Edge mesh technology enables decentralized data processing by connecting multiple edge devices to reduce latency and improve real-time responsiveness, unlike traditional cloud computing which relies on centralized data centers. Cloud computing offers vast scalability and centralized resource management, suitable for large-scale data storage and complex analytics. Explore the differences between edge mesh and cloud computing to understand their unique advantages in transforming digital infrastructure.
Why it is important
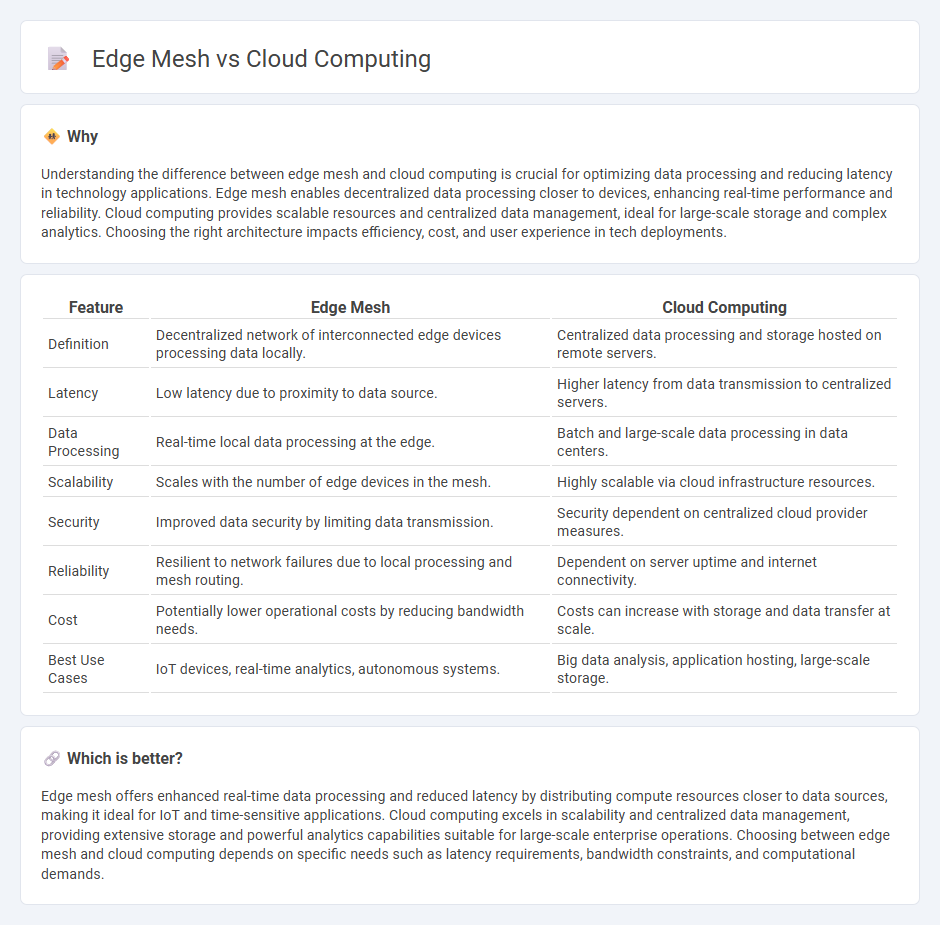
Understanding the difference between edge mesh and cloud computing is crucial for optimizing data processing and reducing latency in technology applications. Edge mesh enables decentralized data processing closer to devices, enhancing real-time performance and reliability. Cloud computing provides scalable resources and centralized data management, ideal for large-scale storage and complex analytics. Choosing the right architecture impacts efficiency, cost, and user experience in tech deployments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Edge Mesh | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decentralized network of interconnected edge devices processing data locally. | Centralized data processing and storage hosted on remote servers. |
| Latency | Low latency due to proximity to data source. | Higher latency from data transmission to centralized servers. |
| Data Processing | Real-time local data processing at the edge. | Batch and large-scale data processing in data centers. |
| Scalability | Scales with the number of edge devices in the mesh. | Highly scalable via cloud infrastructure resources. |
| Security | Improved data security by limiting data transmission. | Security dependent on centralized cloud provider measures. |
| Reliability | Resilient to network failures due to local processing and mesh routing. | Dependent on server uptime and internet connectivity. |
| Cost | Potentially lower operational costs by reducing bandwidth needs. | Costs can increase with storage and data transfer at scale. |
| Best Use Cases | IoT devices, real-time analytics, autonomous systems. | Big data analysis, application hosting, large-scale storage. |
Which is better?
Edge mesh offers enhanced real-time data processing and reduced latency by distributing compute resources closer to data sources, making it ideal for IoT and time-sensitive applications. Cloud computing excels in scalability and centralized data management, providing extensive storage and powerful analytics capabilities suitable for large-scale enterprise operations. Choosing between edge mesh and cloud computing depends on specific needs such as latency requirements, bandwidth constraints, and computational demands.
Connection
Edge mesh networks distribute data processing across multiple interconnected edge devices, reducing latency and enhancing real-time responsiveness. Cloud computing provides scalable storage and centralized management, enabling seamless integration with edge mesh systems for efficient data synchronization and analytics. This synergy supports advanced applications like IoT, autonomous systems, and smart cities by balancing local computation and cloud resources.
Key Terms
Centralized Data Centers (Cloud Computing)
Cloud computing relies on centralized data centers that provide scalable resources and centralized processing power to handle massive amounts of data efficiently. These data centers offer robust infrastructure, high storage capacity, and extensive network connectivity, enabling seamless access and management of cloud services. Explore the advantages of centralized data centers to understand their impact on modern computing architectures.
Decentralized Processing (Edge Mesh)
Decentralized processing in edge mesh architecture distributes data computation closer to the source devices, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to centralized cloud computing. Edge mesh enhances real-time data handling, reliability, and scalability by enabling interconnected nodes to process information collaboratively across diverse locations. Explore the transformative impact of decentralized processing in edge mesh on modern network infrastructures and application performance.
Latency
Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote servers, resulting in higher latency due to long-distance data transmission. Edge mesh distributes computing resources closer to end-users, significantly reducing latency by processing data at the network edge. Explore the intricate latency differences and performance benefits of each architecture to optimize your computing infrastructure.
Source and External Links
What is Cloud Computing? Types, Examples and Benefits - Cloud computing delivers hosted computing and IT services on demand over the internet, allowing users to rent resources like storage, applications, and computing power from remote data centers owned by cloud providers, with dynamic allocation of resources based on user requests.
Cloud computing - Wikipedia - Cloud computing is a paradigm providing network access to scalable and elastic pools of physical or virtual resources with essential characteristics such as on-demand self-service, broad network access, resource pooling, rapid elasticity, and measured service.
What Is Cloud Computing? | IBM - Cloud computing offers on-demand access to computing resources like servers, storage, and applications via the internet with pay-per-use pricing, enabling flexibility and scalability without requiring users to manage physical hardware themselves.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com