Adaptive reuse transforms obsolete buildings into functional spaces, preserving architectural heritage while meeting modern needs. Brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and repurposing contaminated land, turning environmental liabilities into valuable real estate assets. Explore the distinct benefits and challenges of these strategies to optimize property development opportunities.
Why it is important
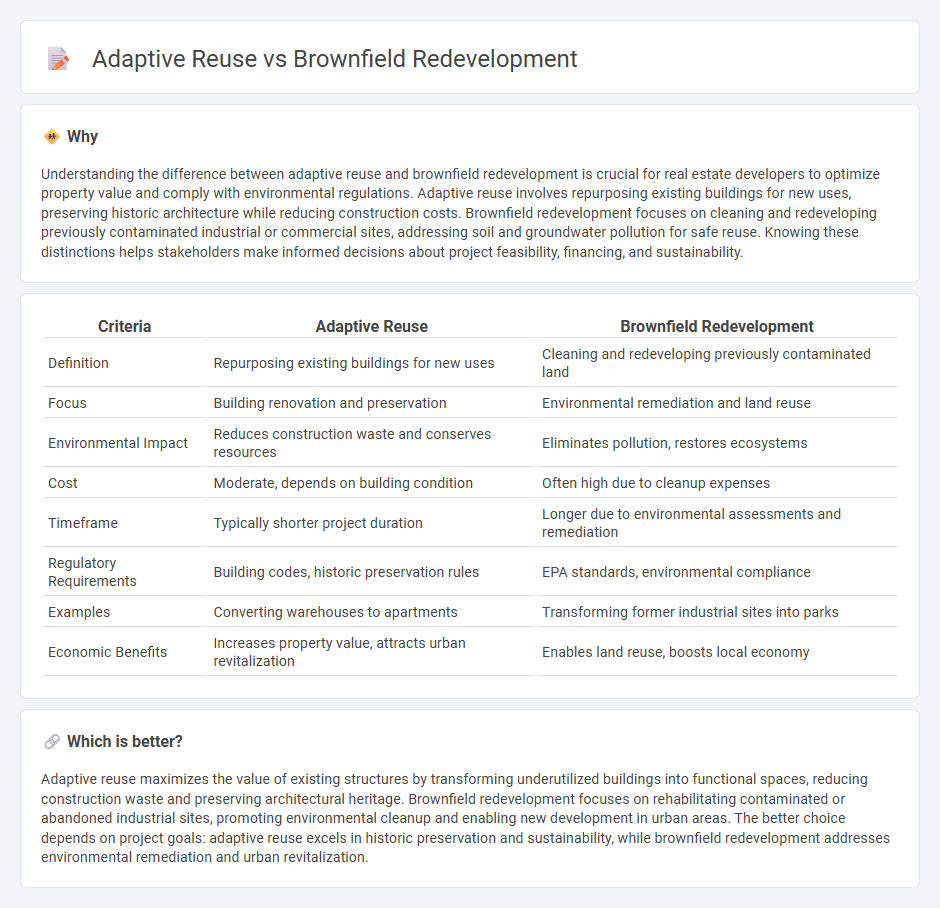
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse and brownfield redevelopment is crucial for real estate developers to optimize property value and comply with environmental regulations. Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, preserving historic architecture while reducing construction costs. Brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and redeveloping previously contaminated industrial or commercial sites, addressing soil and groundwater pollution for safe reuse. Knowing these distinctions helps stakeholders make informed decisions about project feasibility, financing, and sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Adaptive Reuse | Brownfield Redevelopment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Cleaning and redeveloping previously contaminated land |
| Focus | Building renovation and preservation | Environmental remediation and land reuse |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces construction waste and conserves resources | Eliminates pollution, restores ecosystems |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on building condition | Often high due to cleanup expenses |
| Timeframe | Typically shorter project duration | Longer due to environmental assessments and remediation |
| Regulatory Requirements | Building codes, historic preservation rules | EPA standards, environmental compliance |
| Examples | Converting warehouses to apartments | Transforming former industrial sites into parks |
| Economic Benefits | Increases property value, attracts urban revitalization | Enables land reuse, boosts local economy |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse maximizes the value of existing structures by transforming underutilized buildings into functional spaces, reducing construction waste and preserving architectural heritage. Brownfield redevelopment focuses on rehabilitating contaminated or abandoned industrial sites, promoting environmental cleanup and enabling new development in urban areas. The better choice depends on project goals: adaptive reuse excels in historic preservation and sustainability, while brownfield redevelopment addresses environmental remediation and urban revitalization.
Connection
Adaptive reuse transforms existing buildings into new purposes, often targeting brownfield sites--previously contaminated or underutilized land. Brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and revitalizing such lands, making them suitable for adaptive reuse projects. This synergy helps preserve urban heritage, reduces environmental impact, and stimulates sustainable real estate development.
Key Terms
Environmental Remediation
Brownfield redevelopment targets contaminated properties requiring extensive environmental remediation to remove pollutants and restore soil, water, and air quality for safe reuse. Adaptive reuse emphasizes repurposing existing structures with minimal demolition, often addressing limited remediation, focusing on retaining architectural integrity and reducing construction waste. Discover more about how these strategies impact sustainability and urban renewal efforts.
Historic Preservation
Brownfield redevelopment involves rehabilitating contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, often requiring environmental cleanup, while adaptive reuse transforms historic buildings by repurposing their original structure for new functions. Both approaches promote historic preservation by safeguarding architectural heritage and promoting sustainable urban development through the conservation of cultural landmarks. Explore more to understand how combining these strategies enhances community revitalization and heritage conservation.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a critical role in both brownfield redevelopment and adaptive reuse projects by dictating land use, building heights, density, and environmental requirements. Brownfield redevelopment often faces stringent cleanup standards and land-use restrictions due to contamination, while adaptive reuse primarily requires compliance with historic preservation rules and zoning adjustments for new functions. Explore detailed zoning policies and case studies to fully understand their impact on successful urban regeneration projects.
Source and External Links
Anatomy of Brownfields Redevelopment - This document outlines the process of transforming contaminated properties into productive spaces through redevelopment, enhancing community benefits and economic growth.
What is Brownfield Redevelopment? - This guide explains how brownfield redevelopment revitalizes abandoned properties, boosts local economies, and promotes sustainable urban growth.
Brownfields | US EPA - The EPA's Brownfields Program provides grants and assistance for assessing, cleaning up, and sustainably reusing contaminated properties to revitalize communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com