Vertical forests integrate dense vegetation directly into building facades, enhancing urban biodiversity and improving air quality with natural air filtration. Sustainable skyscrapers employ advanced technologies like energy-efficient systems, renewable energy sources, and green roofs to minimize environmental impact and optimize resource use. Discover more about how these innovative structures are transforming urban landscapes and promoting ecological balance.
Why it is important
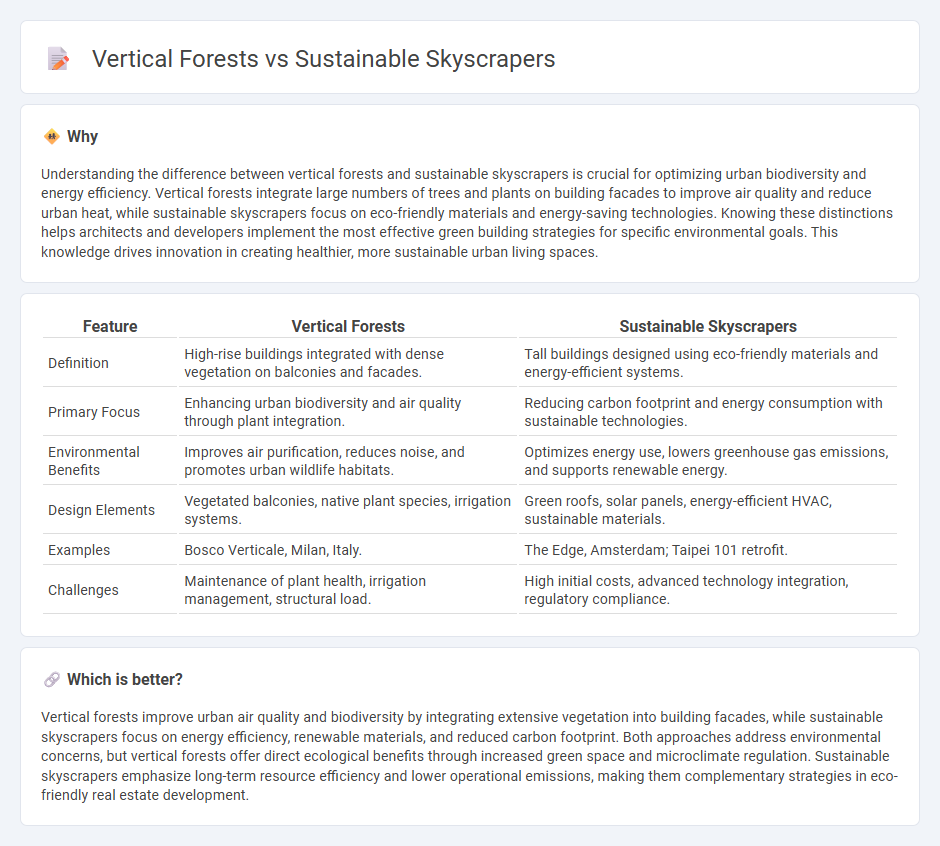
Understanding the difference between vertical forests and sustainable skyscrapers is crucial for optimizing urban biodiversity and energy efficiency. Vertical forests integrate large numbers of trees and plants on building facades to improve air quality and reduce urban heat, while sustainable skyscrapers focus on eco-friendly materials and energy-saving technologies. Knowing these distinctions helps architects and developers implement the most effective green building strategies for specific environmental goals. This knowledge drives innovation in creating healthier, more sustainable urban living spaces.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vertical Forests | Sustainable Skyscrapers |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High-rise buildings integrated with dense vegetation on balconies and facades. | Tall buildings designed using eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient systems. |
| Primary Focus | Enhancing urban biodiversity and air quality through plant integration. | Reducing carbon footprint and energy consumption with sustainable technologies. |
| Environmental Benefits | Improves air purification, reduces noise, and promotes urban wildlife habitats. | Optimizes energy use, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and supports renewable energy. |
| Design Elements | Vegetated balconies, native plant species, irrigation systems. | Green roofs, solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC, sustainable materials. |
| Examples | Bosco Verticale, Milan, Italy. | The Edge, Amsterdam; Taipei 101 retrofit. |
| Challenges | Maintenance of plant health, irrigation management, structural load. | High initial costs, advanced technology integration, regulatory compliance. |
Which is better?
Vertical forests improve urban air quality and biodiversity by integrating extensive vegetation into building facades, while sustainable skyscrapers focus on energy efficiency, renewable materials, and reduced carbon footprint. Both approaches address environmental concerns, but vertical forests offer direct ecological benefits through increased green space and microclimate regulation. Sustainable skyscrapers emphasize long-term resource efficiency and lower operational emissions, making them complementary strategies in eco-friendly real estate development.
Connection
Vertical forests and sustainable skyscrapers share a commitment to integrating nature into urban architecture, enhancing air quality, and reducing the urban heat island effect. These structures utilize advanced green technologies such as photovoltaic panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient building materials to minimize environmental impact. Incorporating abundant vegetation not only supports biodiversity but also improves building insulation, leading to significant energy savings and healthier living environments.
Key Terms
Green Building Certification
Sustainable skyscrapers often achieve Green Building Certification through energy-efficient systems, renewable materials, and reduced carbon footprints, while vertical forests integrate dense vegetation to enhance air quality and biodiversity within urban environments. Both approaches aim to meet standards such as LEED, BREEAM, or WELL certifications, emphasizing environmental performance and occupant well-being. Explore how these innovative designs redefine green architecture and contribute to healthier cities.
Energy Efficiency
Sustainable skyscrapers use advanced insulation, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources to minimize energy consumption, while vertical forests integrate dense vegetation that provides natural cooling and enhances air quality. Energy efficiency in sustainable skyscrapers relies heavily on smart technology and materials that reduce heat gain and optimize daylight, whereas vertical forests leverage plant transpiration and shading to decrease reliance on mechanical cooling. Explore detailed comparisons and innovations in energy-efficient building designs to understand their environmental impact better.
Urban Biodiversity
Sustainable skyscrapers integrate energy-efficient systems and green technologies to minimize environmental impact while supporting urban biodiversity through green roofs and living walls. Vertical forests elevate this approach by densely planting trees and shrubs on building facades, significantly enhancing air quality and providing habitats for birds and insects in urban environments. Explore how these innovative architectural designs contribute uniquely to the future of urban biodiversity.
Source and External Links
Reimagining Urban Architecture: The Flourishing Future of Green Skyscrapers - Discusses the integration of nature into urban architecture, focusing on sustainable practices and energy efficiency in green skyscrapers.
What Are Green Skyscrapers? - Explores green skyscrapers globally, highlighting examples like the International Commerce Centre in Hong Kong and the Shanghai Tower, which demonstrate sustainable design and operation.
Sustainable Skyscraper Mobile - Presents innovative designs for sustainable skyscrapers, including power-generating skins and wastewater treatment systems, aimed at reducing environmental impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com