Sports team ownership shares offer unique investment opportunities tied to exclusive assets and fan loyalty, often providing less liquidity and higher risk compared to traditional public company stocks traded on major exchanges. Public company stocks deliver broader market exposure, diversified portfolios, and regulatory transparency, making them a more accessible choice for many investors seeking steady growth and dividends. Explore the differences in risk, return, and market dynamics to determine which investment aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
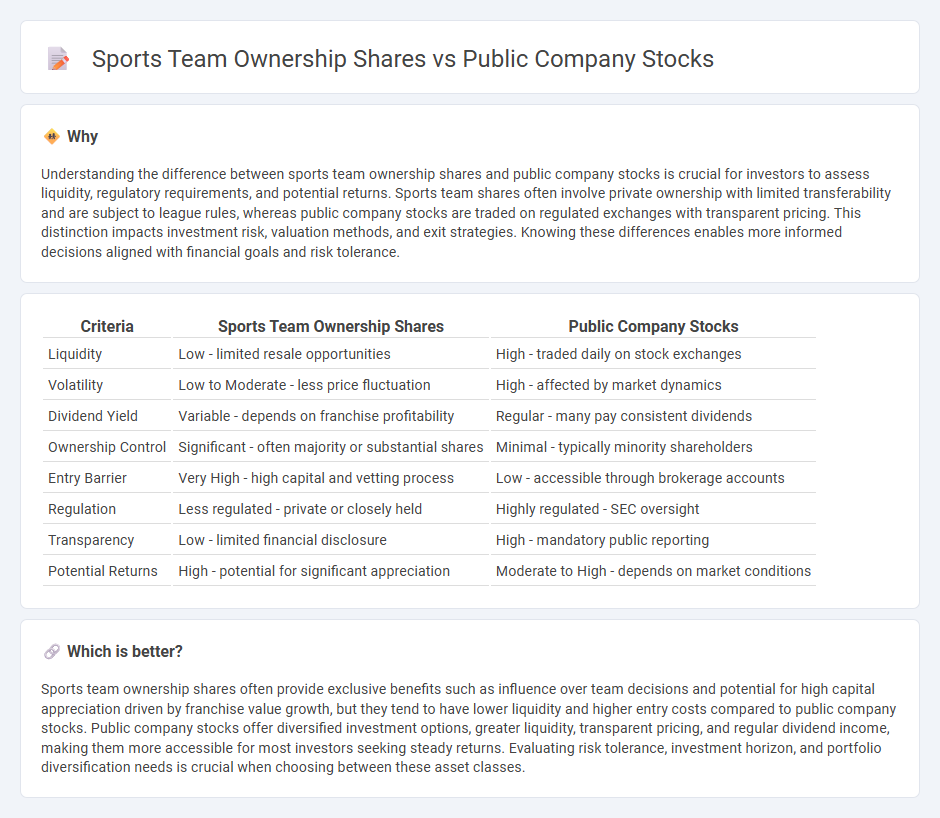
Understanding the difference between sports team ownership shares and public company stocks is crucial for investors to assess liquidity, regulatory requirements, and potential returns. Sports team shares often involve private ownership with limited transferability and are subject to league rules, whereas public company stocks are traded on regulated exchanges with transparent pricing. This distinction impacts investment risk, valuation methods, and exit strategies. Knowing these differences enables more informed decisions aligned with financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Sports Team Ownership Shares | Public Company Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Liquidity | Low - limited resale opportunities | High - traded daily on stock exchanges |
| Volatility | Low to Moderate - less price fluctuation | High - affected by market dynamics |
| Dividend Yield | Variable - depends on franchise profitability | Regular - many pay consistent dividends |
| Ownership Control | Significant - often majority or substantial shares | Minimal - typically minority shareholders |
| Entry Barrier | Very High - high capital and vetting process | Low - accessible through brokerage accounts |
| Regulation | Less regulated - private or closely held | Highly regulated - SEC oversight |
| Transparency | Low - limited financial disclosure | High - mandatory public reporting |
| Potential Returns | High - potential for significant appreciation | Moderate to High - depends on market conditions |
Which is better?
Sports team ownership shares often provide exclusive benefits such as influence over team decisions and potential for high capital appreciation driven by franchise value growth, but they tend to have lower liquidity and higher entry costs compared to public company stocks. Public company stocks offer diversified investment options, greater liquidity, transparent pricing, and regular dividend income, making them more accessible for most investors seeking steady returns. Evaluating risk tolerance, investment horizon, and portfolio diversification needs is crucial when choosing between these asset classes.
Connection
Sports team ownership shares and public company stocks are connected through their underlying principles of equity investment, allowing individuals to purchase partial ownership in entities that generate revenue and build brand value. Both types of shares offer investors opportunities for capital appreciation, dividends, and influence over organizational decisions through voting rights. Market dynamics, financial performance, and fan or shareholder sentiment significantly impact the valuation and trading activity of sports team shares and public company stocks.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Public company stocks offer high liquidity through stock exchanges, enabling investors to buy or sell shares quickly and at transparent prices. Sports team ownership shares typically have limited liquidity due to fewer buyers, private transactions, and restrictions on selling stakes. Explore how these differences impact investment strategies and portfolio diversification.
Valuation
Public company stocks are valued based on market capitalization, earnings, and future growth prospects, providing liquidity and transparency through regulated exchanges. Sports team ownership shares typically involve private valuations influenced by franchise revenue, brand strength, and league agreements, often lacking market liquidity. Explore further to understand the nuanced valuation methods and investment dynamics in both arenas.
Governance
Public company stocks are governed by regulatory bodies such as the SEC, requiring transparency, shareholder voting rights, and adherence to corporate governance standards. Sports team ownership shares often involve private agreements with concentrated control among a few stakeholders, limiting public voting influence and governance disclosures. Explore the unique governance structures shaping investor rights in these distinct ownership forms.
Source and External Links
Public company - Wikipedia - A public company is a business whose ownership is organized via shares of stock freely traded on stock exchanges, allowing it to raise large capital through stock sales and providing transparency and shared risk among shareholders.
All Stocks Listed on The NASDAQ Stock Exchange in The US - This resource lists thousands of public company stocks currently trading on the Nasdaq exchange, including market capitalization, stock prices, and daily changes.
Public Companies | Investor.gov - Public companies are integral to the economy, trading securities on public markets and disclosing financial information regularly to investors and the public, making investing in them a key component of many retirement and investment plans.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com