The secondaries market provides investors with liquidity by enabling the buying and selling of pre-existing private equity fund interests, contrasting with primary private equity investments where capital is committed directly to new funds. Secondaries often offer opportunities to acquire assets at discounts and with reduced risk due to the matured stage of underlying investments. Explore further to understand the strategic benefits and risk profiles of secondaries versus traditional private equity investing.
Why it is important
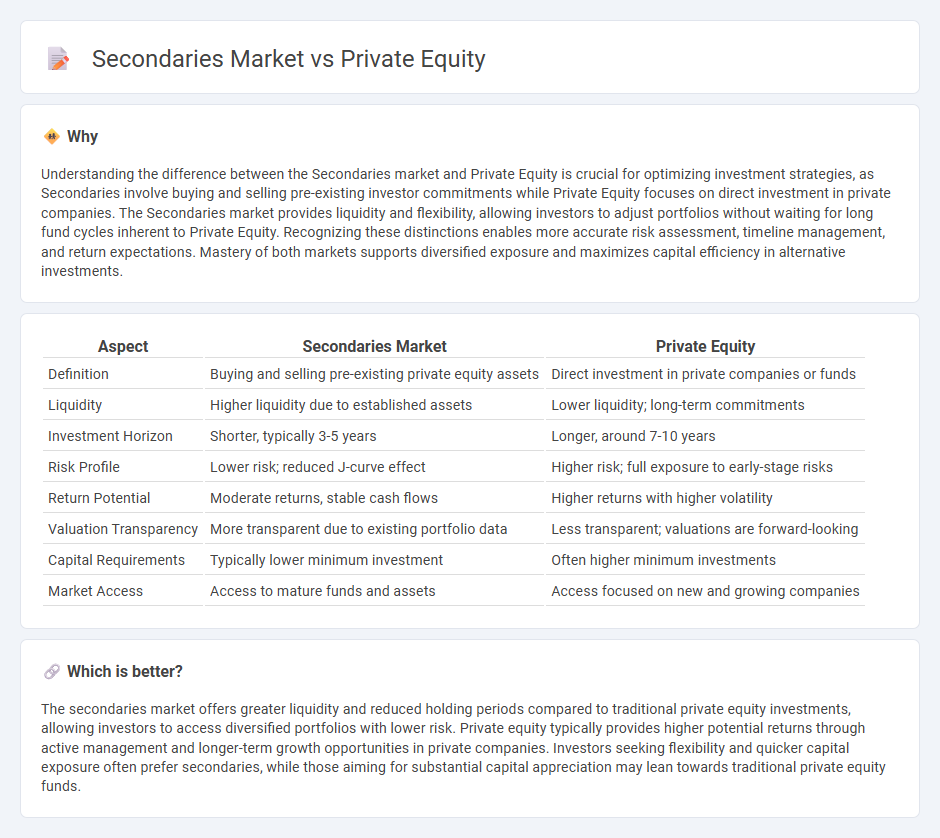
Understanding the difference between the Secondaries market and Private Equity is crucial for optimizing investment strategies, as Secondaries involve buying and selling pre-existing investor commitments while Private Equity focuses on direct investment in private companies. The Secondaries market provides liquidity and flexibility, allowing investors to adjust portfolios without waiting for long fund cycles inherent to Private Equity. Recognizing these distinctions enables more accurate risk assessment, timeline management, and return expectations. Mastery of both markets supports diversified exposure and maximizes capital efficiency in alternative investments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondaries Market | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling pre-existing private equity assets | Direct investment in private companies or funds |
| Liquidity | Higher liquidity due to established assets | Lower liquidity; long-term commitments |
| Investment Horizon | Shorter, typically 3-5 years | Longer, around 7-10 years |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk; reduced J-curve effect | Higher risk; full exposure to early-stage risks |
| Return Potential | Moderate returns, stable cash flows | Higher returns with higher volatility |
| Valuation Transparency | More transparent due to existing portfolio data | Less transparent; valuations are forward-looking |
| Capital Requirements | Typically lower minimum investment | Often higher minimum investments |
| Market Access | Access to mature funds and assets | Access focused on new and growing companies |
Which is better?
The secondaries market offers greater liquidity and reduced holding periods compared to traditional private equity investments, allowing investors to access diversified portfolios with lower risk. Private equity typically provides higher potential returns through active management and longer-term growth opportunities in private companies. Investors seeking flexibility and quicker capital exposure often prefer secondaries, while those aiming for substantial capital appreciation may lean towards traditional private equity funds.
Connection
The Secondaries market facilitates liquidity by enabling investors to buy and sell existing private equity fund interests, providing a crucial mechanism for portfolio rebalancing and capital recycling. This market enhances private equity by offering flexibility and access to mature assets, often at discounted valuations compared to primary investments. Increased activity in the Secondaries market reflects growing investor demand for diversified exposure and risk mitigation within private equity portfolios.
Key Terms
Direct Investment
Direct investments in private equity involve acquiring stakes directly in companies, providing investors with control and tailored value creation opportunities. The secondaries market offers liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell pre-existing private equity fund interests, often at a discount to net asset value, reducing the typical private equity hold period. Explore further to understand the strategic benefits and risk considerations of direct investments compared to secondaries.
Secondary Transactions
Secondary transactions in private equity involve the buying and selling of existing limited partnership interests, providing liquidity to investors before the fund's maturity. These transactions offer market participants opportunities to adjust portfolio exposure and gain access to mature assets with potentially lower risk compared to primary investments. Explore more about how secondary markets enhance flexibility and valuation dynamics in private equity investments.
Fund Liquidity
Private equity investments typically lock capital for 7 to 10 years, limiting fund liquidity and investor access to returns. The secondaries market provides a crucial liquidity solution by enabling the buying and selling of pre-existing private equity fund interests before maturity. Explore how fund liquidity dynamics in private equity and secondaries markets impact portfolio flexibility and investor strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance provided for equity stakes in non-public companies, involving active ownership where investors work closely with management to improve business value, typically holding investments for 4 to 7 years before exiting.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity involves investing in companies not publicly traded by improving management, operations, and strategy to generate returns, and it offers diversification benefits as the public company universe shrinks.
What does a career in private equity look like? - CFA Institute - Private equity firms raise money from limited partners and use it to invest in private or public companies with strategies including venture capital, growth equity, and buyouts to improve and grow their portfolio companies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com