Investment in the space economy focuses on advancing satellite technology, space exploration, and commercial ventures beyond Earth, driving innovation and creating new markets in microgravity research and extraterrestrial mining. Infrastructure investment targets the development and maintenance of physical systems such as transportation, utilities, and communication networks essential for economic growth and societal well-being. Discover how these distinct investment strategies shape the future of technology and economic development.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between space economy investment and infrastructure investment is crucial because space economy focuses on advanced technologies like satellite communications and space exploration, while infrastructure investment targets physical systems such as roads, bridges, and utilities. Space economy investments typically involve high-risk, high-reward ventures driven by innovation and government partnerships, whereas infrastructure investments offer stable, long-term returns essential for societal functioning. Distinguishing these ensures aligned financial strategies, risk management, and policy decisions tailored to each sector's unique characteristics. Informed investors can better allocate capital, support economic growth, and foster technological advancement by understanding these differences.
Comparison Table
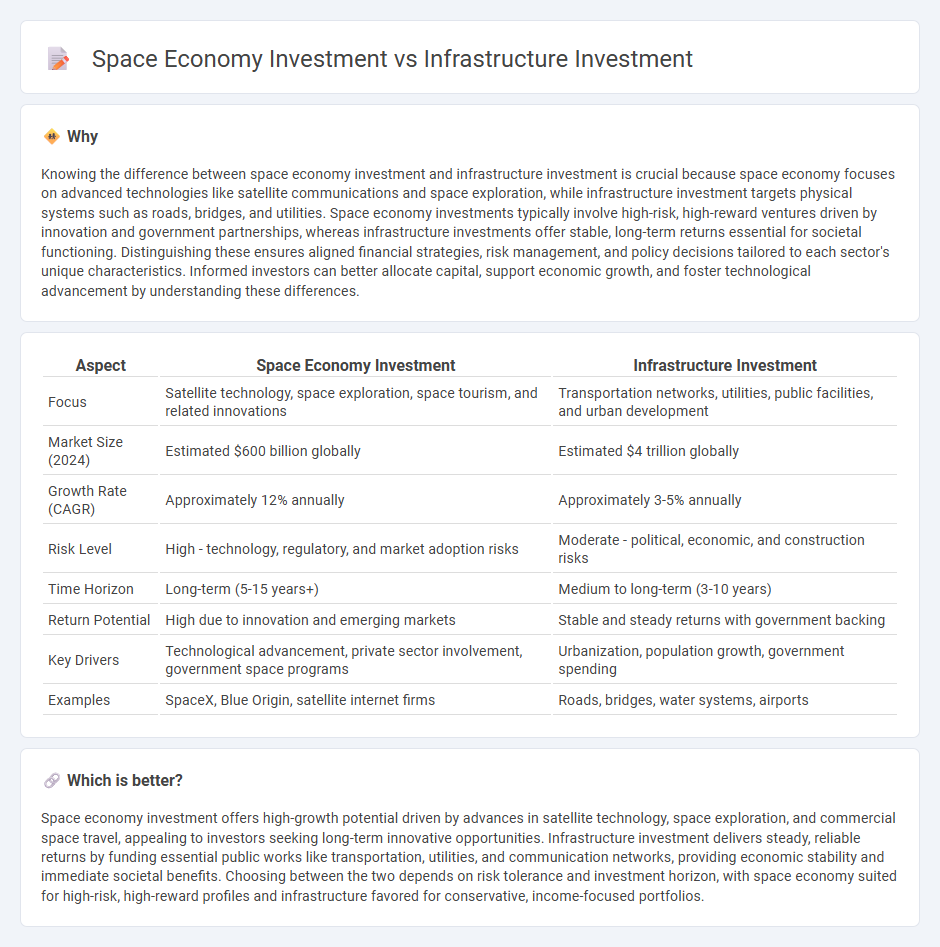
| Aspect | Space Economy Investment | Infrastructure Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Satellite technology, space exploration, space tourism, and related innovations | Transportation networks, utilities, public facilities, and urban development |
| Market Size (2024) | Estimated $600 billion globally | Estimated $4 trillion globally |
| Growth Rate (CAGR) | Approximately 12% annually | Approximately 3-5% annually |
| Risk Level | High - technology, regulatory, and market adoption risks | Moderate - political, economic, and construction risks |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (5-15 years+) | Medium to long-term (3-10 years) |
| Return Potential | High due to innovation and emerging markets | Stable and steady returns with government backing |
| Key Drivers | Technological advancement, private sector involvement, government space programs | Urbanization, population growth, government spending |
| Examples | SpaceX, Blue Origin, satellite internet firms | Roads, bridges, water systems, airports |
Which is better?
Space economy investment offers high-growth potential driven by advances in satellite technology, space exploration, and commercial space travel, appealing to investors seeking long-term innovative opportunities. Infrastructure investment delivers steady, reliable returns by funding essential public works like transportation, utilities, and communication networks, providing economic stability and immediate societal benefits. Choosing between the two depends on risk tolerance and investment horizon, with space economy suited for high-risk, high-reward profiles and infrastructure favored for conservative, income-focused portfolios.
Connection
Investment in the space economy drives advancements in satellite technology, launch infrastructure, and space exploration facilities, which require substantial infrastructure investment. Infrastructure investment supports the development of ground stations, data centers, and transportation networks critical for space operations, creating a symbiotic relationship. This interconnected growth accelerates innovation, enabling scalable economic benefits in telecommunications, Earth observation, and global connectivity sectors.
Key Terms
Asset Tangibility
Infrastructure investment centers on physical assets such as roads, bridges, and utilities, which provide tangible and enduring value to economic development. Space economy investment often involves both tangible assets like satellites and launch vehicles and intangible assets like data services and intellectual property, reflecting a hybrid model of asset tangibility. Explore the distinctions and implications of asset tangibility between these sectors to understand strategic investment opportunities.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory environment plays a pivotal role in shaping infrastructure investment by setting clear compliance standards, zoning laws, and public-private partnership frameworks that ensure project viability and risk management. In contrast, space economy investment is heavily influenced by international treaties, export controls, and technology transfer regulations, which impact collaboration and innovation in space exploration and commercialization. Explore more about how regulatory landscapes drive decision-making in infrastructure and space economy investments.
Risk Profile
Infrastructure investment typically involves lower risk profiles due to stable cash flows and government backing, making it attractive for conservative investors. Space economy investment carries higher risk driven by technological uncertainties, regulatory challenges, and longer development timelines but offers significant growth potential. Explore detailed risk assessments to understand which investment suits your portfolio objectives.
Source and External Links
Investment Pays - ASCE's 2025 Infrastructure Report Card - The U.S. faces a $3.7 trillion infrastructure funding gap, with $9.1 trillion needed for essential systems like roads, bridges, schools, and water, but only $5.4 trillion currently expected to be funded over the next decade.
Infrastructure investment - OECD - Infrastructure investment covers spending on new and improved transport networks--roads, rail, waterways, ports, and airports--delivering economic and social benefits by boosting productivity, creating jobs, and connecting communities.
The basics of infrastructure investing | abrdn - Long-term infrastructure investment is driven by energy transition, demographic shifts, and urbanization, while offering diversified opportunities from renewable energy projects to urban transport upgrades and rural broadband expansion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com