Algorithmic bias auditing identifies and mitigates unfair or discriminatory outcomes in AI systems to promote ethical technology use. Data privacy impact assessment evaluates risks related to personal data processing, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding user privacy. Explore further to understand how these frameworks enhance responsible technology development.
Why it is important
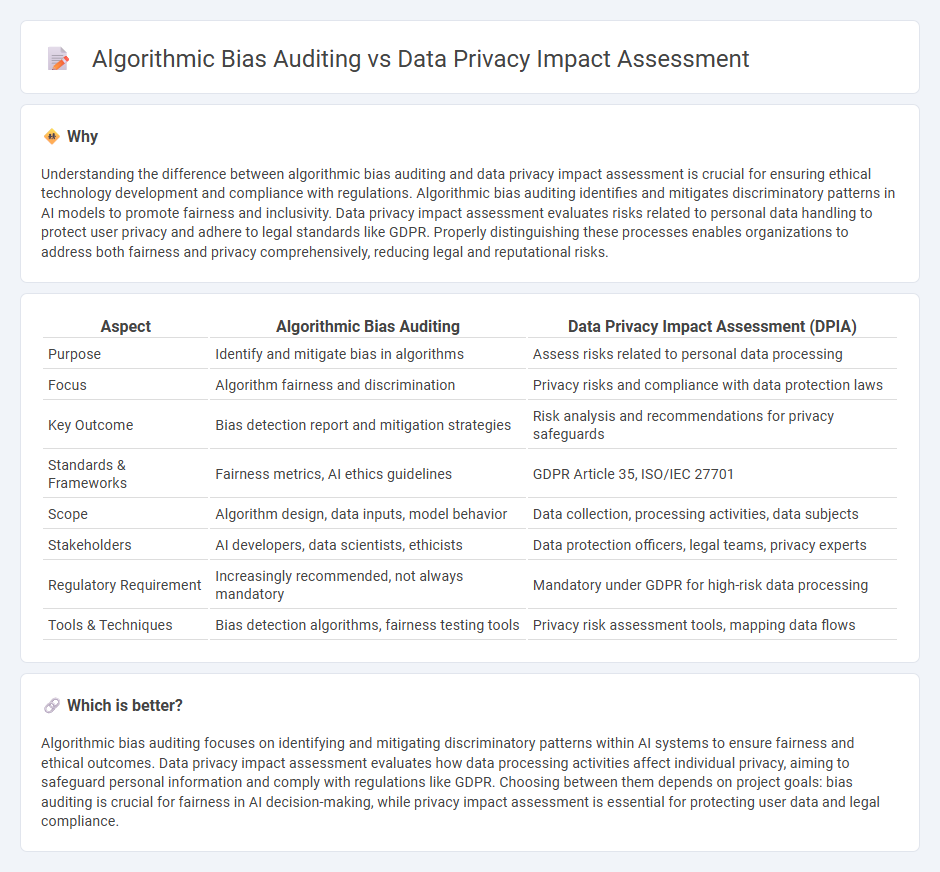
Understanding the difference between algorithmic bias auditing and data privacy impact assessment is crucial for ensuring ethical technology development and compliance with regulations. Algorithmic bias auditing identifies and mitigates discriminatory patterns in AI models to promote fairness and inclusivity. Data privacy impact assessment evaluates risks related to personal data handling to protect user privacy and adhere to legal standards like GDPR. Properly distinguishing these processes enables organizations to address both fairness and privacy comprehensively, reducing legal and reputational risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Bias Auditing | Data Privacy Impact Assessment (DPIA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify and mitigate bias in algorithms | Assess risks related to personal data processing |
| Focus | Algorithm fairness and discrimination | Privacy risks and compliance with data protection laws |
| Key Outcome | Bias detection report and mitigation strategies | Risk analysis and recommendations for privacy safeguards |
| Standards & Frameworks | Fairness metrics, AI ethics guidelines | GDPR Article 35, ISO/IEC 27701 |
| Scope | Algorithm design, data inputs, model behavior | Data collection, processing activities, data subjects |
| Stakeholders | AI developers, data scientists, ethicists | Data protection officers, legal teams, privacy experts |
| Regulatory Requirement | Increasingly recommended, not always mandatory | Mandatory under GDPR for high-risk data processing |
| Tools & Techniques | Bias detection algorithms, fairness testing tools | Privacy risk assessment tools, mapping data flows |
Which is better?
Algorithmic bias auditing focuses on identifying and mitigating discriminatory patterns within AI systems to ensure fairness and ethical outcomes. Data privacy impact assessment evaluates how data processing activities affect individual privacy, aiming to safeguard personal information and comply with regulations like GDPR. Choosing between them depends on project goals: bias auditing is crucial for fairness in AI decision-making, while privacy impact assessment is essential for protecting user data and legal compliance.
Connection
Algorithmic bias auditing identifies and mitigates discriminatory patterns within AI systems, ensuring fair and ethical decision-making. Data privacy impact assessment evaluates how personal data is collected, stored, and used, minimizing risks of unauthorized access and misuse. Together, these processes enhance transparency, accountability, and trust in technology applications by safeguarding both fairness and privacy.
Key Terms
**Data Privacy Impact Assessment:**
Data Privacy Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a systematic process designed to identify and mitigate risks related to the processing of personal data, ensuring compliance with regulations such as GDPR. DPIAs evaluate data flow, potential privacy vulnerabilities, and the measures implemented to safeguard user information. Explore comprehensive strategies and tools to enhance your organization's data protection through an effective DPIA.
Data Minimization
Data privacy impact assessments evaluate how data collection and processing adhere to principles like data minimization, ensuring only necessary information is gathered to protect user privacy. Algorithmic bias auditing scrutinizes machine learning models to identify and mitigate bias without excessive data use, promoting fairness with minimal data exposure. Explore the key differences and synergies between these approaches to enhance ethical data handling.
Consent Management
Data privacy impact assessment (DPIA) evaluates risks to personal data during processing activities, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR, particularly in managing user consent. Algorithmic bias auditing scrutinizes machine learning models for discriminatory patterns that may affect user rights and potentially violate consent agreements. Explore how integrating DPIA and bias audits enhances robust consent management systems and protects user autonomy.
Source and External Links
Data protection impact assessments | ICO - A DPIA is a tool to help organizations comply with data protection laws and identify high-risk processing activities that could impact individuals' rights and freedoms, requiring assessment before such processing begins.
Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) - GDPR.eu - Under GDPR, a DPIA is mandatory for projects likely to result in high risk to personal data, and must systematically describe processing operations, assess risks, and outline measures to mitigate those risks.
US Privacy Law: When to Conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment and What to Include - A PIA under US state laws involves identifying privacy risks, documenting data flows and mitigation strategies, and setting up ongoing review to monitor safeguards as projects evolve.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com