Remanufacturing focuses on restoring used products to like-new condition by disassembling, cleaning, repairing, and replacing components, thereby reducing waste and conserving resources. Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste throughout the production process by optimizing workflows, improving efficiency, and continuously enhancing quality to minimize costs and lead times. Explore the key differences and benefits between remanufacturing and lean manufacturing to enhance your production strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between remanufacturing and lean manufacturing is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and sustainability strategies. Remanufacturing involves restoring used products to like-new condition, reducing material waste and environmental impact, while lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste and improving process flow within production. Distinguishing these concepts allows manufacturers to implement targeted cost-saving measures and enhance product lifecycle management. Knowing these differences supports strategic decision-making that aligns with organizational goals for quality and environmental responsibility.
Comparison Table
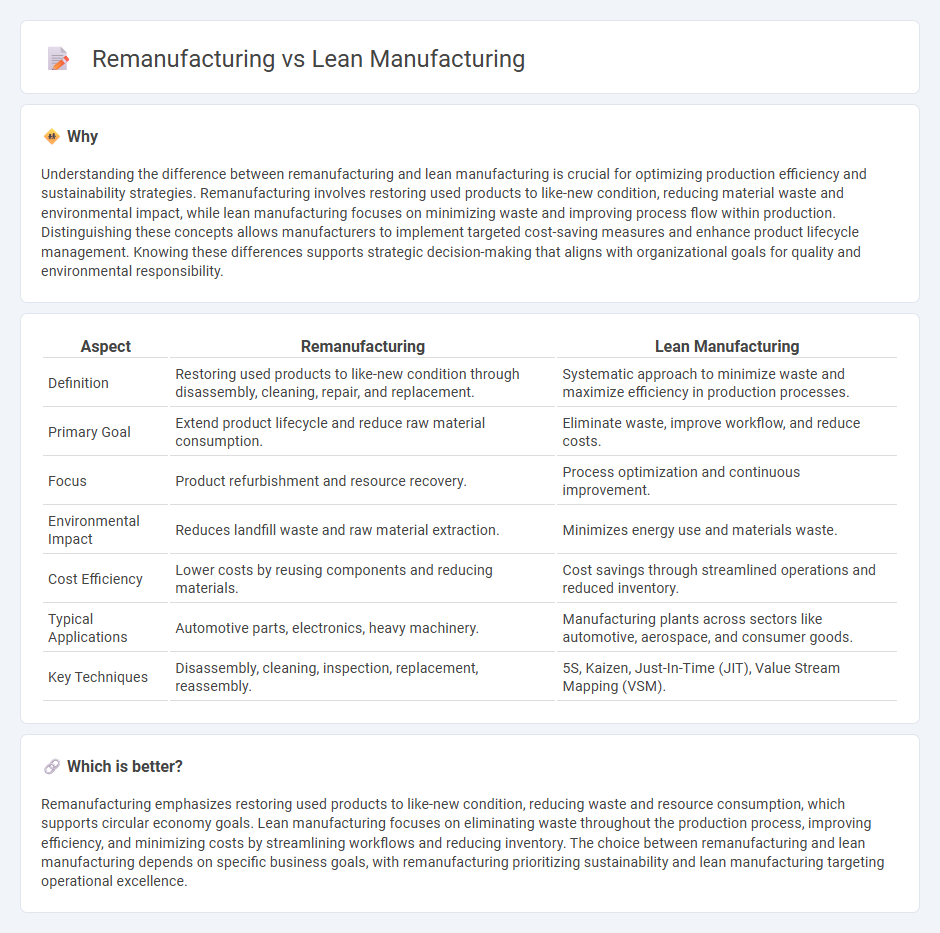
| Aspect | Remanufacturing | Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Restoring used products to like-new condition through disassembly, cleaning, repair, and replacement. | Systematic approach to minimize waste and maximize efficiency in production processes. |
| Primary Goal | Extend product lifecycle and reduce raw material consumption. | Eliminate waste, improve workflow, and reduce costs. |
| Focus | Product refurbishment and resource recovery. | Process optimization and continuous improvement. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and raw material extraction. | Minimizes energy use and materials waste. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs by reusing components and reducing materials. | Cost savings through streamlined operations and reduced inventory. |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, heavy machinery. | Manufacturing plants across sectors like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. |
| Key Techniques | Disassembly, cleaning, inspection, replacement, reassembly. | 5S, Kaizen, Just-In-Time (JIT), Value Stream Mapping (VSM). |
Which is better?
Remanufacturing emphasizes restoring used products to like-new condition, reducing waste and resource consumption, which supports circular economy goals. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste throughout the production process, improving efficiency, and minimizing costs by streamlining workflows and reducing inventory. The choice between remanufacturing and lean manufacturing depends on specific business goals, with remanufacturing prioritizing sustainability and lean manufacturing targeting operational excellence.
Connection
Remanufacturing and lean manufacturing are connected through their shared focus on resource efficiency and waste reduction, which enhances overall production sustainability. Lean manufacturing principles streamline processes by minimizing non-value-added activities, while remanufacturing revives used products to near-new quality, reducing material consumption and energy use. Together, these approaches optimize manufacturing workflows, lower costs, and support circular economy initiatives.
Key Terms
Waste Reduction (Lean Manufacturing)
Lean manufacturing significantly reduces waste by emphasizing value-added processes, continuous improvement, and the elimination of non-value-added activities such as excess inventory, overproduction, and defects. This methodology uses tools like Just-In-Time (JIT), 5S, and Kaizen to optimize efficiency and minimize resource consumption. Explore how implementing lean manufacturing principles can transform your production system with measurable waste reduction benefits.
Product Lifecycle Extension (Remanufacturing)
Lean manufacturing minimizes waste and enhances efficiency throughout product production, focusing on reducing cycle times and resource use. Remanufacturing extends product lifecycle by restoring used components to like-new condition, thereby reducing environmental impact and resource consumption. Discover how remanufacturing drives sustainability and cost savings through lifecycle extension.
Value Stream Mapping (Lean Manufacturing)
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) in lean manufacturing identifies and eliminates waste through detailed analysis of production processes, enhancing flow and reducing lead times. In contrast, remanufacturing applies VSM to disassemble, refurbish, and reassemble products, focusing on resource recovery and sustainability while maintaining quality standards. Explore how VSM optimizes efficiency in both lean manufacturing and remanufacturing to boost operational performance.
Source and External Links
Lean manufacturing - Wikipedia - Lean manufacturing is a method focused on minimizing waste and reducing production cycle times by eliminating activities that do not add value for the customer, originally developed as part of the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing? | Definition from TechTarget - Lean manufacturing is a methodology aimed at minimizing waste in manufacturing systems while maximizing productivity, based on continuous improvement and rooted in the Toyota Production System.
What is Lean Manufacturing and the 5 Principles Used? - TWI - Lean manufacturing is a production process that maximizes productivity and minimizes waste, guided by five core principles: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com