Self-healing networks automatically detect and repair faults to maintain continuous connectivity, enhancing reliability in critical systems. Mesh networks consist of multiple interconnected nodes that dynamically route data, providing robust and scalable coverage across large areas. Explore the key differences and applications of self-healing and mesh networks to optimize your technological infrastructure.
Why it is important
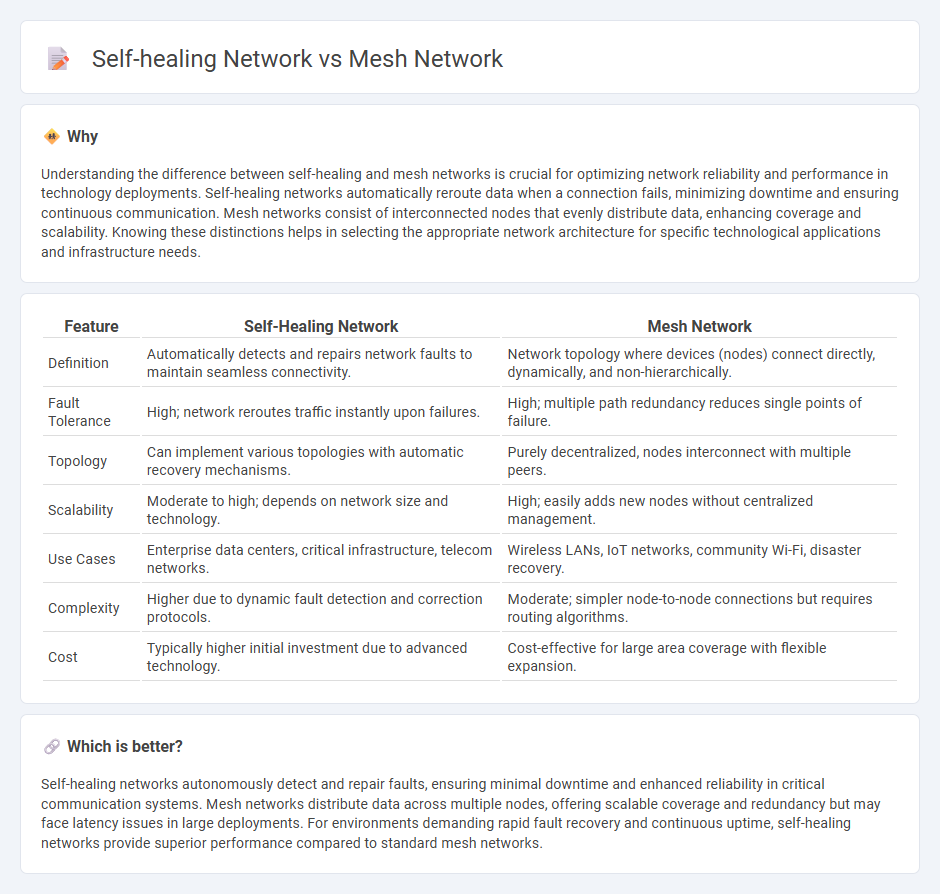
Understanding the difference between self-healing and mesh networks is crucial for optimizing network reliability and performance in technology deployments. Self-healing networks automatically reroute data when a connection fails, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous communication. Mesh networks consist of interconnected nodes that evenly distribute data, enhancing coverage and scalability. Knowing these distinctions helps in selecting the appropriate network architecture for specific technological applications and infrastructure needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Self-Healing Network | Mesh Network |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatically detects and repairs network faults to maintain seamless connectivity. | Network topology where devices (nodes) connect directly, dynamically, and non-hierarchically. |
| Fault Tolerance | High; network reroutes traffic instantly upon failures. | High; multiple path redundancy reduces single points of failure. |
| Topology | Can implement various topologies with automatic recovery mechanisms. | Purely decentralized, nodes interconnect with multiple peers. |
| Scalability | Moderate to high; depends on network size and technology. | High; easily adds new nodes without centralized management. |
| Use Cases | Enterprise data centers, critical infrastructure, telecom networks. | Wireless LANs, IoT networks, community Wi-Fi, disaster recovery. |
| Complexity | Higher due to dynamic fault detection and correction protocols. | Moderate; simpler node-to-node connections but requires routing algorithms. |
| Cost | Typically higher initial investment due to advanced technology. | Cost-effective for large area coverage with flexible expansion. |
Which is better?
Self-healing networks autonomously detect and repair faults, ensuring minimal downtime and enhanced reliability in critical communication systems. Mesh networks distribute data across multiple nodes, offering scalable coverage and redundancy but may face latency issues in large deployments. For environments demanding rapid fault recovery and continuous uptime, self-healing networks provide superior performance compared to standard mesh networks.
Connection
Self-healing networks utilize mesh network architecture to enhance connectivity resilience by automatically rerouting data through alternative paths when link failures occur. Mesh networks distribute data across multiple nodes, creating redundant communication routes that enable the self-healing process to maintain seamless network performance. This synergy improves network reliability, reduces downtime, and supports scalable, fault-tolerant infrastructure in IoT and enterprise environments.
Key Terms
Topology
Mesh networks feature interconnected nodes where each device communicates directly, creating a decentralized topology that enhances coverage and reliability. Self-healing networks utilize redundant paths within various topologies to automatically reroute traffic when nodes or connections fail, ensuring continuous operation without manual intervention. Discover how these topologies impact performance, resilience, and deployment strategies.
Redundancy
Mesh networks provide robust redundancy by interconnecting multiple nodes, ensuring continuous data flow even if some links fail. Self-healing networks enhance this redundancy with intelligent algorithms that automatically detect and reroute around failures, minimizing downtime. Explore the nuances and technologies behind these resilient network architectures for deeper insights.
Fault Tolerance
Mesh networks provide robust fault tolerance by creating multiple pathways for data to travel, ensuring communication persists even if one or more nodes fail. Self-healing networks enhance this capability by automatically detecting and reconfiguring around faults in real-time, minimizing downtime and maintaining service stability. Explore the differences in fault tolerance mechanisms to optimize your network design.
Source and External Links
What is a mesh network? - Google Nest Help - A mesh network uses multiple Wi-Fi devices that act as a single network to provide wider coverage and stronger signals throughout your home, unlike a traditional network with just one router.
What Is Mesh Wifi? Our 2024 Exclusive Guide - Netgear - Mesh Wi-Fi systems include a main router and satellite nodes that work together to blanket large areas with seamless, overlapping wireless coverage, automatically routing data between nodes for optimal performance.
What is Mesh WiFi? | Whole Home Mesh WiFi - TP-Link - Mesh WiFi systems use multiple interconnected nodes to eliminate dead zones and deliver fast, reliable, and uninterrupted internet access as you move around your home.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com