RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) known for its modularity, scalability, and extensive ecosystem support, enabling flexible implementation across a wide range of devices from microcontrollers to supercomputers. Elbrus, developed by the Russian scientific center MCST, is a proprietary architecture featuring VLIW (Very Long Instruction Word) technology designed primarily for high-performance computing within Russian defense and scientific sectors. Explore the technical contrasts and unique benefits of RISC-V and Elbrus architectures to understand their impact on the future of processor design.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between RISC-V and Elbrus architectures is crucial for optimizing computing performance and software compatibility in specialized applications. RISC-V is an open-source ISA known for its modularity and adaptability in embedded systems and academic research. Elbrus, a Russian-developed architecture, emphasizes high performance in domestic computing solutions and security. Knowledge of both enables informed decisions in processor selection tailored to industry-specific needs and geopolitical considerations.
Comparison Table
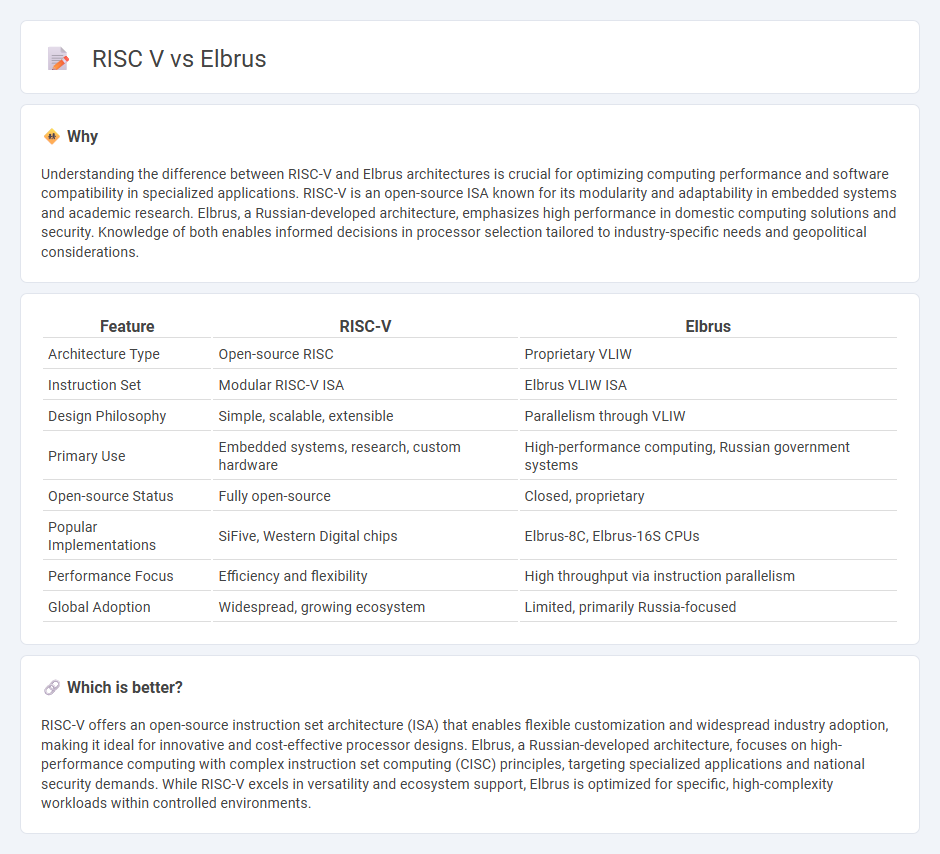
| Feature | RISC-V | Elbrus |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Open-source RISC | Proprietary VLIW |
| Instruction Set | Modular RISC-V ISA | Elbrus VLIW ISA |
| Design Philosophy | Simple, scalable, extensible | Parallelism through VLIW |
| Primary Use | Embedded systems, research, custom hardware | High-performance computing, Russian government systems |
| Open-source Status | Fully open-source | Closed, proprietary |
| Popular Implementations | SiFive, Western Digital chips | Elbrus-8C, Elbrus-16S CPUs |
| Performance Focus | Efficiency and flexibility | High throughput via instruction parallelism |
| Global Adoption | Widespread, growing ecosystem | Limited, primarily Russia-focused |
Which is better?
RISC-V offers an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) that enables flexible customization and widespread industry adoption, making it ideal for innovative and cost-effective processor designs. Elbrus, a Russian-developed architecture, focuses on high-performance computing with complex instruction set computing (CISC) principles, targeting specialized applications and national security demands. While RISC-V excels in versatility and ecosystem support, Elbrus is optimized for specific, high-complexity workloads within controlled environments.
Connection
RISC-V and Elbrus are connected through their shared influence in advancing open and customizable processor architectures. RISC-V is an open-standard instruction set architecture (ISA) promoting modularity and extensibility, while Elbrus processors incorporate unique VLIW (Very Long Instruction Word) architecture elements, emphasizing innovation in CPU design. Both contribute to diversifying the global semiconductor landscape by offering alternatives to dominant architectures like x86 and ARM.
Key Terms
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
Elbrus and RISC-V differ significantly in their Instruction Set Architecture, with Elbrus employing a VLIW (Very Long Instruction Word) architecture that enables parallel instruction execution, while RISC-V utilizes a simpler, modular RISC architecture designed for scalability and open-source flexibility. Elbrus ISAs are proprietary and optimized for high-performance computing tasks, contrasted by RISC-V's open ISA fostering widespread adoption and customization across various hardware designs. Explore in-depth comparisons of Elbrus and RISC-V ISAs to understand their impact on processor performance and development ecosystems.
Microprocessor Design
Elbrus microprocessors leverage VLIW architecture to achieve high instruction-level parallelism and efficient task execution, while RISC-V emphasizes modular, open-source ISA design for customizable and scalable processor development. Elbrus chips are optimized for complex computing workloads often used in scientific and defense applications, whereas RISC-V cores cater to a broad range of embedded and general-purpose systems with flexibility and portability. Explore the intricate design principles and performance trade-offs between Elbrus and RISC-V architectures to deepen your understanding of modern microprocessor innovation.
Compatibility
Elbrus processors, developed by MCST, emphasize backward compatibility with x86 and other legacy architectures through dynamic binary translation, ensuring existing software runs efficiently. RISC-V, an open-source instruction set architecture, prioritizes modularity and extensibility but requires software recompilation or emulation for compatibility with x86 applications. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how compatibility strategies impact performance and ecosystem adoption.
Source and External Links
Mount Elbrus | Europe's, Highest Peak, Caucasus - Mount Elbrus is the highest peak of the Caucasus Mountains in southwestern Russia, an extinct volcano with twin cones reaching 5,642 meters (18,510 feet), and a major center for mountaineering and tourism.
Mount Elbrus - It is the highest mountain in Russia and Europe, a dormant stratovolcano with two summits, the higher one at 5,642 meters (18,510 feet), located in the Kabardino-Balkaria region of southern Russia.
Mount Elbrus - Mount Elbrus, a double-topped pyramid in the Caucasus Mountains, is the tallest mountain in Europe and Russia, famed as one of the Seven Summits and a popular mountaineering destination offering guided expeditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com