Music royalties offer steady income streams backed by intellectual property rights, appealing to investors seeking long-term, passive revenue. Private equity involves acquiring ownership stakes in private companies, focusing on capital growth through strategic management and operational improvements. Explore the key differences between these investment opportunities to determine which aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
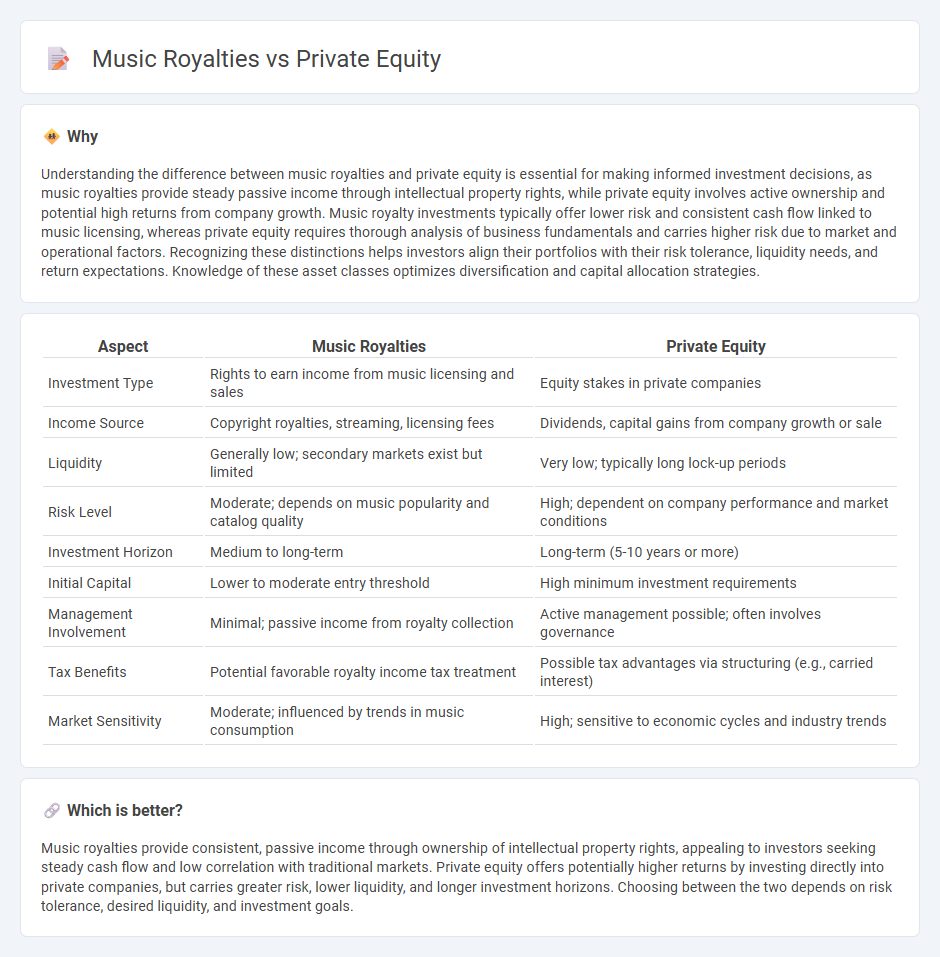
Understanding the difference between music royalties and private equity is essential for making informed investment decisions, as music royalties provide steady passive income through intellectual property rights, while private equity involves active ownership and potential high returns from company growth. Music royalty investments typically offer lower risk and consistent cash flow linked to music licensing, whereas private equity requires thorough analysis of business fundamentals and carries higher risk due to market and operational factors. Recognizing these distinctions helps investors align their portfolios with their risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and return expectations. Knowledge of these asset classes optimizes diversification and capital allocation strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Music Royalties | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Type | Rights to earn income from music licensing and sales | Equity stakes in private companies |
| Income Source | Copyright royalties, streaming, licensing fees | Dividends, capital gains from company growth or sale |
| Liquidity | Generally low; secondary markets exist but limited | Very low; typically long lock-up periods |
| Risk Level | Moderate; depends on music popularity and catalog quality | High; dependent on company performance and market conditions |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term | Long-term (5-10 years or more) |
| Initial Capital | Lower to moderate entry threshold | High minimum investment requirements |
| Management Involvement | Minimal; passive income from royalty collection | Active management possible; often involves governance |
| Tax Benefits | Potential favorable royalty income tax treatment | Possible tax advantages via structuring (e.g., carried interest) |
| Market Sensitivity | Moderate; influenced by trends in music consumption | High; sensitive to economic cycles and industry trends |
Which is better?
Music royalties provide consistent, passive income through ownership of intellectual property rights, appealing to investors seeking steady cash flow and low correlation with traditional markets. Private equity offers potentially higher returns by investing directly into private companies, but carries greater risk, lower liquidity, and longer investment horizons. Choosing between the two depends on risk tolerance, desired liquidity, and investment goals.
Connection
Music royalties and private equity intersect as private equity firms invest capital into music catalogues, acquiring royalty rights to generate predictable income streams. These investments leverage the growing demand for streaming and licensing revenues, offering diversified returns beyond traditional asset classes. The valuation of music royalties depends on factors like historical earnings, artist popularity, and contract terms, making private equity a strategic player in the entertainment finance sector.
Key Terms
Ownership stake
Private equity involves acquiring an ownership stake in a company, granting investors voting rights and influence over business decisions, while music royalties represent a revenue stream from intellectual property without direct control over the artist or catalog. Ownership in private equity typically includes equity shares that can appreciate over time, whereas music royalty investors earn income based on song usage and licensing agreements. Discover more about how ownership structures impact investment returns and control dynamics in these asset classes.
Recurring revenue
Private equity generates recurring revenue through structured investments, creating predictable cash flows via dividends and interest payments. Music royalties provide continuous income streams as rights holders earn fees from song plays, licenses, and broadcasts worldwide. Explore more about the benefits and risks of these recurring revenue models to make informed investment decisions.
Exit strategy
Private equity exit strategies typically involve initial public offerings (IPOs), mergers, or acquisitions to realize returns within a 3-7 year timeframe. Music royalties offer a distinct exit approach by allowing investors to sell future royalty streams on secondary markets or platforms, providing liquidity without the need for company restructuring. Explore detailed financial comparisons to understand which exit strategy aligns best with your investment goals.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment managers raising funds from institutional investors to buy equity stakes in private companies, with strategies centered on revenue growth, margin expansion, cash flow generation, and valuation multiple expansion over a typical 4-7 year horizon.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term capital provided in exchange for equity in unquoted companies, supporting business growth through active ownership and governance alongside management, usually holding investments for 4-7 years before exiting.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity fund managers invest in non-publicly traded companies to enhance their performance through strategies such as strengthening management, expanding markets, improving operations, and optimizing capital structure to generate returns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com