Carbon offset investing involves funding projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, creating measurable carbon credits that support environmental sustainability. Green bonds are debt securities issued to finance projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or clean transportation, appealing to investors seeking both returns and climate benefits. Explore the key differences, benefits, and risks of carbon offset investing versus green bonds to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
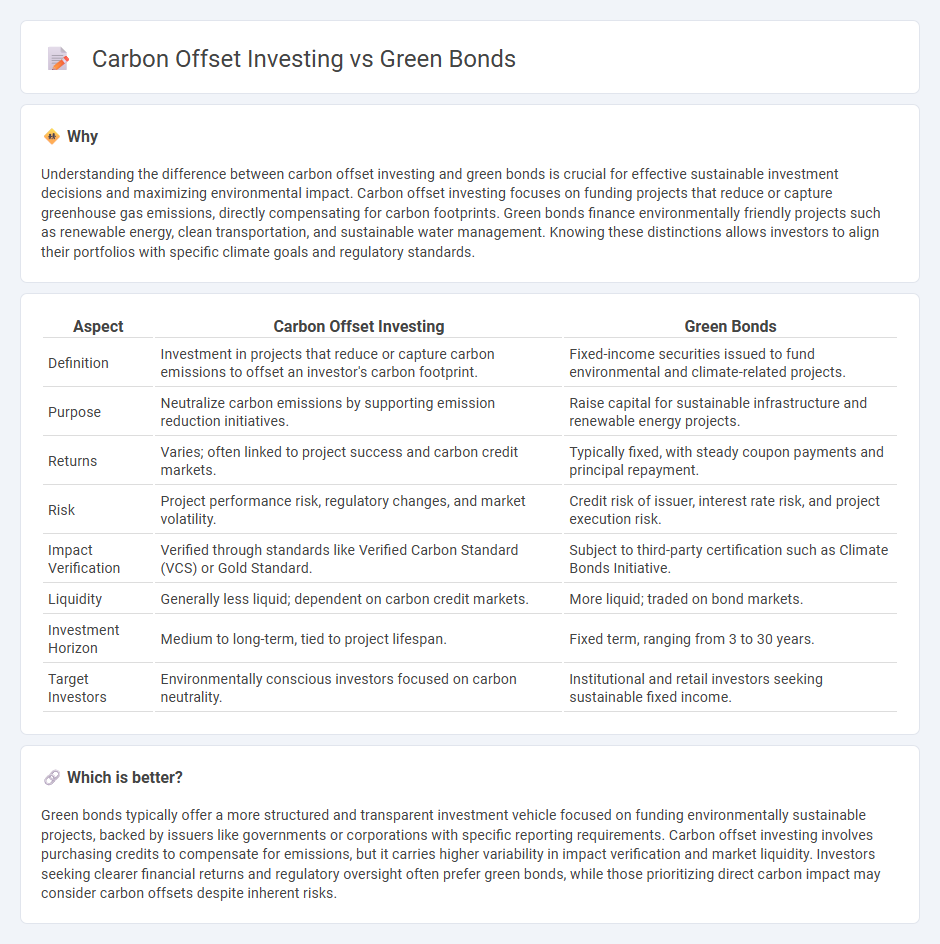
Understanding the difference between carbon offset investing and green bonds is crucial for effective sustainable investment decisions and maximizing environmental impact. Carbon offset investing focuses on funding projects that reduce or capture greenhouse gas emissions, directly compensating for carbon footprints. Green bonds finance environmentally friendly projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. Knowing these distinctions allows investors to align their portfolios with specific climate goals and regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Offset Investing | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in projects that reduce or capture carbon emissions to offset an investor's carbon footprint. | Fixed-income securities issued to fund environmental and climate-related projects. |
| Purpose | Neutralize carbon emissions by supporting emission reduction initiatives. | Raise capital for sustainable infrastructure and renewable energy projects. |
| Returns | Varies; often linked to project success and carbon credit markets. | Typically fixed, with steady coupon payments and principal repayment. |
| Risk | Project performance risk, regulatory changes, and market volatility. | Credit risk of issuer, interest rate risk, and project execution risk. |
| Impact Verification | Verified through standards like Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) or Gold Standard. | Subject to third-party certification such as Climate Bonds Initiative. |
| Liquidity | Generally less liquid; dependent on carbon credit markets. | More liquid; traded on bond markets. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term, tied to project lifespan. | Fixed term, ranging from 3 to 30 years. |
| Target Investors | Environmentally conscious investors focused on carbon neutrality. | Institutional and retail investors seeking sustainable fixed income. |
Which is better?
Green bonds typically offer a more structured and transparent investment vehicle focused on funding environmentally sustainable projects, backed by issuers like governments or corporations with specific reporting requirements. Carbon offset investing involves purchasing credits to compensate for emissions, but it carries higher variability in impact verification and market liquidity. Investors seeking clearer financial returns and regulatory oversight often prefer green bonds, while those prioritizing direct carbon impact may consider carbon offsets despite inherent risks.
Connection
Carbon offset investing and green bonds both target reducing environmental impact by funding projects that lower carbon emissions and promote sustainable development. Investors in carbon offset projects purchase credits that finance renewable energy, reforestation, or energy efficiency, while green bonds raise capital explicitly for eco-friendly initiatives, offering a fixed-income investment vehicle. The connection lies in their shared goal of mobilizing private capital to combat climate change and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Green bonds finance projects that deliver measurable environmental benefits, particularly in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure, providing transparent reporting to investors. Carbon offset investing involves purchasing credits that compensate for emissions by funding projects like reforestation or methane capture, often used by companies to achieve carbon neutrality. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which approach better aligns with your sustainability goals.
Emissions reduction
Green bonds finance projects specifically designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure. Carbon offset investing allows individuals or companies to compensate for their emissions by funding projects that capture or avoid emissions, such as reforestation or methane capture. Explore how these approaches differ in impact and suitability for effective emissions reduction strategies.
Impact measurement
Green bonds finance projects specifically designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote environmental sustainability, with impact measurement based on predefined metrics such as CO2 reduction and renewable energy capacity. Carbon offset investing involves purchasing credits to compensate for emissions elsewhere, but impact measurement challenges include verifying the authenticity and permanence of offset projects. Explore further to understand the methodologies and standards used to ensure credibility and effectiveness in both approaches.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used exclusively to finance projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, pollution control, and climate change adaptation, allowing investors to meet ESG goals.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued by public or private entities, committed to use proceeds solely for environmentally sustainable or climate change-related projects like renewable energy and clean transportation.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles provide voluntary guidelines to ensure transparency and integrity in green bond issuance to finance projects fostering a net-zero emissions economy, recommending clearer disclosure and tracking of environmental impacts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com