core data center. Centralized networks offer simplified management and consolidated security but may face bottlenecks and increased risks during outages. Explore the advantages and applications of edge mesh and centralized networks to understand which technology best fits your needs.
Why it is important
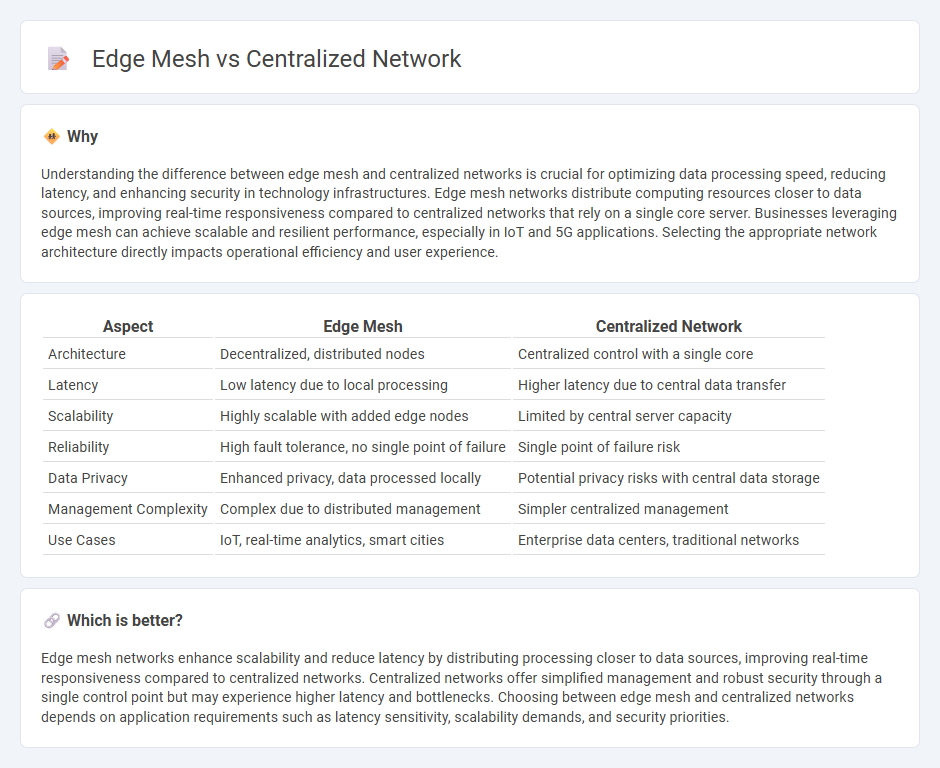
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and centralized networks is crucial for optimizing data processing speed, reducing latency, and enhancing security in technology infrastructures. Edge mesh networks distribute computing resources closer to data sources, improving real-time responsiveness compared to centralized networks that rely on a single core server. Businesses leveraging edge mesh can achieve scalable and resilient performance, especially in IoT and 5G applications. Selecting the appropriate network architecture directly impacts operational efficiency and user experience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Edge Mesh | Centralized Network |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Decentralized, distributed nodes | Centralized control with a single core |
| Latency | Low latency due to local processing | Higher latency due to central data transfer |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with added edge nodes | Limited by central server capacity |
| Reliability | High fault tolerance, no single point of failure | Single point of failure risk |
| Data Privacy | Enhanced privacy, data processed locally | Potential privacy risks with central data storage |
| Management Complexity | Complex due to distributed management | Simpler centralized management |
| Use Cases | IoT, real-time analytics, smart cities | Enterprise data centers, traditional networks |
Which is better?
Edge mesh networks enhance scalability and reduce latency by distributing processing closer to data sources, improving real-time responsiveness compared to centralized networks. Centralized networks offer simplified management and robust security through a single control point but may experience higher latency and bottlenecks. Choosing between edge mesh and centralized networks depends on application requirements such as latency sensitivity, scalability demands, and security priorities.
Connection
Edge mesh and centralized network architectures connect by distributing data processing closer to the data source in edge mesh, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional centralized networks that rely on a single data center. Edge mesh leverages interconnected edge nodes to enable real-time analytics and improved scalability while central networks focus on centralized control and resource management. This integration enhances overall network efficiency, combining the responsiveness of edge computing with the comprehensive oversight of centralized management.
Key Terms
Control Authority
Centralized networks consolidate control authority within a single central node, simplifying management but creating potential bottlenecks and single points of failure. Edge mesh networks distribute control authority across multiple edge nodes, enhancing resilience, reducing latency, and improving scalability by enabling autonomous decision-making closer to data sources. Explore deeper insights into how control authority impacts network performance and security.
Data Latency
Centralized networks process data at a single core location, causing increased data latency due to longer transmission distances and potential bottlenecks. Edge mesh networks distribute processing closer to data sources, significantly reducing latency by enabling real-time data handling and faster response times. Learn more about how edge mesh architecture optimizes network performance and minimizes data delays.
Scalability
Centralized networks offer limited scalability due to bottlenecks at the central hub, restricting the system's ability to handle increased data traffic efficiently. Edge mesh architectures distribute processing across numerous nodes near the data source, enhancing scalability by reducing latency and balancing load dynamically. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize network design for scalable performance.
Source and External Links
What are Centralized and Decentralized Networks? | NinjaOne - A centralized network functions under one main server that controls all data transmission, storage, and processing, making it efficient to manage but vulnerable to single points of failure and cyberattacks.
The Difference Between Centralized and Decentralized Networks - Centralized network architecture relies on a single server handling all processing, offering consistency and affordability but limited scalability and risk of total downtime if the server fails.
Centralized vs. Decentralized vs. Distributed Systems - GeeksforGeeks - Centralized systems have a single point of control making them simpler and efficient to maintain, but they suffer from scalability issues and are prone to complete failure if the central server goes offline.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com