Private credit funds offer established companies access to debt financing with predictable returns, focusing on steady income through interest payments. Venture capital targets early-stage startups, providing equity investments with high growth potential but increased risk. Explore the differences between these investment vehicles to determine which aligns with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between private credit funds and venture capital is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance and return expectations with appropriate asset classes. Private credit funds primarily focus on debt investments with fixed income returns, offering more predictable cash flow and lower risk. Venture capital entails equity investments in early-stage companies, carrying higher risk but potential for substantial growth. This distinction enables investors to optimize portfolio diversification and strategic financial planning.
Comparison Table
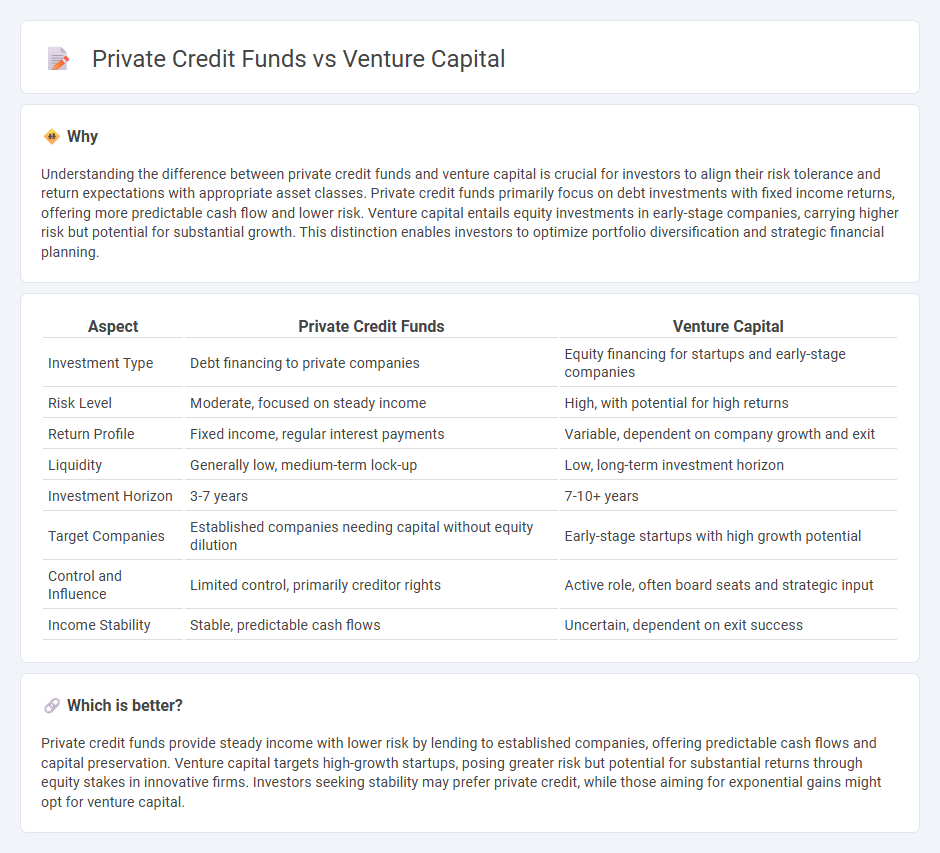
| Aspect | Private Credit Funds | Venture Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Debt financing to private companies | Equity financing for startups and early-stage companies |
| Risk Level | Moderate, focused on steady income | High, with potential for high returns |
| Return Profile | Fixed income, regular interest payments | Variable, dependent on company growth and exit |
| Liquidity | Generally low, medium-term lock-up | Low, long-term investment horizon |
| Investment Horizon | 3-7 years | 7-10+ years |
| Target Companies | Established companies needing capital without equity dilution | Early-stage startups with high growth potential |
| Control and Influence | Limited control, primarily creditor rights | Active role, often board seats and strategic input |
| Income Stability | Stable, predictable cash flows | Uncertain, dependent on exit success |
Which is better?
Private credit funds provide steady income with lower risk by lending to established companies, offering predictable cash flows and capital preservation. Venture capital targets high-growth startups, posing greater risk but potential for substantial returns through equity stakes in innovative firms. Investors seeking stability may prefer private credit, while those aiming for exponential gains might opt for venture capital.
Connection
Private credit funds and venture capital intersect in providing alternative financing for growing companies outside traditional banking channels. Private credit funds offer debt financing with flexible terms, supporting startups and mid-sized enterprises that venture capital backs through equity investments, jointly enabling scalable business growth. This complementary relationship enhances access to capital, driving innovation and expansion across diverse industries.
Key Terms
Equity (Venture Capital)
Venture capital funds primarily invest in early-stage companies by providing equity capital to fuel innovation and high-growth potential startups, often taking significant ownership stakes in exchange for equity. These funds aim for substantial returns through capital appreciation as portfolio companies mature and reach liquidity events like IPOs or acquisitions. Explore how venture capital differs from private credit funds in risk profile, investment horizon, and return expectations for a comprehensive understanding.
Debt Financing (Private Credit Funds)
Private credit funds specialize in providing debt financing to mid-market companies, offering flexible loan structures that often bypass traditional bank lending restrictions. These funds typically target higher yields through direct lending, mezzanine loans, and distressed debt, focusing on predictable cash flow rather than equity upside. Explore how private credit funds are reshaping corporate financing by delivering tailored debt solutions beyond venture capital equity stakes.
Risk Profile
Venture capital funds primarily invest in early-stage startups with high growth potential, exposing investors to significant market and business risks due to the uncertainty of new ventures. Private credit funds offer debt financing to established companies, presenting lower risk by prioritizing steady interest payments and collateral-backed assets. Explore their distinct risk profiles in greater detail to determine the best fit for your investment strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Venture Capital? - Venture capital (VC) is funding that supports new, high-growth companies by turning innovative ideas into market-transforming products, often involving long-term and high-risk investments with active collaboration between investors and entrepreneurs.
Fund your business | U.S. Small Business Administration - Venture capital differs from traditional loans by providing equity investment in exchange for ownership and often board seats, focusing on startups with high growth potential and taking higher risks for potentially higher returns.
What is venture capital? - Silicon Valley Bank - Venture capital is a form of private equity that supports early-stage companies, providing not only funding but also strategic and managerial support, with VCs receiving ownership stakes and sometimes board seats in return.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com