Song catalog purchases involve acquiring rights to musical compositions, generating revenue through royalties and licensing, while stock acquisitions entail buying shares in companies to gain ownership stakes and potential dividends. Both investment strategies offer diversification but differ significantly in risk profiles, liquidity, and income sources. Explore the benefits and challenges of each approach to determine the best fit for your portfolio.
Why it is important
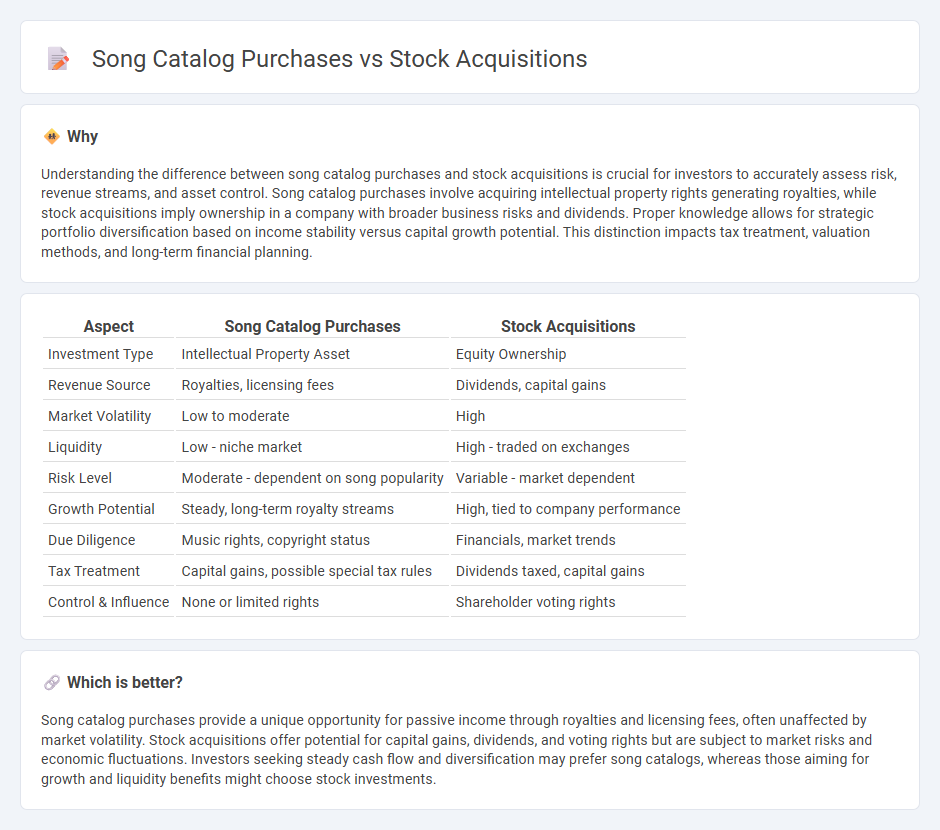
Understanding the difference between song catalog purchases and stock acquisitions is crucial for investors to accurately assess risk, revenue streams, and asset control. Song catalog purchases involve acquiring intellectual property rights generating royalties, while stock acquisitions imply ownership in a company with broader business risks and dividends. Proper knowledge allows for strategic portfolio diversification based on income stability versus capital growth potential. This distinction impacts tax treatment, valuation methods, and long-term financial planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Song Catalog Purchases | Stock Acquisitions |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Intellectual Property Asset | Equity Ownership |
| Revenue Source | Royalties, licensing fees | Dividends, capital gains |
| Market Volatility | Low to moderate | High |
| Liquidity | Low - niche market | High - traded on exchanges |
| Risk Level | Moderate - dependent on song popularity | Variable - market dependent |
| Growth Potential | Steady, long-term royalty streams | High, tied to company performance |
| Due Diligence | Music rights, copyright status | Financials, market trends |
| Tax Treatment | Capital gains, possible special tax rules | Dividends taxed, capital gains |
| Control & Influence | None or limited rights | Shareholder voting rights |
Which is better?
Song catalog purchases provide a unique opportunity for passive income through royalties and licensing fees, often unaffected by market volatility. Stock acquisitions offer potential for capital gains, dividends, and voting rights but are subject to market risks and economic fluctuations. Investors seeking steady cash flow and diversification may prefer song catalogs, whereas those aiming for growth and liquidity benefits might choose stock investments.
Connection
Song catalog purchases and stock acquisitions both represent strategic investments that generate passive income through asset appreciation and revenue streams. Investors acquire song catalogs to secure rights and royalties, similar to how stock acquisitions offer ownership stakes and dividends in companies. Both investment types leverage intellectual property and business equity to diversify portfolios and enhance long-term financial returns.
Key Terms
Equity Ownership
Stock acquisitions grant buyers equity ownership in the entire company, including all assets and liabilities, providing control over business operations and future profits. Song catalog purchases involve acquiring specific intellectual property rights, generating revenue from royalties without ownership stakes or company control. Explore more about the strategic differences and financial implications of these investment approaches.
Intellectual Property Rights
Stock acquisitions involve buying a company's ownership shares, granting broad control over its assets, including intellectual property rights tied to music catalogs. Song catalog purchases target specific intellectual property assets, transferring copyright ownership and related royalties without assuming the entire company. Explore the nuances between these transactions to optimize your intellectual property strategy.
Valuation Methods
Stock acquisitions are valued based on company financials, including assets, liabilities, and future earnings potential, often utilizing discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis and market comparables. Song catalog purchases focus on intellectual property valuation, relying heavily on projected royalty streams, licensing income, and historical earnings, frequently assessed through income capitalization and multi-period excess earnings methods. Explore detailed valuation techniques and their implications in music industry transactions for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Differences between asset and stock acquisitions in M&A - A stock acquisition involves a buyer purchasing a controlling interest in the target company, thereby acquiring all of its assets and liabilities, and can be paid for with stock, cash, or a combination of both.
Stock Acquisition - Definition, How It Works, Pros and Cons - In a stock acquisition, the buyer assumes ownership of the target company as a going concern, inheriting all existing assets, liabilities, and potential legal risks from the previous owners.
Stock-for-Stock Merger: Key Concepts and Examples - A stock-for-stock merger is a specific type of stock acquisition where the acquirer pays for the target's shares using its own stock, based on an agreed exchange ratio, and typically requires shareholder approval from both companies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com