Litigation finance involves funding legal cases in exchange for a portion of the judgment or settlement, offering high-risk, high-reward investment opportunities with returns uncorrelated to traditional markets. Infrastructure investment focuses on long-term assets like transportation, utilities, and energy projects, providing steady cash flows and lower risk profiles through essential service demands. Explore the distinct advantages and considerations of these investment types to optimize your portfolio strategy.
Why it is important
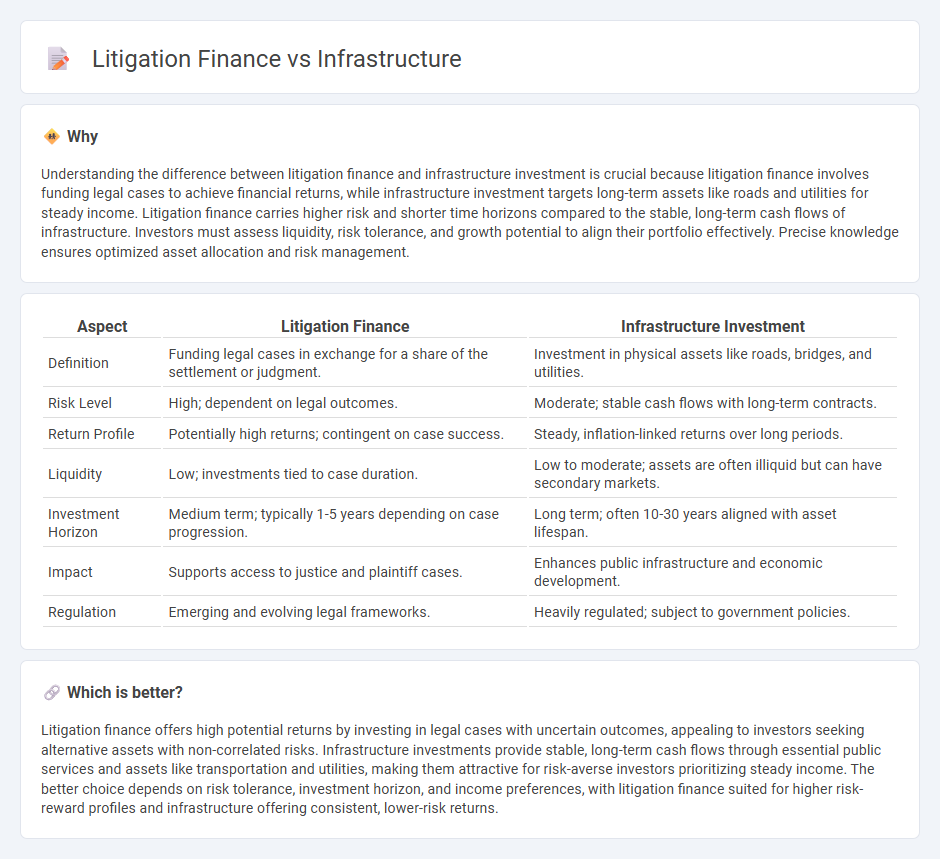
Understanding the difference between litigation finance and infrastructure investment is crucial because litigation finance involves funding legal cases to achieve financial returns, while infrastructure investment targets long-term assets like roads and utilities for steady income. Litigation finance carries higher risk and shorter time horizons compared to the stable, long-term cash flows of infrastructure. Investors must assess liquidity, risk tolerance, and growth potential to align their portfolio effectively. Precise knowledge ensures optimized asset allocation and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Litigation Finance | Infrastructure Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding legal cases in exchange for a share of the settlement or judgment. | Investment in physical assets like roads, bridges, and utilities. |
| Risk Level | High; dependent on legal outcomes. | Moderate; stable cash flows with long-term contracts. |
| Return Profile | Potentially high returns; contingent on case success. | Steady, inflation-linked returns over long periods. |
| Liquidity | Low; investments tied to case duration. | Low to moderate; assets are often illiquid but can have secondary markets. |
| Investment Horizon | Medium term; typically 1-5 years depending on case progression. | Long term; often 10-30 years aligned with asset lifespan. |
| Impact | Supports access to justice and plaintiff cases. | Enhances public infrastructure and economic development. |
| Regulation | Emerging and evolving legal frameworks. | Heavily regulated; subject to government policies. |
Which is better?
Litigation finance offers high potential returns by investing in legal cases with uncertain outcomes, appealing to investors seeking alternative assets with non-correlated risks. Infrastructure investments provide stable, long-term cash flows through essential public services and assets like transportation and utilities, making them attractive for risk-averse investors prioritizing steady income. The better choice depends on risk tolerance, investment horizon, and income preferences, with litigation finance suited for higher risk-reward profiles and infrastructure offering consistent, lower-risk returns.
Connection
Litigation finance attracts investment by providing capital to plaintiffs in exchange for a share of the financial recovery, creating new asset classes within infrastructure portfolios. Infrastructure funds increasingly allocate resources to litigation finance firms, leveraging steady cash flows from legal claims as alternative, low-correlation investments. This synergy enhances portfolio diversification and generates attractive risk-adjusted returns in both sectors.
Key Terms
Infrastructure:
Infrastructure finance involves funding long-term physical assets such as roads, bridges, and power plants that generate steady cash flows and economic growth. It typically demands substantial capital investment, carries moderate risk, and offers predictable returns over extended periods through tolls, tariffs, or government payments. Discover how investing in infrastructure finance can diversify your portfolio and support essential community development projects.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) leverage infrastructure finance to develop essential public assets, utilizing private sector investment to enhance efficiency and spread financial risk. Litigation finance, by contrast, funds legal claims and lawsuits, offering liquidity to plaintiffs while potentially yielding high returns independent of infrastructure projects. Explore the distinct roles and strategic advantages of PPP infrastructure and litigation finance to understand their impact on economic development.
Greenfield Project
Greenfield projects involve developing new infrastructure from scratch, often requiring substantial upfront capital and extended timelines, which distinguishes them from litigation finance typically focused on funding legal claims for returns. Infrastructure finance for Greenfield projects centers on long-term investments with risks tied to construction, regulatory approvals, and market demand, whereas litigation finance is more short-term and contingent on case outcomes. Explore detailed comparisons and strategic financing options for Greenfield projects to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
Source and External Links
Infrastructure - Wikipedia - Infrastructure consists of public and private physical structures such as roads, bridges, airports, water supply, and energy systems, with financing sourced from government, private investors, and international aid, and notable underinvestment issues especially in the U.S.
H.R.3684 - Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act - A major U.S. law providing funding for a wide range of infrastructure projects, including roads, bridges, rail, broadband, water systems, electric vehicle charging, and environmental remediation.
Infrastructure | FEMA.gov - Defines U.S. public infrastructure projects covering roads, bridges, transportation, water systems, energy facilities, utilities, broadband, and properties related to energy generation and distribution including EV charging.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com