Last mile logistics hubs are crucial for efficient urban delivery, reducing transit times and enhancing supply chain responsiveness in densely populated areas. Retail storefronts, by contrast, focus on direct consumer engagement and immediate product availability, driving foot traffic and brand visibility. Explore the strategic advantages of each to optimize your real estate investments and operational logistics.
Why it is important
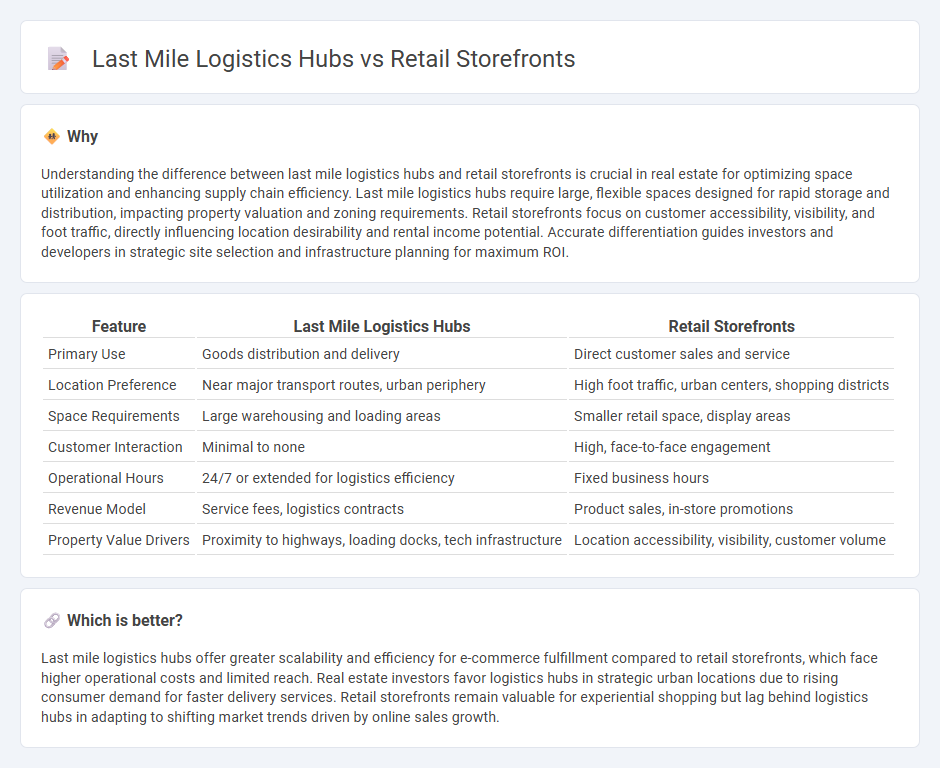
Understanding the difference between last mile logistics hubs and retail storefronts is crucial in real estate for optimizing space utilization and enhancing supply chain efficiency. Last mile logistics hubs require large, flexible spaces designed for rapid storage and distribution, impacting property valuation and zoning requirements. Retail storefronts focus on customer accessibility, visibility, and foot traffic, directly influencing location desirability and rental income potential. Accurate differentiation guides investors and developers in strategic site selection and infrastructure planning for maximum ROI.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Last Mile Logistics Hubs | Retail Storefronts |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Goods distribution and delivery | Direct customer sales and service |
| Location Preference | Near major transport routes, urban periphery | High foot traffic, urban centers, shopping districts |
| Space Requirements | Large warehousing and loading areas | Smaller retail space, display areas |
| Customer Interaction | Minimal to none | High, face-to-face engagement |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 or extended for logistics efficiency | Fixed business hours |
| Revenue Model | Service fees, logistics contracts | Product sales, in-store promotions |
| Property Value Drivers | Proximity to highways, loading docks, tech infrastructure | Location accessibility, visibility, customer volume |
Which is better?
Last mile logistics hubs offer greater scalability and efficiency for e-commerce fulfillment compared to retail storefronts, which face higher operational costs and limited reach. Real estate investors favor logistics hubs in strategic urban locations due to rising consumer demand for faster delivery services. Retail storefronts remain valuable for experiential shopping but lag behind logistics hubs in adapting to shifting market trends driven by online sales growth.
Connection
Last mile logistics hubs and retail storefronts create a seamless supply chain by facilitating rapid, localized distribution of goods to consumers. These hubs reduce delivery times and transportation costs, improving inventory management and enhancing customer satisfaction. Retail storefronts leverage proximity to logistics hubs to maintain stock levels, enabling efficient omnichannel fulfillment strategies.
Key Terms
Foot Traffic
Retail storefronts generate high foot traffic, serving as primary locations where customers physically engage with products and brands. Last mile logistics hubs prioritize efficiency in delivery operations, typically operating in low foot traffic areas to streamline order fulfillment. Explore how optimizing foot traffic impacts both retail success and delivery speed in urban environments.
Location Proximity
Retail storefronts thrive in high-traffic urban areas with maximum consumer visibility to drive foot traffic and impulse purchases. Last mile logistics hubs prioritize proximity to residential zones and major transportation routes for efficient delivery and reduced transit times. Explore further to understand how location strategy impacts retail and logistics performance.
Zoning Regulations
Retail storefronts and last mile logistics hubs face distinct zoning regulations that shape their placement and operations. Retail storefronts are typically located in commercial zones emphasizing customer accessibility and visibility, while last mile logistics hubs often require industrial or mixed-use zoning to accommodate larger vehicles and storage needs. Explore how these zoning distinctions impact urban planning and business strategies.
Source and External Links
Storefront - Wikipedia - A storefront is the facade or entryway of a retail store located on the ground floor or street level of a commercial building, often including display windows to attract customers.
Retail Storefront Design Tips (+ Examples) - Shopify - Provides a guide to designing retail storefronts with tips on lighting, signage, and accessibility to attract customers and enhance the retail experience.
Flexible Retail Spaces For Rent in Glendale - Storefront - Offers a range of temporary and flexible retail spaces in Glendale, including pop-up stores and event venues, suitable for various commercial uses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com