Wine cask aging involves investing in barrels of wine as they mature, offering potential appreciation based on vintage quality and market demand, while venture capital focuses on funding early-stage startups with high growth potential but increased risk. Both investment strategies require careful market analysis and risk assessment to maximize returns effectively. Discover how these distinct approaches can diversify your portfolio and optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
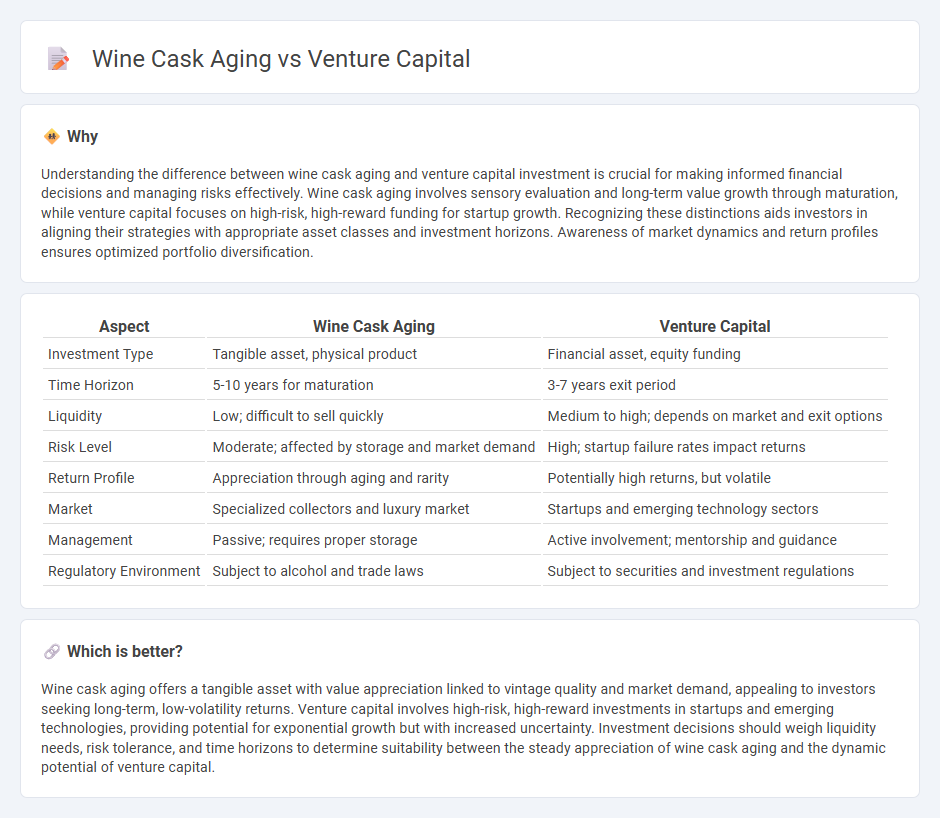
Understanding the difference between wine cask aging and venture capital investment is crucial for making informed financial decisions and managing risks effectively. Wine cask aging involves sensory evaluation and long-term value growth through maturation, while venture capital focuses on high-risk, high-reward funding for startup growth. Recognizing these distinctions aids investors in aligning their strategies with appropriate asset classes and investment horizons. Awareness of market dynamics and return profiles ensures optimized portfolio diversification.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Wine Cask Aging | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Tangible asset, physical product | Financial asset, equity funding |
| Time Horizon | 5-10 years for maturation | 3-7 years exit period |
| Liquidity | Low; difficult to sell quickly | Medium to high; depends on market and exit options |
| Risk Level | Moderate; affected by storage and market demand | High; startup failure rates impact returns |
| Return Profile | Appreciation through aging and rarity | Potentially high returns, but volatile |
| Market | Specialized collectors and luxury market | Startups and emerging technology sectors |
| Management | Passive; requires proper storage | Active involvement; mentorship and guidance |
| Regulatory Environment | Subject to alcohol and trade laws | Subject to securities and investment regulations |
Which is better?
Wine cask aging offers a tangible asset with value appreciation linked to vintage quality and market demand, appealing to investors seeking long-term, low-volatility returns. Venture capital involves high-risk, high-reward investments in startups and emerging technologies, providing potential for exponential growth but with increased uncertainty. Investment decisions should weigh liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and time horizons to determine suitability between the steady appreciation of wine cask aging and the dynamic potential of venture capital.
Connection
Wine cask aging and venture capital both rely on the principle of patience to maximize value, as the aging process enhances wine's quality and the investment horizon allows startups to mature and increase valuation. Both require expertise in timing and risk assessment to optimize growth, whether through environmental control for wine or market analysis for startups. Understanding the interplay of time, quality, and risk underpins successful outcomes in these seemingly distinct but analogous investment approaches.
Key Terms
Equity stake
Venture capital investments typically involve acquiring an equity stake in a growing company in exchange for funding, allowing investors to share in the company's future profits and valuation increases. Wine cask aging, on the other hand, does not confer any ownership interest or equity; it is a process to enhance wine quality and value but retains the producer's full control. Discover more about the implications of equity stakes in these distinct investment opportunities.
Maturation period
Venture capital investment timelines typically span 5 to 10 years, allowing startups to mature while they scale operations, refine products, and achieve market traction. Wine cask aging ranges from several months to decades, with flavor and complexity deepening as chemical reactions occur over time, enhancing quality and value. Explore how the concept of maturation drives growth and refinement in both high-risk investments and artisanal winemaking.
Exit strategy
Venture capital exit strategies typically include acquisitions, initial public offerings (IPOs), or secondary sales, aiming for significant financial returns within a defined timeframe. In contrast, wine cask aging focuses on the natural maturation process over years, with the exit strategy centered on selling the matured product at premium value or auction. Explore the nuances of exit strategies in these distinct industries to understand their unique financial dynamics.
Source and External Links
What is Venture Capital? | National Venture Capital Association - Venture capital is a form of financing provided by institutional investors to high-growth, innovative startups in exchange for equity, offering not just capital but also strategic guidance and industry connections to help young companies scale rapidly and create significant economic impact.
What is Venture Capital? | J.P. Morgan - Venture capital funds early-stage companies developing novel technologies by investing equity (or convertible debt) for ownership stakes, accepting high risk of failure in exchange for the potential of outsized returns if the company succeeds through acquisition or IPO, typically using a diversified portfolio approach to manage risk.
Fund your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Venture capital focuses on high-growth businesses, provides funding in return for equity rather than debt, involves higher risk and longer investment horizons than traditional financing, and usually requires entrepreneurs to cede some control and board participation in exchange for investment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com