Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to share partial equity in high-value assets like real estate or luxury goods, providing diversification with lower capital requirements. Private equity involves direct investment in private companies, focusing on long-term growth and value creation through active management and strategic guidance. Explore the differences to determine which investment model aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
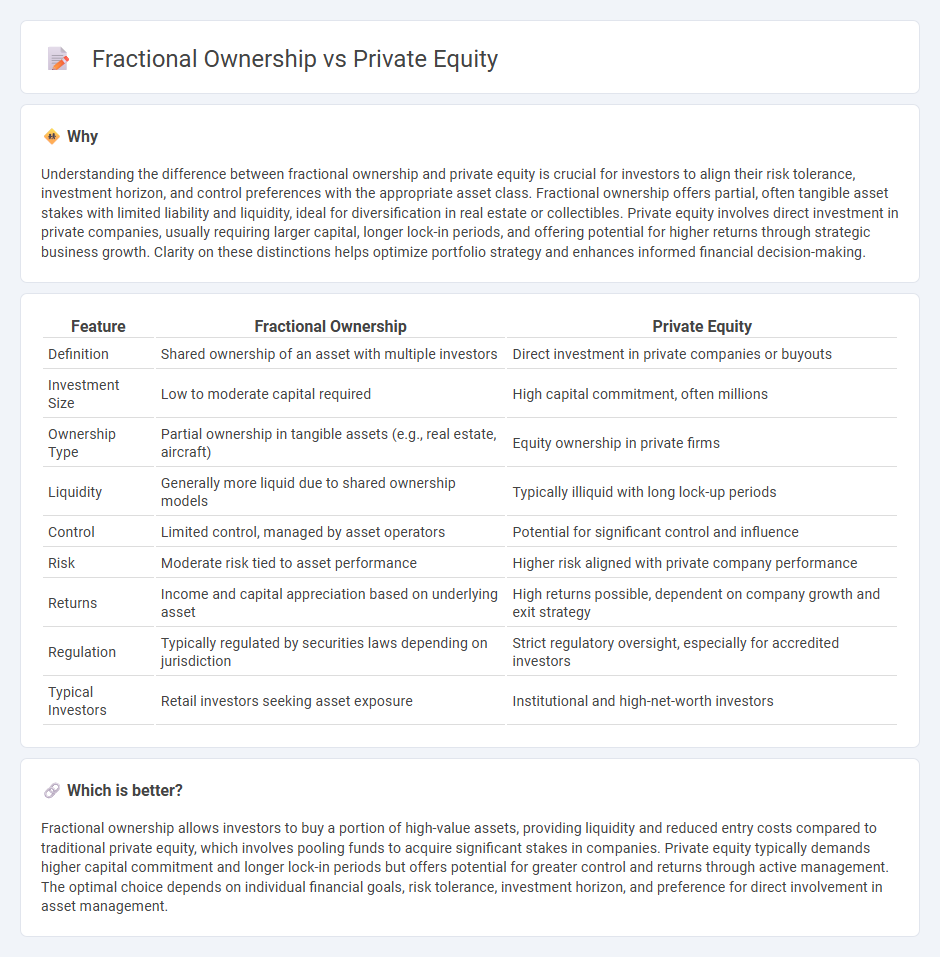
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership and private equity is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and control preferences with the appropriate asset class. Fractional ownership offers partial, often tangible asset stakes with limited liability and liquidity, ideal for diversification in real estate or collectibles. Private equity involves direct investment in private companies, usually requiring larger capital, longer lock-in periods, and offering potential for higher returns through strategic business growth. Clarity on these distinctions helps optimize portfolio strategy and enhances informed financial decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fractional Ownership | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared ownership of an asset with multiple investors | Direct investment in private companies or buyouts |
| Investment Size | Low to moderate capital required | High capital commitment, often millions |
| Ownership Type | Partial ownership in tangible assets (e.g., real estate, aircraft) | Equity ownership in private firms |
| Liquidity | Generally more liquid due to shared ownership models | Typically illiquid with long lock-up periods |
| Control | Limited control, managed by asset operators | Potential for significant control and influence |
| Risk | Moderate risk tied to asset performance | Higher risk aligned with private company performance |
| Returns | Income and capital appreciation based on underlying asset | High returns possible, dependent on company growth and exit strategy |
| Regulation | Typically regulated by securities laws depending on jurisdiction | Strict regulatory oversight, especially for accredited investors |
| Typical Investors | Retail investors seeking asset exposure | Institutional and high-net-worth investors |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership allows investors to buy a portion of high-value assets, providing liquidity and reduced entry costs compared to traditional private equity, which involves pooling funds to acquire significant stakes in companies. Private equity typically demands higher capital commitment and longer lock-in periods but offers potential for greater control and returns through active management. The optimal choice depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preference for direct involvement in asset management.
Connection
Fractional ownership allows investors to purchase a portion of high-value assets, which aligns closely with private equity's model of pooling capital to acquire stakes in private companies. Both mechanisms enable diversified investment portfolios by lowering capital requirements while providing access to exclusive or illiquid markets. This synergy enhances liquidity and democratizes wealth-building opportunities traditionally reserved for institutional investors.
Key Terms
Equity Stake
Private equity involves acquiring a substantial or controlling equity stake in a company, typically through direct investment or buyouts, granting investors significant influence or control over business decisions. Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to hold smaller, divisible equity shares in high-value assets or businesses, reducing individual capital outlay while diversifying risk exposure. Explore the nuances between these equity stake models to better understand investment structures and returns.
Liquidity
Private equity investments typically require long-term commitments, often locking capital for several years, which limits liquidity for investors. Fractional ownership offers enhanced liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell smaller portions of assets more flexibly, often through secondary markets or platforms. Explore how liquidity differences impact your investment strategy and opportunities in private equity and fractional ownership.
Governance
Private equity investments typically involve centralized governance with significant control concentrated among limited partners and fund managers, enabling decisive strategic decisions and active portfolio management. Fractional ownership features distributed governance where multiple owners share decision-making authority, often leading to a more democratic but potentially slower process. Explore detailed comparisons of governance structures to determine which investment model aligns best with your strategic goals.
Source and External Links
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity is medium to long-term finance provided in exchange for an equity stake in potentially high-growth, unquoted companies, typically supporting management buyouts and working closely with company management to drive business growth and value creation.
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment managers raising capital from institutional investors to acquire equity stakes in private companies, aiming to improve performance and generate returns through strategies like revenue growth, cost reduction, and governance restructuring, usually with a 4-7 year investment horizon.
Private Equity Funds | Investor.gov - Private equity funds are pooled investment vehicles managed by private equity firms that take controlling or minority stakes in companies, actively engage in management to increase value, and typically have a long-term investment focus, often spanning a decade or more.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com