Spatial computing integrates digital information within real-world environments by mapping physical spaces using sensors and 3D models, enabling seamless interaction between humans and machines. Augmented reality overlays virtual objects onto the real world through devices like smartphones and AR glasses, enhancing user perception without altering spatial structure. Explore deeper insights into how these technologies transform user experiences and digital interaction.
Why it is important
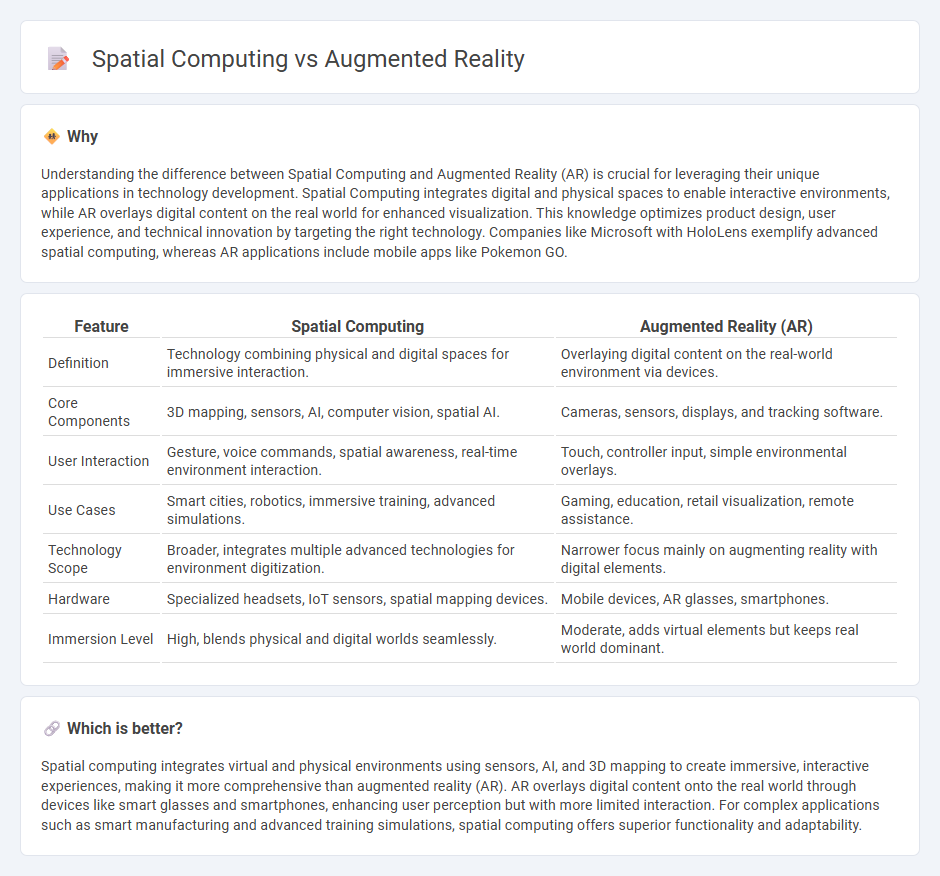
Understanding the difference between Spatial Computing and Augmented Reality (AR) is crucial for leveraging their unique applications in technology development. Spatial Computing integrates digital and physical spaces to enable interactive environments, while AR overlays digital content on the real world for enhanced visualization. This knowledge optimizes product design, user experience, and technical innovation by targeting the right technology. Companies like Microsoft with HoloLens exemplify advanced spatial computing, whereas AR applications include mobile apps like Pokemon GO.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Spatial Computing | Augmented Reality (AR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology combining physical and digital spaces for immersive interaction. | Overlaying digital content on the real-world environment via devices. |
| Core Components | 3D mapping, sensors, AI, computer vision, spatial AI. | Cameras, sensors, displays, and tracking software. |
| User Interaction | Gesture, voice commands, spatial awareness, real-time environment interaction. | Touch, controller input, simple environmental overlays. |
| Use Cases | Smart cities, robotics, immersive training, advanced simulations. | Gaming, education, retail visualization, remote assistance. |
| Technology Scope | Broader, integrates multiple advanced technologies for environment digitization. | Narrower focus mainly on augmenting reality with digital elements. |
| Hardware | Specialized headsets, IoT sensors, spatial mapping devices. | Mobile devices, AR glasses, smartphones. |
| Immersion Level | High, blends physical and digital worlds seamlessly. | Moderate, adds virtual elements but keeps real world dominant. |
Which is better?
Spatial computing integrates virtual and physical environments using sensors, AI, and 3D mapping to create immersive, interactive experiences, making it more comprehensive than augmented reality (AR). AR overlays digital content onto the real world through devices like smart glasses and smartphones, enhancing user perception but with more limited interaction. For complex applications such as smart manufacturing and advanced training simulations, spatial computing offers superior functionality and adaptability.
Connection
Spatial computing integrates digital information into physical environments, enabling augmented reality (AR) applications to overlay interactive virtual elements onto the real world. AR relies on spatial computing technologies such as 3D mapping, sensor fusion, and real-time data processing to accurately position digital content within a user's spatial context. This synergy enhances user experiences in industries like gaming, healthcare, and education by blending digital and physical realities seamlessly.
Key Terms
Immersive interaction
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the physical environment by overlaying digital content, whereas spatial computing integrates real and virtual spaces to enable seamless, immersive interaction through gesture, voice, and environmental understanding. AR primarily relies on devices like smartphones and AR glasses, while spatial computing employs advanced sensors, spatial mapping, and AI to create highly interactive environments. Discover how these technologies transform user experiences in gaming, education, and industry by exploring their immersive interaction capabilities.
Real-world integration
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the physical world, enhancing real-world integration by blending virtual objects with real environments for interactive experiences. Spatial computing extends this concept by enabling machines to understand and interact with the three-dimensional space around them, facilitating more immersive and context-aware applications in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and gaming. Discover how these technologies revolutionize user engagement and operational efficiency.
Environment mapping
Environment mapping in augmented reality (AR) relies on capturing and overlaying digital content onto real-world surroundings using cameras and sensors for accurate alignment. Spatial computing enhances this process by creating a detailed 3D model of the environment, enabling interactive and context-aware experiences through advanced depth sensing and real-time environmental analysis. Explore the evolving technologies behind environment mapping to understand their impact on immersive digital interaction.
Source and External Links
What is Augmented Reality? | IBM - AR is the real-time integration of digital information into a user's physical environment using devices like smartphones, tablets, or smart glasses, which overlay digital content onto the real world to enrich perception without replacing it.
Augmented reality - Wikipedia - AR overlays interactive, digital 3D content onto the real world through devices such as headsets or smartphones, seamlessly blending virtual and real elements to enhance the user's ongoing perception of their environment.
Augmented reality | Britannica - AR combines computer-generated data with real-time video or photographic displays, such as in heads-up displays for pilots, sports graphics for viewers, or apps that show information about locations, products, and more when viewed through a device.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com