Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated or manipulated content by analyzing inconsistencies in visual, auditory, or textual data patterns. Content authentication verifies the origin and integrity of digital media through cryptographic methods and metadata validation to ensure trustworthiness. Explore advanced techniques in synthetic media detection and content authentication to safeguard digital information effectively.
Why it is important
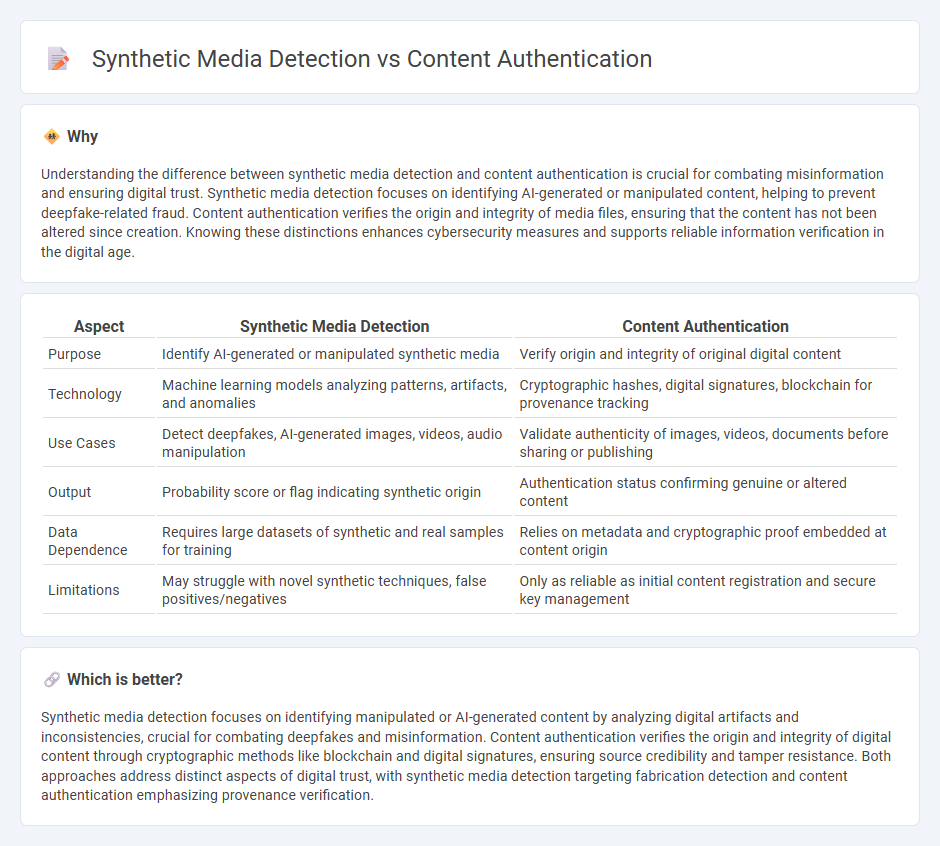
Understanding the difference between synthetic media detection and content authentication is crucial for combating misinformation and ensuring digital trust. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated or manipulated content, helping to prevent deepfake-related fraud. Content authentication verifies the origin and integrity of media files, ensuring that the content has not been altered since creation. Knowing these distinctions enhances cybersecurity measures and supports reliable information verification in the digital age.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Media Detection | Content Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify AI-generated or manipulated synthetic media | Verify origin and integrity of original digital content |
| Technology | Machine learning models analyzing patterns, artifacts, and anomalies | Cryptographic hashes, digital signatures, blockchain for provenance tracking |
| Use Cases | Detect deepfakes, AI-generated images, videos, audio manipulation | Validate authenticity of images, videos, documents before sharing or publishing |
| Output | Probability score or flag indicating synthetic origin | Authentication status confirming genuine or altered content |
| Data Dependence | Requires large datasets of synthetic and real samples for training | Relies on metadata and cryptographic proof embedded at content origin |
| Limitations | May struggle with novel synthetic techniques, false positives/negatives | Only as reliable as initial content registration and secure key management |
Which is better?
Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content by analyzing digital artifacts and inconsistencies, crucial for combating deepfakes and misinformation. Content authentication verifies the origin and integrity of digital content through cryptographic methods like blockchain and digital signatures, ensuring source credibility and tamper resistance. Both approaches address distinct aspects of digital trust, with synthetic media detection targeting fabrication detection and content authentication emphasizing provenance verification.
Connection
Synthetic media detection employs advanced algorithms to identify AI-generated content by analyzing inconsistencies in visual, audio, or textual data. Content authentication ensures the integrity and origin of digital media by verifying metadata and cryptographic signatures, preventing tampering or misinformation. Both technologies collaborate to enhance digital trust by distinguishing genuine content from manipulated or synthetic media in cybersecurity and digital forensics.
Key Terms
Deepfake Detection
Content authentication involves verifying the originality and integrity of digital media by analyzing metadata and cryptographic signatures, while synthetic media detection specifically targets the identification of artificially generated content such as deepfakes. Deepfake detection employs advanced machine learning algorithms to examine visual inconsistencies, facial movements, and audio anomalies that are characteristic of manipulated videos. Explore the latest techniques and tools in deepfake detection to enhance digital content security and trustworthiness.
Digital Watermarking
Content authentication relies on digital watermarking techniques that embed imperceptible information into media files, verifying their originality and integrity. Synthetic media detection focuses on identifying manipulated or AI-generated content through analysis of inconsistencies or artifacts often absent in genuine watermarked media. Explore how advanced digital watermarking enhances both content authentication and synthetic media detection for robust media security solutions.
Content Provenance
Content authentication ensures the originality and integrity of digital media by verifying its source and history, while synthetic media detection focuses on identifying AI-generated or manipulated content designed to deceive. Content provenance plays a crucial role in both by providing transparent and traceable metadata that documents the creation, modification, and distribution lifecycle of media files. Explore more to understand how advanced provenance frameworks enhance trust and combat misinformation in digital ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Content Authenticity Verification Tools | ScoreDetect Blog - Content authentication uses hashcodes and digital signatures to verify that digital content has not been altered and to prove the identity of its creator, while metadata provides provenance that traces the content's lifecycle for end-to-end authenticity verification.
How it works - Content Authenticity Initiative - Content authentication involves cryptographically hashing and signing digital assets to create tamper-evident, persistent records of their origin and editing history, supported by open-source tools and industry standards like C2PA's Content Credentials.
C2PA | Verifying Media Content Sources - The Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) sets open technical standards that enable publishers, creators, and consumers to establish and verify the origin and edits of digital content through Content Credentials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com