Edge mesh networks distribute computing resources closer to data sources, reducing latency and improving real-time processing for IoT devices and mobile applications. Data centers centralize processing power and storage, offering robust infrastructure for large-scale data management and enterprise applications. Explore the advantages of edge mesh versus data center architectures to optimize your technology strategy.
Why it is important
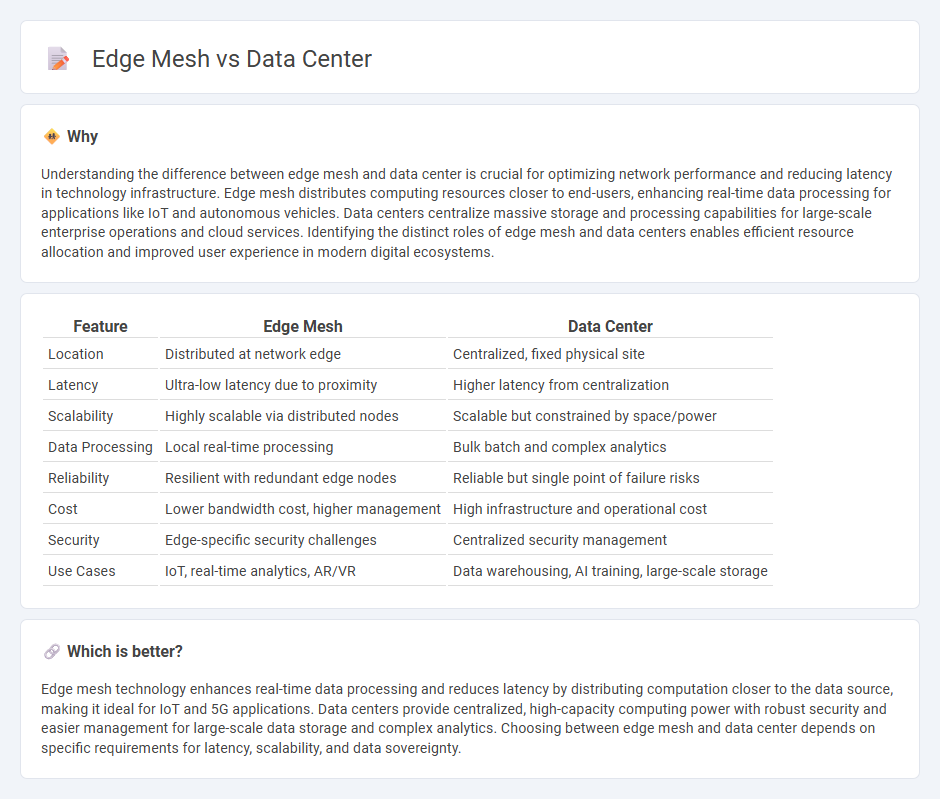
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and data center is crucial for optimizing network performance and reducing latency in technology infrastructure. Edge mesh distributes computing resources closer to end-users, enhancing real-time data processing for applications like IoT and autonomous vehicles. Data centers centralize massive storage and processing capabilities for large-scale enterprise operations and cloud services. Identifying the distinct roles of edge mesh and data centers enables efficient resource allocation and improved user experience in modern digital ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Mesh | Data Center |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Distributed at network edge | Centralized, fixed physical site |
| Latency | Ultra-low latency due to proximity | Higher latency from centralization |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via distributed nodes | Scalable but constrained by space/power |
| Data Processing | Local real-time processing | Bulk batch and complex analytics |
| Reliability | Resilient with redundant edge nodes | Reliable but single point of failure risks |
| Cost | Lower bandwidth cost, higher management | High infrastructure and operational cost |
| Security | Edge-specific security challenges | Centralized security management |
| Use Cases | IoT, real-time analytics, AR/VR | Data warehousing, AI training, large-scale storage |
Which is better?
Edge mesh technology enhances real-time data processing and reduces latency by distributing computation closer to the data source, making it ideal for IoT and 5G applications. Data centers provide centralized, high-capacity computing power with robust security and easier management for large-scale data storage and complex analytics. Choosing between edge mesh and data center depends on specific requirements for latency, scalability, and data sovereignty.
Connection
Edge mesh networks distribute computing resources closer to data sources by interconnecting multiple edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Data centers serve as centralized hubs that manage and process vast amounts of data generated by edge mesh nodes, ensuring efficient data aggregation and storage. The symbiotic connection between edge mesh and data centers optimizes real-time data processing and enhances overall network performance.
Key Terms
Latency
Data centers typically centralize processing power and storage, leading to higher latency due to physical distance from end users, which can affect real-time applications. Edge mesh architecture distributes computing resources closer to the data source, significantly reducing latency by minimizing data travel time and enabling faster response rates. Explore the differences between data center and edge mesh latency to optimize your network performance.
Scalability
Data centers provide centralized scalability by aggregating massive computing resources in a single location, facilitating efficient resource management and high-performance workloads. Edge mesh, in contrast, offers distributed scalability by deploying interconnected nodes closer to data sources, reducing latency and handling localized processing demands. Explore the advantages of each approach to determine the best scalability solution for your infrastructure needs.
Proximity
Data centers centralize computing resources to provide robust processing power and storage, while edge mesh networks distribute computing closer to the data source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness. Proximity in edge mesh environments enables faster data processing for IoT devices and critical applications by minimizing the distance data travels, improving performance and reliability. Explore how proximity differences between data centers and edge mesh impact your network architecture and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Data center - Wikipedia - A data center is a dedicated building or space for housing computer systems, telecommunications, and storage systems, designed with redundancy in power, communication, and environmental controls to ensure business continuity.
What Is a Data Center? - Cisco - A data center is a physical facility that stores and shares applications and data through a network of routers, switches, servers, and storage systems, supporting both on-premises and cloud environments.
What is a Data Center? - Check Point - Modern data centers are composed of compute, storage, and network components supported by infrastructure that ensures high performance and security for enterprise needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com