RISC-V and OpenPOWER represent two influential open-source hardware architectures reshaping modern computing. RISC-V offers a modular, scalable instruction set architecture (ISA) designed for flexibility and efficiency in a wide range of devices, from IoT to high-performance servers. Explore the distinct advantages and applications of RISC-V versus OpenPOWER to understand their impact on future technology innovation.
Why it is important
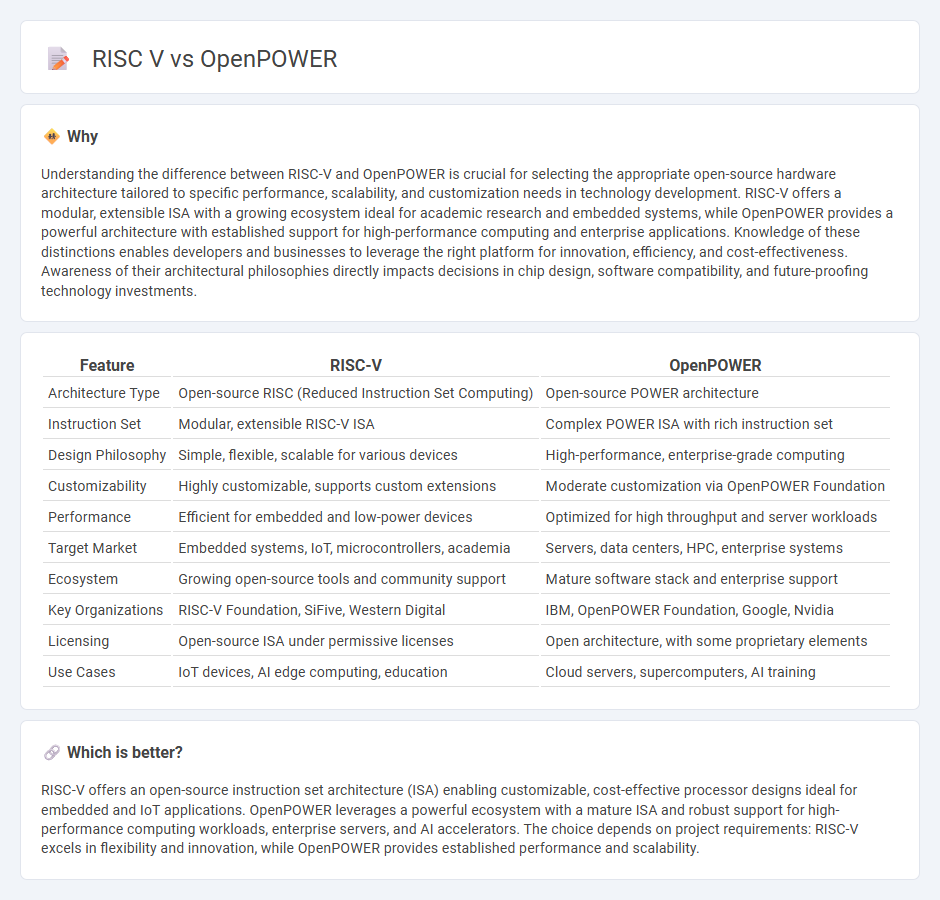
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and OpenPOWER is crucial for selecting the appropriate open-source hardware architecture tailored to specific performance, scalability, and customization needs in technology development. RISC-V offers a modular, extensible ISA with a growing ecosystem ideal for academic research and embedded systems, while OpenPOWER provides a powerful architecture with established support for high-performance computing and enterprise applications. Knowledge of these distinctions enables developers and businesses to leverage the right platform for innovation, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Awareness of their architectural philosophies directly impacts decisions in chip design, software compatibility, and future-proofing technology investments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RISC-V | OpenPOWER |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Open-source RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) | Open-source POWER architecture |
| Instruction Set | Modular, extensible RISC-V ISA | Complex POWER ISA with rich instruction set |
| Design Philosophy | Simple, flexible, scalable for various devices | High-performance, enterprise-grade computing |
| Customizability | Highly customizable, supports custom extensions | Moderate customization via OpenPOWER Foundation |
| Performance | Efficient for embedded and low-power devices | Optimized for high throughput and server workloads |
| Target Market | Embedded systems, IoT, microcontrollers, academia | Servers, data centers, HPC, enterprise systems |
| Ecosystem | Growing open-source tools and community support | Mature software stack and enterprise support |
| Key Organizations | RISC-V Foundation, SiFive, Western Digital | IBM, OpenPOWER Foundation, Google, Nvidia |
| Licensing | Open-source ISA under permissive licenses | Open architecture, with some proprietary elements |
| Use Cases | IoT devices, AI edge computing, education | Cloud servers, supercomputers, AI training |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) enabling customizable, cost-effective processor designs ideal for embedded and IoT applications. OpenPOWER leverages a powerful ecosystem with a mature ISA and robust support for high-performance computing workloads, enterprise servers, and AI accelerators. The choice depends on project requirements: RISC-V excels in flexibility and innovation, while OpenPOWER provides established performance and scalability.
Connection
RISC-V and OpenPOWER share a foundation in open-source hardware architectures, promoting innovation through community-driven development. Both ecosystems emphasize transparency and customization, enabling developers to optimize processors for diverse applications, from embedded systems to high-performance computing. Collaboration between RISC-V's modular instruction set architecture and OpenPOWER's scalable CPU designs accelerates advancements in efficient and flexible computing solutions.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
OpenPOWER architecture emphasizes a complex instruction set computer (CISC) approach with a rich set of established instructions designed for high-performance computing and enterprise servers, leveraging decades of IBM's innovation in POWER ISA. RISC-V is a modular, open standard reduced instruction set computer (RISC) ISA that offers flexibility and extensibility, encouraging customization for embedded systems, AI, and edge computing applications due to its simplistic, scalable design. Explore more to understand how these distinct ISAs influence application development and hardware ecosystem growth.
Open Source Hardware
OpenPOWER, developed by IBM, offers an open architecture enabling collaboration and innovation in enterprise-grade processors, contrasting with RISC-V's open-standard ISA designed for flexibility across diverse applications. Both ecosystems emphasize open-source hardware principles, with OpenPOWER leveraging a mature software stack and RISC-V promoting modularity and scalability in custom chip designs. Explore the evolving landscape of open-source hardware by diving deeper into the unique strengths of OpenPOWER and RISC-V platforms.
Ecosystem
OpenPOWER benefits from a mature and robust ecosystem supported by IBM and key industry partners, offering extensive software compatibility and specialized hardware accelerators. RISC-V, as an open-source instruction set architecture, fosters rapid innovation and broad adoption across academic, commercial, and hobbyist communities with flexible customization options. Explore the unique ecosystem advantages that drive the evolution of both architectures.
Source and External Links
OpenPOWER Foundation - Wikipedia - The OpenPOWER Foundation is a collaborative initiative started by IBM in 2013 to openly license and develop hardware and software around the Power ISA, enabling ecosystem partners to create customized servers and other technology components with royalty-free patents and open collaboration models; it merged with the Linux Foundation in 2019.
OpenPOWER Foundation: Home - The OpenPOWER Foundation drives open innovation in computing using the sophisticated POWER ISA, fostering collaboration among 350+ members to develop customizable hardware and software stacks for advanced applications like AI, supercomputing, and hyperscale environments.
Ask HN: Does anyone care about OpenPOWER? - Hacker News Discussion - OpenPOWER is recognized for leveraging IBM's high-end POWER chips to offer alternatives to x86_64 systems with a focus on ownership and control of computing, though it faces challenges in cost and ecosystem size compared to more hobbyist-friendly ARM devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com