Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to divide property ownership into digital tokens, offering enhanced liquidity and fractional investment opportunities compared to traditional real estate syndication, which pools funds from investors but often involves limited transferability and longer timelines. This innovation reduces entry barriers and increases transparency through smart contracts, whereas traditional syndications rely on legal structures and manual processes. Discover more about the advantages and practical applications of tokenized real estate to transform your investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between tokenized real estate and traditional real estate syndication is crucial for investors seeking liquidity, transparency, and lower entry barriers. Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership, faster transactions, and enhanced security. Traditional syndication often involves longer timelines, higher minimum investments, and less transparent ownership structures. Choosing the right method impacts investment flexibility, regulatory compliance, and potential returns.
Comparison Table
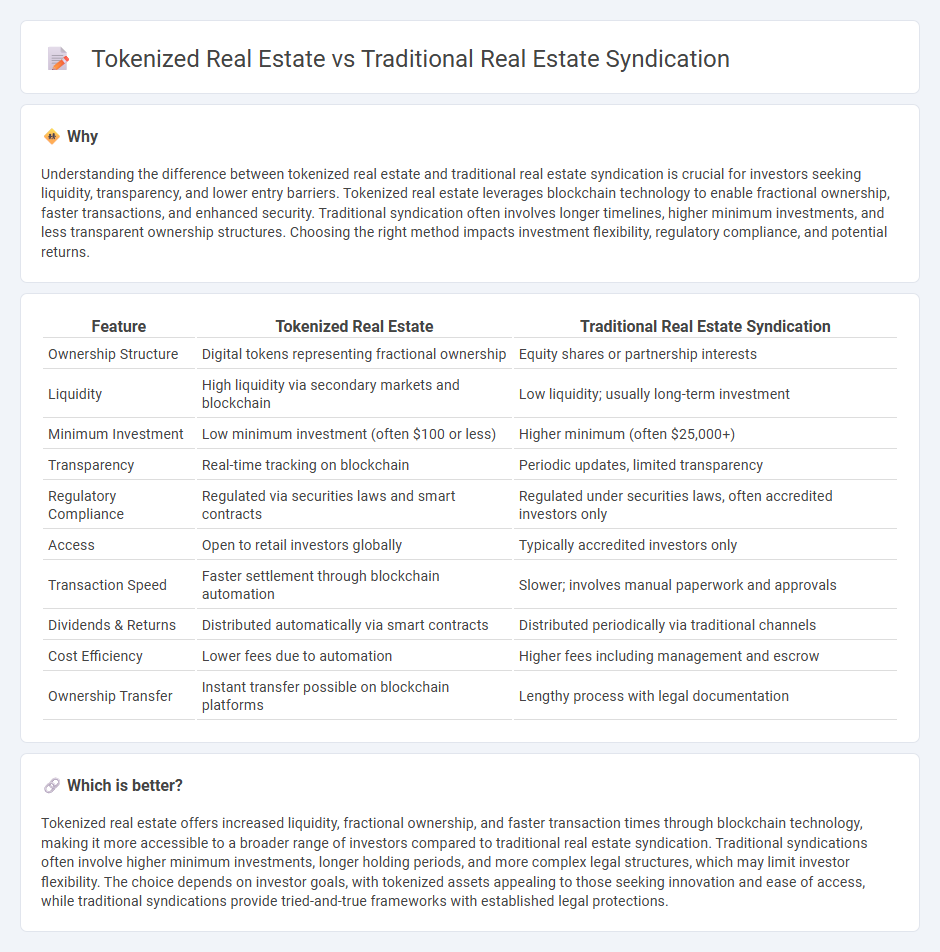
| Feature | Tokenized Real Estate | Traditional Real Estate Syndication |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Structure | Digital tokens representing fractional ownership | Equity shares or partnership interests |
| Liquidity | High liquidity via secondary markets and blockchain | Low liquidity; usually long-term investment |
| Minimum Investment | Low minimum investment (often $100 or less) | Higher minimum (often $25,000+) |
| Transparency | Real-time tracking on blockchain | Periodic updates, limited transparency |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regulated via securities laws and smart contracts | Regulated under securities laws, often accredited investors only |
| Access | Open to retail investors globally | Typically accredited investors only |
| Transaction Speed | Faster settlement through blockchain automation | Slower; involves manual paperwork and approvals |
| Dividends & Returns | Distributed automatically via smart contracts | Distributed periodically via traditional channels |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fees due to automation | Higher fees including management and escrow |
| Ownership Transfer | Instant transfer possible on blockchain platforms | Lengthy process with legal documentation |
Which is better?
Tokenized real estate offers increased liquidity, fractional ownership, and faster transaction times through blockchain technology, making it more accessible to a broader range of investors compared to traditional real estate syndication. Traditional syndications often involve higher minimum investments, longer holding periods, and more complex legal structures, which may limit investor flexibility. The choice depends on investor goals, with tokenized assets appealing to those seeking innovation and ease of access, while traditional syndications provide tried-and-true frameworks with established legal protections.
Connection
Tokenized real estate and traditional real estate syndication both enable fractional ownership of real estate assets, allowing multiple investors to pool capital for property acquisition. Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to digitize ownership shares, enhancing liquidity, transparency, and ease of transfer compared to traditional syndications, which rely on legal agreements and centralized management. This connection bridges conventional investment models with innovative digital frameworks, expanding access and efficiency in real estate investment markets.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Traditional real estate syndication typically involves a limited partnership structure where investors hold ownership through shares managed by a general partner, often resulting in limited liquidity and higher entry barriers. Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to digitize ownership into fractional tokens, enabling seamless transferability, increased transparency, and broader access for smaller investors. Explore how tokenization is revolutionizing real estate ownership and investment opportunities.
Liquidity
Traditional real estate syndication often involves illiquid investments with lengthy holding periods, restricting investors' ability to quickly access capital. Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to enable fractional ownership and secondary market trading, significantly enhancing liquidity and investor flexibility. Explore how tokenization is reshaping real estate liquidity and investment strategies.
Regulatory Compliance
Traditional real estate syndication involves pooling investor funds under strict securities regulations such as SEC Rule 506(b) exemptions, requiring detailed disclosures and accredited investor status to ensure regulatory compliance. Tokenized real estate leverages blockchain technology to create digital securities, often navigating evolving regulatory frameworks like the SEC's guidance on digital asset offerings and adopting KYC/AML protocols for enhanced transparency. Explore how these evolving compliance landscapes impact investor protection and market accessibility.
Source and External Links
Real Estate Syndicates and Investment Trusts - Traditional real estate syndication involves pooling money from individual investors combined with management by a sponsor in a three-phase cycle: origination, operation, and eventual disposition of the property, enabling investment in larger properties otherwise difficult to finance individually.
Real Estate Syndication: The 2025 Accredited Investor's Guide - The historical development of real estate syndications began with informal cooperative land ownership models in the 18th and 19th centuries U.S., evolving into more standardized legal and structural frameworks in the 20th century to protect investors and sponsors.
An Introduction to Real Estate Syndication - Traditional syndications typically use one-class or two-class equity structures to organize investor and sponsor ownership interests, balancing capital input and profit distribution in the syndicate setup.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com