Zero trust and network segmentation are critical security strategies designed to protect digital infrastructures by minimizing unauthorized access and containing potential breaches. Zero trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," requiring continuous authentication for every user and device, while network segmentation divides networks into isolated zones to limit lateral movement of threats. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches enhance cybersecurity resilience and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
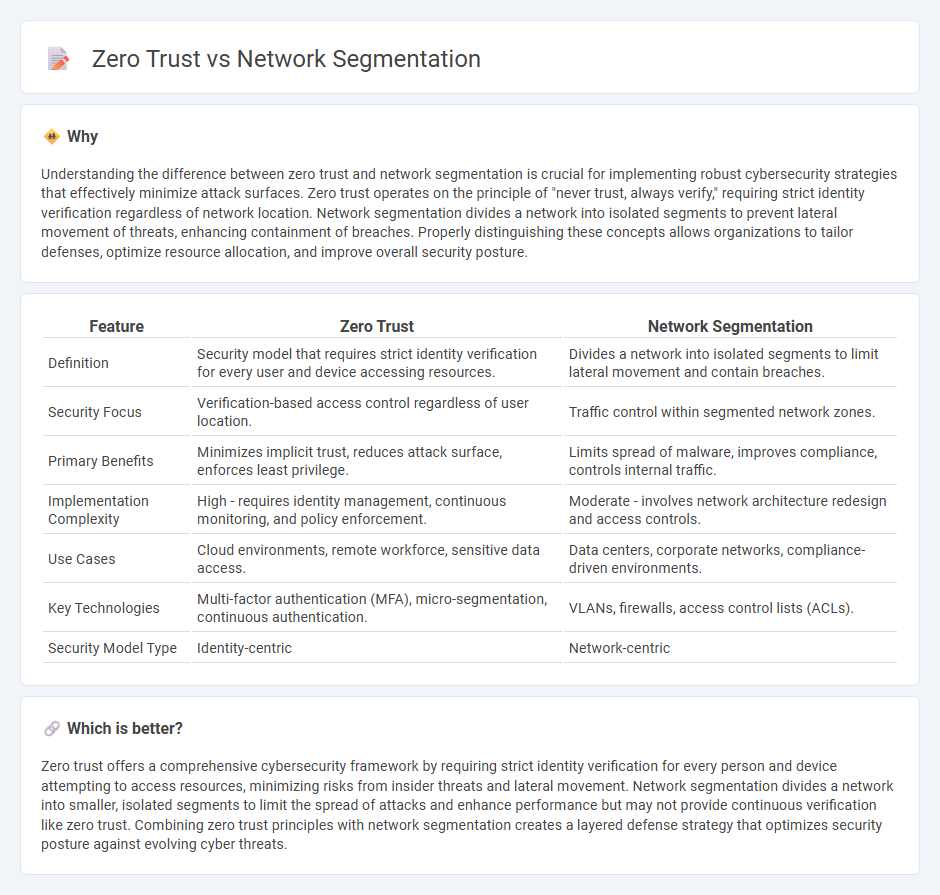
Understanding the difference between zero trust and network segmentation is crucial for implementing robust cybersecurity strategies that effectively minimize attack surfaces. Zero trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," requiring strict identity verification regardless of network location. Network segmentation divides a network into isolated segments to prevent lateral movement of threats, enhancing containment of breaches. Properly distinguishing these concepts allows organizations to tailor defenses, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall security posture.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust | Network Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model that requires strict identity verification for every user and device accessing resources. | Divides a network into isolated segments to limit lateral movement and contain breaches. |
| Security Focus | Verification-based access control regardless of user location. | Traffic control within segmented network zones. |
| Primary Benefits | Minimizes implicit trust, reduces attack surface, enforces least privilege. | Limits spread of malware, improves compliance, controls internal traffic. |
| Implementation Complexity | High - requires identity management, continuous monitoring, and policy enforcement. | Moderate - involves network architecture redesign and access controls. |
| Use Cases | Cloud environments, remote workforce, sensitive data access. | Data centers, corporate networks, compliance-driven environments. |
| Key Technologies | Multi-factor authentication (MFA), micro-segmentation, continuous authentication. | VLANs, firewalls, access control lists (ACLs). |
| Security Model Type | Identity-centric | Network-centric |
Which is better?
Zero trust offers a comprehensive cybersecurity framework by requiring strict identity verification for every person and device attempting to access resources, minimizing risks from insider threats and lateral movement. Network segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the spread of attacks and enhance performance but may not provide continuous verification like zero trust. Combining zero trust principles with network segmentation creates a layered defense strategy that optimizes security posture against evolving cyber threats.
Connection
Zero trust security relies on network segmentation to limit access and contain potential breaches by dividing a network into isolated zones where access permissions are strictly enforced. Network segmentation supports zero trust principles by minimizing lateral movement of attackers within a network, enforcing least privilege access, and enhancing monitoring capabilities. Implementing both zero trust and network segmentation significantly improves an organization's cybersecurity posture by reducing risk exposure and preventing unauthorized access.
Key Terms
Perimeter-based Security
Perimeter-based security relies on dividing a network into segments to control access and contain potential threats within defined boundaries, reducing the risk of lateral movement by attackers. Zero trust, in contrast, eliminates implicit trust in the network perimeter and enforces strict identity verification and least-privilege access across all segments, regardless of location. Explore deeper insights into how perimeter-based security compares with zero trust models to enhance your organization's defense strategy.
Micro-segmentation
Network segmentation divides a network into isolated zones to limit access and reduce attack surfaces, while Zero Trust incorporates continuous verification and strict access controls regardless of network location. Micro-segmentation, a core Zero Trust strategy, enforces granular security policies within these zones down to individual workloads and applications, significantly enhancing lateral movement prevention. Explore how micro-segmentation upgrades traditional network segmentation within Zero Trust frameworks for robust cybersecurity.
Least Privilege
Network segmentation divides a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit access and reduce attack surfaces, while Zero Trust implements continuous verification of user and device identities, enforcing least privilege access across all resources. Least privilege in network segmentation restricts permissions based on segment boundaries, whereas Zero Trust applies granular, dynamic access controls beyond just network layers, minimizing risks from compromised credentials. Explore how integrating both strategies can enhance security by tightly controlling access and reducing potential breach impacts.
Source and External Links
Auvik - Network Segmentation: What It Is & How It Works - Network segmentation divides a large network into smaller, isolated subnetworks, either physically through hardware or logically using virtual methods like VLANs and IP subnets.
Palo Alto Networks - What Is Network Segmentation? - Network segmentation enhances security by limiting the spread of threats, reduces network congestion, and helps decrease compliance scope by isolating critical systems.
Cisco - What Is Network Segmentation? - Segmentation controls network traffic flow between segments, enforces security policies (e.g., access restrictions), and modern approaches use software-defined access for more flexible, granular control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com