Ambient intelligence integrates sensors, artificial intelligence, and user-centric design to enable environments that adapt proactively to human presence and behavior. Smart environments encompass interconnected devices and systems that collect and analyze data to optimize comfort, efficiency, and safety in real time. Explore the evolving technologies and applications that distinguish ambient intelligence from smart environments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Ambient Intelligence (AmI) and Smart Environment is crucial because AmI focuses on creating proactive, adaptive systems that seamlessly integrate into users' daily lives, while Smart Environments emphasize sensor-based automation and data collection within a physical space. This distinction helps developers design more user-centric technologies that enhance comfort, efficiency, and security. Recognizing the unique features of each aids in selecting appropriate solutions for applications in healthcare, smart homes, and urban planning. Clear differentiation also guides investment in research and development tailored to specific user experience goals.
Comparison Table
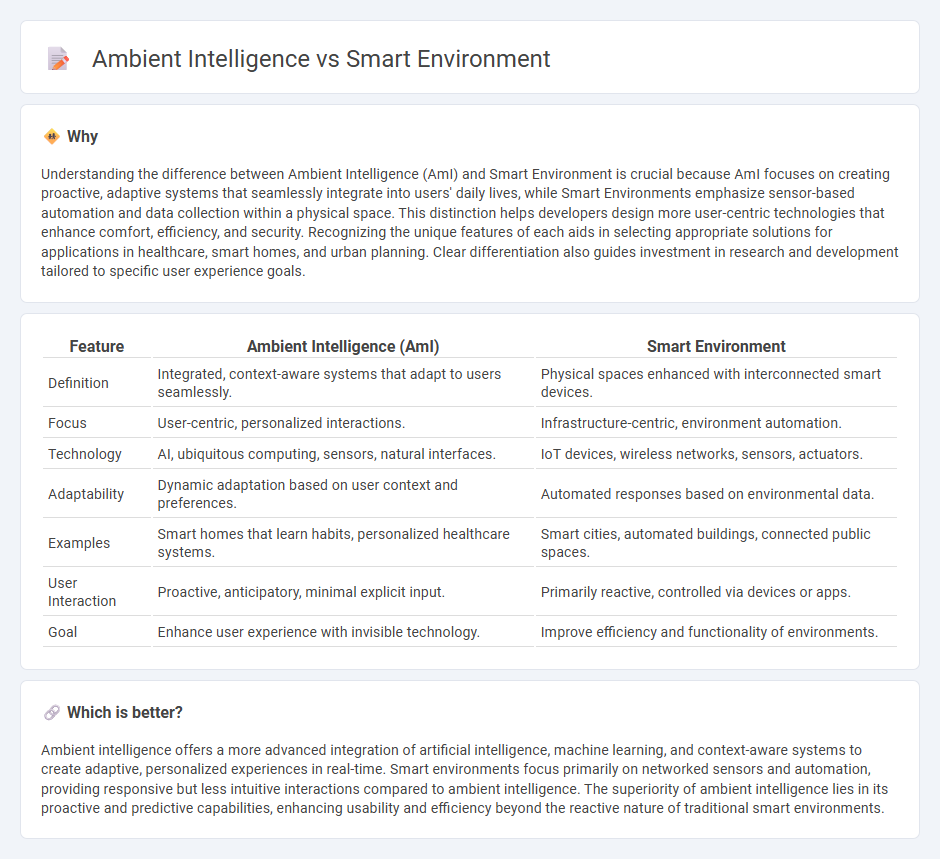
| Feature | Ambient Intelligence (AmI) | Smart Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated, context-aware systems that adapt to users seamlessly. | Physical spaces enhanced with interconnected smart devices. |
| Focus | User-centric, personalized interactions. | Infrastructure-centric, environment automation. |
| Technology | AI, ubiquitous computing, sensors, natural interfaces. | IoT devices, wireless networks, sensors, actuators. |
| Adaptability | Dynamic adaptation based on user context and preferences. | Automated responses based on environmental data. |
| Examples | Smart homes that learn habits, personalized healthcare systems. | Smart cities, automated buildings, connected public spaces. |
| User Interaction | Proactive, anticipatory, minimal explicit input. | Primarily reactive, controlled via devices or apps. |
| Goal | Enhance user experience with invisible technology. | Improve efficiency and functionality of environments. |
Which is better?
Ambient intelligence offers a more advanced integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and context-aware systems to create adaptive, personalized experiences in real-time. Smart environments focus primarily on networked sensors and automation, providing responsive but less intuitive interactions compared to ambient intelligence. The superiority of ambient intelligence lies in its proactive and predictive capabilities, enhancing usability and efficiency beyond the reactive nature of traditional smart environments.
Connection
Ambient intelligence integrates sensors, devices, and software within smart environments to enable context-aware computing that responds adaptively to user needs. Smart environments utilize ambient intelligence technologies to create interconnected spaces that enhance convenience, efficiency, and personalization through real-time data processing. The synergy between ambient intelligence and smart environments drives advancements in home automation, healthcare monitoring, and urban infrastructure management.
Key Terms
Sensors
Smart environments integrate various sensors such as temperature, motion, and light detectors to create responsive and adaptive physical spaces. Ambient intelligence enhances this framework by embedding context-aware sensors that process real-time data to predict and meet user needs proactively. Explore how advanced sensor technologies drive these innovations in environment automation and personalized experiences.
Context-awareness
Smart environments utilize sensors and devices to monitor and respond to physical spaces, emphasizing automated functions based on predefined rules. Ambient intelligence advances this concept by integrating advanced context-awareness, enabling systems to interpret user behavior, preferences, and environmental changes in real-time to provide personalized, adaptive experiences. Explore deeper insights into how context-awareness differentiates ambient intelligence from traditional smart environments.
Ubiquitous computing
Smart environments integrate interconnected devices and sensors to create responsive spaces, enhancing daily living through automated control and context-aware services. Ambient intelligence builds on ubiquitous computing by embedding intelligence into the environment, enabling seamless interaction between humans and technology through adaptive systems that anticipate user needs. Explore further to understand how ubiquitous computing drives innovation in both smart environments and ambient intelligence.
Source and External Links
Smart environment - Wikipedia - Smart environments integrate computers and smart devices into everyday settings, featuring sensors, interconnected systems, and data-driven technologies to improve efficiency and sustainability in smart homes, cities, health, and factories.
Internet of Things (IoT) Applications for Smart Environment - Semtech - IoT technology enables scalable networks of sensors for environmental monitoring, improving conservation, deforestation prevention, pollution monitoring, and wildlife protection through low-power, long-range communication solutions.
Towards Users' Optimal and Pleasurable Experience in Smart ... - Smart environments emphasize user interactivity and experience with conceptual models such as smart homes and immersive technologies, enhancing usability and well-being, especially for the elderly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com