Hedge fund replication aims to mimic the performance and risk profile of hedge funds using liquid, transparent securities, whereas smart beta strategies focus on systematic, factor-based investment rules to capture specific risk premia. Both methods strive to enhance return potential and control costs compared to traditional active management. Explore the nuances of hedge fund replication and smart beta to optimize your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between hedge fund replication and smart beta is crucial for investors to optimize portfolio diversification and manage risk effectively. Hedge fund replication aims to mimic hedge fund returns through alternative strategies, often reducing fees and increasing transparency. Smart beta focuses on systematic, rules-based investment strategies that target specific risk factors or market inefficiencies. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align their investment choices with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
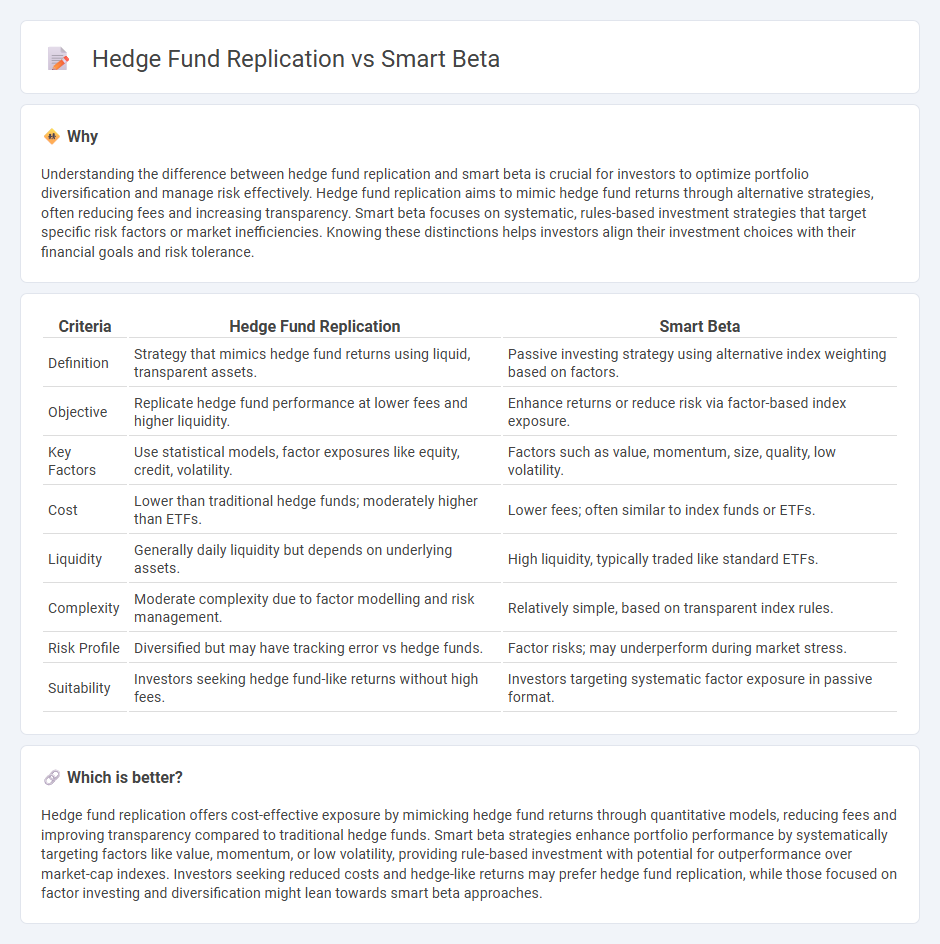
| Criteria | Hedge Fund Replication | Smart Beta |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy that mimics hedge fund returns using liquid, transparent assets. | Passive investing strategy using alternative index weighting based on factors. |
| Objective | Replicate hedge fund performance at lower fees and higher liquidity. | Enhance returns or reduce risk via factor-based index exposure. |
| Key Factors | Use statistical models, factor exposures like equity, credit, volatility. | Factors such as value, momentum, size, quality, low volatility. |
| Cost | Lower than traditional hedge funds; moderately higher than ETFs. | Lower fees; often similar to index funds or ETFs. |
| Liquidity | Generally daily liquidity but depends on underlying assets. | High liquidity, typically traded like standard ETFs. |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity due to factor modelling and risk management. | Relatively simple, based on transparent index rules. |
| Risk Profile | Diversified but may have tracking error vs hedge funds. | Factor risks; may underperform during market stress. |
| Suitability | Investors seeking hedge fund-like returns without high fees. | Investors targeting systematic factor exposure in passive format. |
Which is better?
Hedge fund replication offers cost-effective exposure by mimicking hedge fund returns through quantitative models, reducing fees and improving transparency compared to traditional hedge funds. Smart beta strategies enhance portfolio performance by systematically targeting factors like value, momentum, or low volatility, providing rule-based investment with potential for outperformance over market-cap indexes. Investors seeking reduced costs and hedge-like returns may prefer hedge fund replication, while those focused on factor investing and diversification might lean towards smart beta approaches.
Connection
Hedge fund replication and Smart Beta are connected through their shared goal of capturing hedge fund-like returns at lower costs by systematically targeting specific risk factors and investment strategies. Both approaches employ quantitative models to mimic hedge fund exposures, utilizing alternative beta strategies such as momentum, value, and volatility to achieve diversified alpha. This combination allows investors to access hedge fund-style performance while benefiting from greater transparency, liquidity, and reduced fees.
Key Terms
Factor exposure
Smart beta strategies systematically target factor exposures such as value, momentum, size, and quality to enhance risk-adjusted returns while maintaining transparency and lower costs compared to traditional hedge funds. Hedge fund replication techniques attempt to mimic hedge fund performance by decomposing returns into factor exposures and replicating these factors using liquid securities, often resulting in reduced fees and increased accessibility. Explore detailed comparisons and insights to understand which approach aligns better with your investment goals.
Alternative beta
Alternative beta strategies leverage systematic risk factors that capture sources of returns traditionally accessible through hedge funds, offering cost-efficient exposure compared to active management. Smart beta employs rules-based index construction targeting specific factors like value, momentum, or volatility, while hedge fund replication models attempt to mimic hedge fund return profiles using liquid factor exposures. Explore how alternative beta techniques can optimize portfolio diversification and reduce fees relative to hedge fund investments.
Strategy replication
Strategy replication in smart beta focuses on systematically capturing specific risk factors or investment styles to mimic desired market exposures with lower fees and transparency. Hedge fund replication aims to emulate hedge fund returns by modeling their complex strategies using liquid asset portfolios and advanced quantitative techniques. Explore more to understand the nuances and practical applications of these replication approaches.
Source and External Links
What are smart beta strategies? A guide to modern diversification - Smart beta strategies combine passive and active investing by using factor-based selection (e.g., value, momentum, low volatility, quality, size) and alternative rules-based weighting methods (equal, fundamental, factor weighting) to tailor portfolio risk and returns beyond traditional market-cap weighting.
Smart Beta - Overview, How It Works, Trading Strategies - Smart beta is a hybrid investment approach combining passive and active elements, optimizing portfolios based on factors like value, liquidity, quality, and momentum to capture market inefficiencies and improve diversification compared to traditional indexing.
Smart Beta ETFs | Charles Schwab - Smart beta ETFs use rules-based indexes that weight securities by factors other than market capitalization, such as equal weighting, fundamental weighting, minimum variance, or low volatility, offering a cost-effective way to implement factor-based strategic investing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com