Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data sovereignty and compliance by ensuring data remains within specific national boundaries, appealing to organizations with strict regulatory requirements. Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud infrastructures, providing flexibility and scalability while balancing security and cost-effectiveness. Explore the key differences between sovereign cloud and hybrid cloud to determine which suits your business needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sovereign cloud and hybrid cloud is crucial for compliance with data sovereignty laws and optimizing data security strategies. Sovereign clouds ensure that data remains within specific national borders, meeting strict regulatory requirements. Hybrid clouds combine on-premises and public cloud resources, offering flexibility and scalability but requiring careful management of data residency. Businesses benefit from this knowledge to balance legal obligations with operational efficiency in cloud adoption.
Comparison Table
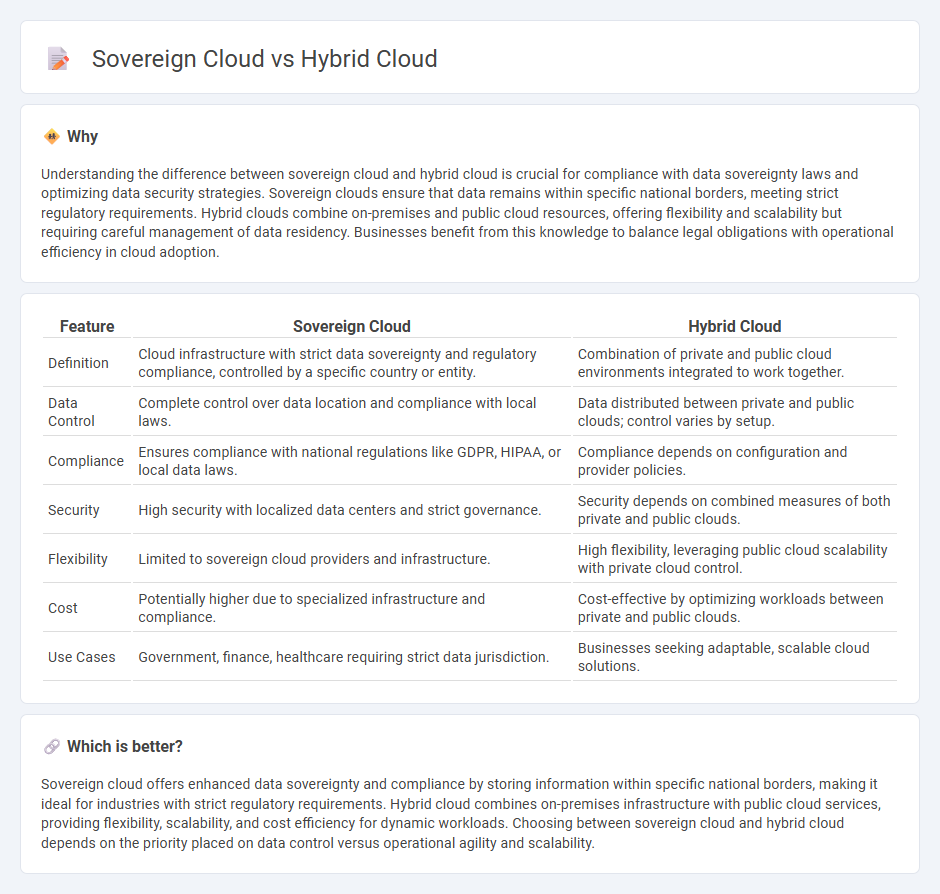
| Feature | Sovereign Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud infrastructure with strict data sovereignty and regulatory compliance, controlled by a specific country or entity. | Combination of private and public cloud environments integrated to work together. |
| Data Control | Complete control over data location and compliance with local laws. | Data distributed between private and public clouds; control varies by setup. |
| Compliance | Ensures compliance with national regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or local data laws. | Compliance depends on configuration and provider policies. |
| Security | High security with localized data centers and strict governance. | Security depends on combined measures of both private and public clouds. |
| Flexibility | Limited to sovereign cloud providers and infrastructure. | High flexibility, leveraging public cloud scalability with private cloud control. |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to specialized infrastructure and compliance. | Cost-effective by optimizing workloads between private and public clouds. |
| Use Cases | Government, finance, healthcare requiring strict data jurisdiction. | Businesses seeking adaptable, scalable cloud solutions. |
Which is better?
Sovereign cloud offers enhanced data sovereignty and compliance by storing information within specific national borders, making it ideal for industries with strict regulatory requirements. Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, providing flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency for dynamic workloads. Choosing between sovereign cloud and hybrid cloud depends on the priority placed on data control versus operational agility and scalability.
Connection
Sovereign cloud and hybrid cloud are connected through their shared emphasis on data sovereignty and regulatory compliance while enabling flexible cloud deployment models. Hybrid cloud architectures integrate private sovereign cloud environments with public cloud services to balance security, control, and scalability. This connection allows organizations to maintain ownership of sensitive data within sovereign clouds while leveraging the resource efficiency of hybrid cloud strategies.
Key Terms
Data Residency
Hybrid cloud solutions combine private and public cloud environments, offering flexibility in data storage and processing locations to support compliance with regional data residency laws. Sovereign cloud services prioritize data residency by ensuring that data remains within specific national or regional boundaries, aligning with strict legal and regulatory requirements. Explore deeper insights into data residency strategies by comparing hybrid and sovereign cloud models for your enterprise needs.
Interoperability
Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud infrastructures to enhance workload portability and flexibility, leveraging interoperability standards such as APIs and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes. Sovereign cloud emphasizes data sovereignty and compliance within a specific jurisdiction, often limiting interoperability due to strict regulatory controls and localized infrastructure. Explore the key differences in interoperability features, security protocols, and compliance requirements between hybrid and sovereign clouds to optimize your cloud strategy.
Compliance
Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud environments, offering flexibility while maintaining control over sensitive data to meet compliance requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA. Sovereign cloud emphasizes strict data residency and regulatory compliance by keeping data within specific geopolitical boundaries, ensuring adherence to local laws and reducing risks related to data sovereignty. Explore the nuances of hybrid and sovereign cloud solutions to determine the most compliant approach for your organization's data governance.
Source and External Links
What is a Hybrid Cloud? - A hybrid cloud is a mixed computing environment combining resources and services from both public and private clouds or on-premises environments, integrating them via networking and orchestration technologies for flexibility and regulatory compliance.
What Is Hybrid Cloud? Use Cases, Pros and Cons - Hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud infrastructures to enable shared management and data exchange, offering flexibility and supporting phased migration from on-premises to cloud environments.
What is Hybrid Cloud? - Hybrid cloud unifies public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises infrastructure into a flexible IT setup that enables agility, cost optimization, and access to advanced technologies like AI and edge computing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com