Fractional real estate investing allows individuals to purchase a portion of a specific property, offering direct ownership and potential rental income, while real estate mutual funds pool investors' money to invest in a diversified portfolio of real estate assets managed by professionals. Fractional investing provides tangible asset control and transparency, whereas real estate mutual funds offer liquidity and diversification with fewer entry barriers. Explore the benefits and drawbacks of each to determine the best investment strategy for your financial goals.
Why it is important
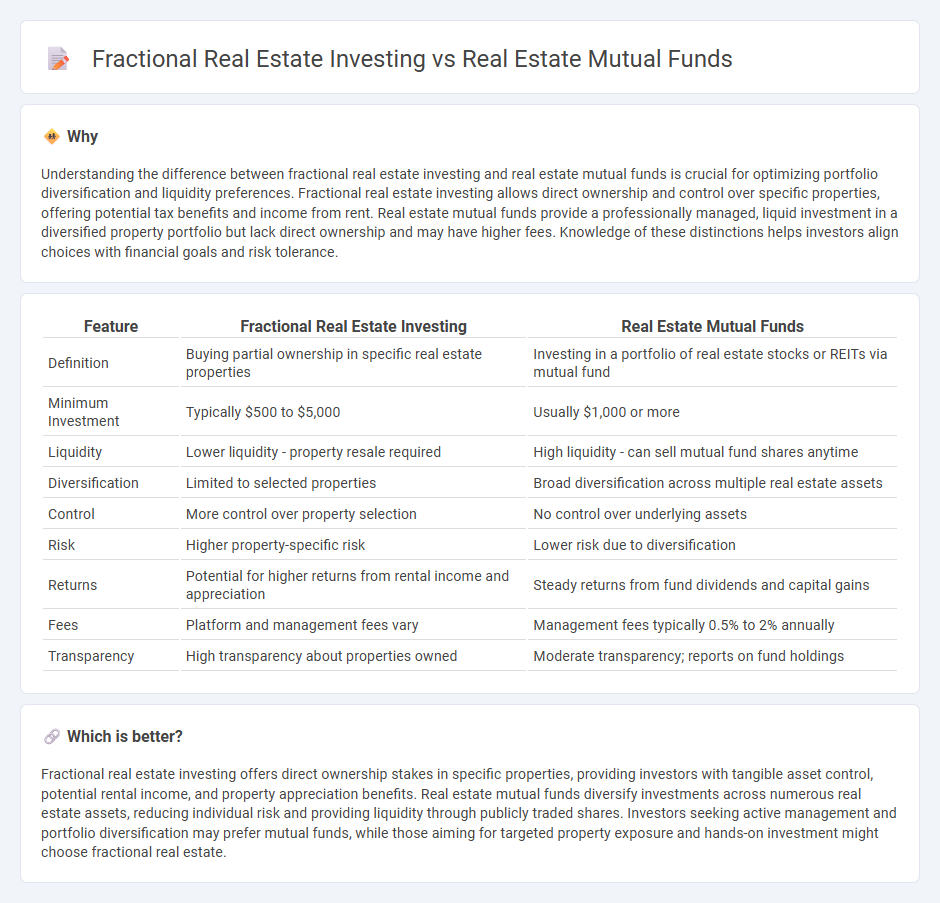
Understanding the difference between fractional real estate investing and real estate mutual funds is crucial for optimizing portfolio diversification and liquidity preferences. Fractional real estate investing allows direct ownership and control over specific properties, offering potential tax benefits and income from rent. Real estate mutual funds provide a professionally managed, liquid investment in a diversified property portfolio but lack direct ownership and may have higher fees. Knowledge of these distinctions helps investors align choices with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fractional Real Estate Investing | Real Estate Mutual Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying partial ownership in specific real estate properties | Investing in a portfolio of real estate stocks or REITs via mutual fund |
| Minimum Investment | Typically $500 to $5,000 | Usually $1,000 or more |
| Liquidity | Lower liquidity - property resale required | High liquidity - can sell mutual fund shares anytime |
| Diversification | Limited to selected properties | Broad diversification across multiple real estate assets |
| Control | More control over property selection | No control over underlying assets |
| Risk | Higher property-specific risk | Lower risk due to diversification |
| Returns | Potential for higher returns from rental income and appreciation | Steady returns from fund dividends and capital gains |
| Fees | Platform and management fees vary | Management fees typically 0.5% to 2% annually |
| Transparency | High transparency about properties owned | Moderate transparency; reports on fund holdings |
Which is better?
Fractional real estate investing offers direct ownership stakes in specific properties, providing investors with tangible asset control, potential rental income, and property appreciation benefits. Real estate mutual funds diversify investments across numerous real estate assets, reducing individual risk and providing liquidity through publicly traded shares. Investors seeking active management and portfolio diversification may prefer mutual funds, while those aiming for targeted property exposure and hands-on investment might choose fractional real estate.
Connection
Fractional real estate investing and real estate mutual funds both enable investors to gain exposure to property markets without purchasing entire properties, allowing for diversified investment portfolios. Fractional real estate investing divides ownership into shares, providing direct equity stakes in specific properties, while real estate mutual funds pool capital to invest broadly across multiple real estate assets. Both investment methods minimize individual risk, enhance liquidity, and offer access to real estate opportunities typically reserved for large-scale investors.
Key Terms
Diversification
Real estate mutual funds pool investors' capital to buy diversified portfolios of real estate assets, offering exposure to commercial, residential, and industrial properties managed by professionals. Fractional real estate investing allows individuals to purchase shares of specific properties, which may limit diversification but provides more direct control and tangible asset ownership. Explore the benefits and trade-offs between these investment options to optimize your real estate portfolio diversification.
Liquidity
Real estate mutual funds offer high liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell shares on the stock exchange with ease, while fractional real estate investing typically involves longer holding periods with limited secondary market options. Mutual funds provide daily liquidity enabling quick access to capital, whereas fractional ownership requires more time to liquidate due to property-specific regulations and fewer buyers. Explore our detailed comparison to better understand which investment suits your liquidity needs.
Ownership structure
Real estate mutual funds pool investors' money to purchase diversified portfolios of properties managed by professionals, offering indirect ownership without direct control over specific assets. Fractional real estate investing provides partial ownership in individual properties, allowing investors to hold actual equity shares and benefit from property-specific returns. Explore the detailed differences in ownership structure to choose the best real estate investment strategy for your goals.
Source and External Links
Understanding REITs and Mutual Funds: Differences, Similarities - Real estate mutual funds pool capital from investors to buy shares in a diversified mix of REITs and various real estate companies, offering professional management and the potential for capital appreciation, though typically with higher fees than REITs.
Real Estate - Fidelity Investments - Fidelity offers a range of real estate mutual funds and ETFs, such as the Fidelity Real Estate Investment Portfolio and Fidelity Real Estate Index Fund, that provide sector-specific exposure to real estate companies and REITs, with tools for research and performance analysis.
PGIM US Real Estate Fund - The PGIM US Real Estate Fund seeks both capital appreciation and income by investing primarily in a diversified portfolio of domestic real estate securities, including REITs and real estate operating companies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com