Quantum advantage refers to the practical achievement where quantum computers perform specific tasks faster or more efficiently than classical computers, whereas quantum supremacy denotes the milestone when a quantum device solves a problem that no classical supercomputer can solve in a feasible amount of time. Both concepts highlight significant breakthroughs in quantum computing, with quantum supremacy representing a theoretical proof of concept and quantum advantage focusing on real-world applicability. Explore the distinctions and implications of these quantum milestones to understand the future of computing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between quantum advantage and quantum supremacy is crucial for accurately assessing the practical impact of quantum computing on real-world problems. Quantum supremacy refers to a quantum computer performing a task impossible for classical computers, while quantum advantage means a quantum computer outperforms classical ones on useful, practical tasks. Knowing these distinctions helps in setting realistic expectations for technological advancements and investment in quantum research. Clear comprehension guides strategic development and application across industries leveraging quantum technologies.
Comparison Table
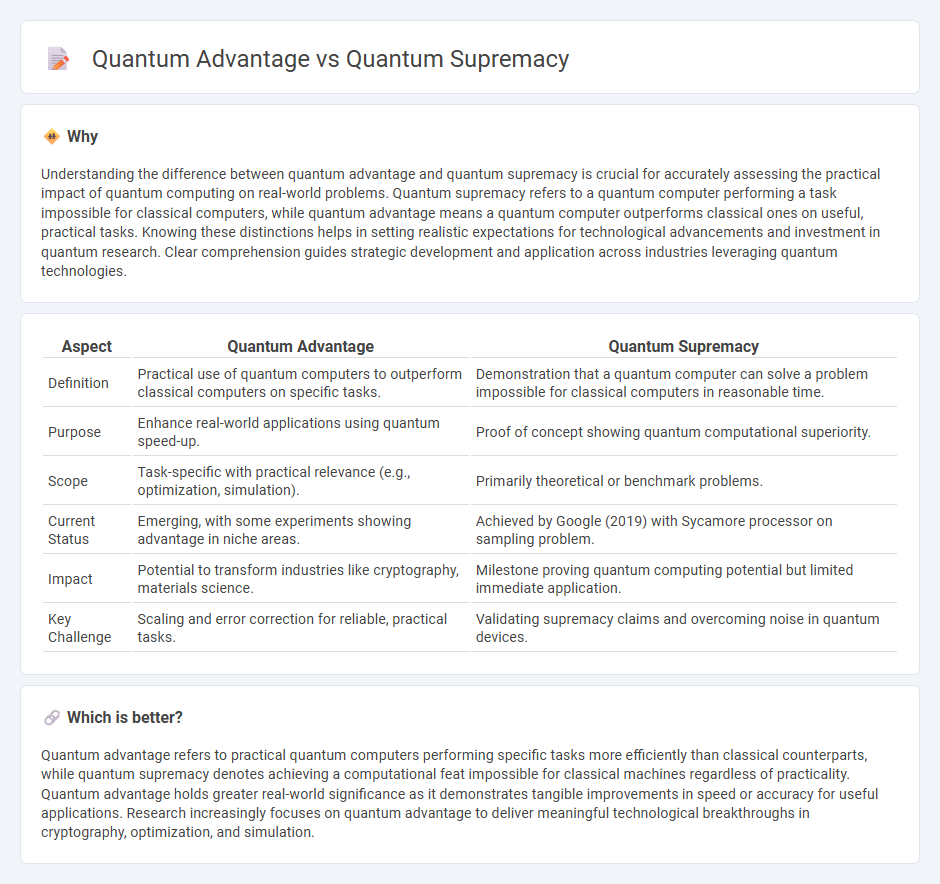
| Aspect | Quantum Advantage | Quantum Supremacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practical use of quantum computers to outperform classical computers on specific tasks. | Demonstration that a quantum computer can solve a problem impossible for classical computers in reasonable time. |
| Purpose | Enhance real-world applications using quantum speed-up. | Proof of concept showing quantum computational superiority. |
| Scope | Task-specific with practical relevance (e.g., optimization, simulation). | Primarily theoretical or benchmark problems. |
| Current Status | Emerging, with some experiments showing advantage in niche areas. | Achieved by Google (2019) with Sycamore processor on sampling problem. |
| Impact | Potential to transform industries like cryptography, materials science. | Milestone proving quantum computing potential but limited immediate application. |
| Key Challenge | Scaling and error correction for reliable, practical tasks. | Validating supremacy claims and overcoming noise in quantum devices. |
Which is better?
Quantum advantage refers to practical quantum computers performing specific tasks more efficiently than classical counterparts, while quantum supremacy denotes achieving a computational feat impossible for classical machines regardless of practicality. Quantum advantage holds greater real-world significance as it demonstrates tangible improvements in speed or accuracy for useful applications. Research increasingly focuses on quantum advantage to deliver meaningful technological breakthroughs in cryptography, optimization, and simulation.
Connection
Quantum advantage refers to quantum computers performing specific tasks more efficiently than classical counterparts, while quantum supremacy marks the milestone where quantum machines solve problems impossible for classical systems. Both concepts signify breakthroughs in computational power, with quantum supremacy highlighting the initial demonstration of such superiority. Advancements in quantum algorithms and hardware drive the transition from achieving quantum advantage toward the broader goal of quantum supremacy.
Key Terms
Qubits
Quantum supremacy refers to the point where a quantum computer can solve a problem faster than the most powerful classical supercomputers, typically involving thousands of qubits operating in complex entangled states. Quantum advantage, on the other hand, emphasizes practical applications where quantum computers outperform classical counterparts in real-world tasks, often achievable with fewer qubits but higher fidelity and error correction. Explore the nuances between quantum supremacy and quantum advantage to understand their impact on the future of quantum computing technology.
Classical Computation
Quantum supremacy refers to the point at which a quantum computer performs a specific task faster than the most powerful classical supercomputers, highlighting a significant milestone in classical computation comparison. Quantum advantage, however, emphasizes practical improvements in solving real-world problems more efficiently than classical methods, showcasing tangible benefits beyond mere speed. Explore the nuances and implications of these concepts in advancing computational technology.
Computational Complexity
Quantum supremacy refers to a quantum computer's ability to solve a problem that is practically infeasible for classical supercomputers, often demonstrated through tasks like random circuit sampling with exponential computational complexity. Quantum advantage, however, emphasizes achieving a practical performance benefit in real-world applications by outperforming classical algorithms in terms of speed or accuracy, particularly in domains such as optimization and simulation where computational complexity scales more favorably. Explore deeper insights into how these milestones define progress in quantum computing and their implications for computational complexity theory.
Source and External Links
Quantum supremacy - Quantum supremacy is the demonstration that a programmable quantum computer can solve a computational problem that no classical computer can solve in any feasible amount of time, even if the specific problem is not otherwise useful.
Quantum Supremacy - Quantum supremacy describes the experimental demonstration of a quantum computer's dominance over classical computers by performing calculations previously considered impossible at unmatched speeds.
Google and NASA Achieve Quantum Supremacy - Google's 2019 experiment with a 54-qubit processor achieved a computational task in minutes that would take the world's leading supercomputer thousands of years, marking a recognized milestone in quantum supremacy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com