Fractional ownership allows investors to buy a specific percentage of a high-value asset, offering direct control and potential tax benefits, while unit trusts pool investors' money to purchase a diversified portfolio managed by professionals. This contrast highlights differences in liquidity, management fees, and investment accessibility. Explore these options further to determine which investment strategy suits your financial goals best.
Why it is important
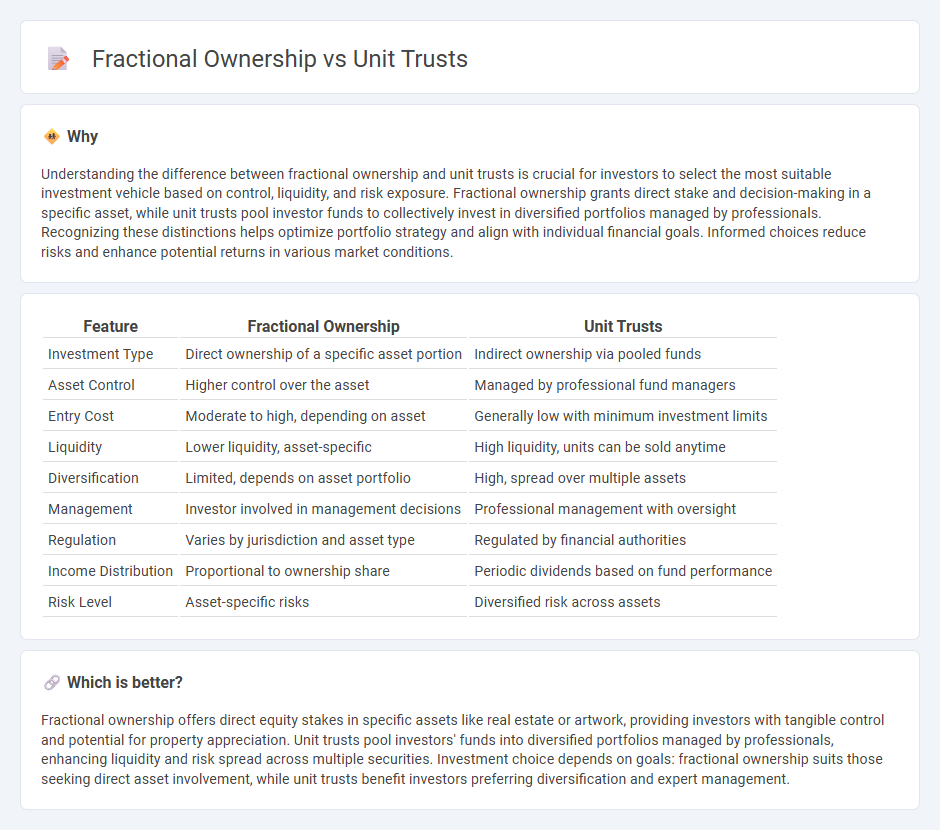
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership and unit trusts is crucial for investors to select the most suitable investment vehicle based on control, liquidity, and risk exposure. Fractional ownership grants direct stake and decision-making in a specific asset, while unit trusts pool investor funds to collectively invest in diversified portfolios managed by professionals. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize portfolio strategy and align with individual financial goals. Informed choices reduce risks and enhance potential returns in various market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fractional Ownership | Unit Trusts |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Direct ownership of a specific asset portion | Indirect ownership via pooled funds |
| Asset Control | Higher control over the asset | Managed by professional fund managers |
| Entry Cost | Moderate to high, depending on asset | Generally low with minimum investment limits |
| Liquidity | Lower liquidity, asset-specific | High liquidity, units can be sold anytime |
| Diversification | Limited, depends on asset portfolio | High, spread over multiple assets |
| Management | Investor involved in management decisions | Professional management with oversight |
| Regulation | Varies by jurisdiction and asset type | Regulated by financial authorities |
| Income Distribution | Proportional to ownership share | Periodic dividends based on fund performance |
| Risk Level | Asset-specific risks | Diversified risk across assets |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership offers direct equity stakes in specific assets like real estate or artwork, providing investors with tangible control and potential for property appreciation. Unit trusts pool investors' funds into diversified portfolios managed by professionals, enhancing liquidity and risk spread across multiple securities. Investment choice depends on goals: fractional ownership suits those seeking direct asset involvement, while unit trusts benefit investors preferring diversification and expert management.
Connection
Fractional ownership and unit trusts are connected through their shared principle of allowing investors to pool resources to access high-value assets or diversified portfolios. Fractional ownership divides a single asset, such as real estate or collectibles, into smaller, manageable shares, enabling multiple investors to hold portions of the asset. Unit trusts operate similarly by aggregating investor funds to purchase a diversified range of securities, providing collective investment benefits and risk distribution.
Key Terms
Diversification
Unit trusts offer broad diversification by pooling investors' funds to invest in a wide range of assets, reducing individual risk through professional management. Fractional ownership, while allowing investors to own a portion of high-value assets like real estate or art, typically involves less diversified holdings concentrated in specific properties or items. Explore the key benefits and limitations of each option to determine which diversification strategy aligns best with your investment goals.
Liquidity
Unit trusts offer higher liquidity as investors can buy or sell units daily at the fund's net asset value, providing easy access to cash. Fractional ownership involves purchasing portions of high-value assets like real estate, which typically have lower liquidity due to longer transaction times and market availability. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which investment suits your liquidity needs best.
Minimum Investment
Unit trusts typically require a minimum investment amount ranging from $500 to $5,000, allowing investors to pool their funds for diversified portfolio management. Fractional ownership offers lower entry barriers, often permitting investments as small as $100, providing more accessibility to high-value assets like real estate and collectibles. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of minimum investment options for both unit trusts and fractional ownership to make informed decisions.
Source and External Links
Unit Trust - A unit trust is a form of collective investment constituted under a trust deed, pooling investors' money into a fund managed by a fund manager.
Invest in Unit Trust Funds - Unit trusts provide cost-effective access to fixed income and stock markets, offering diversification and professional management.
What is a Unit Trust? - A unit trust is an open-ended investment, allowing unlimited investors to pool their money with a fund manager to manage the investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com