Private credit funds focus on providing direct loans to companies, often targeting middle-market firms with flexible financing solutions. Hedge funds employ diverse strategies, including long and short positions, derivatives, and arbitrage, aiming to generate high returns across various asset classes. Explore the distinct risk profiles, liquidity features, and performance metrics to understand which investment approach aligns with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between private credit funds and hedge funds is crucial for investors seeking tailored risk-return profiles, as private credit funds typically focus on direct lending with more predictable income streams, while hedge funds employ diverse strategies aiming for high returns with greater volatility. Private credit funds generally provide steady cash flow through loans to private companies, offering lower risk compared to hedge funds' complex, leveraged investments across various asset classes. This knowledge allows investors to align their portfolios with specific financial goals and risk tolerance, optimizing capital allocation. Recognizing the structural, liquidity, and regulatory distinctions between these fund types enhances informed decision-making and portfolio diversification.
Comparison Table
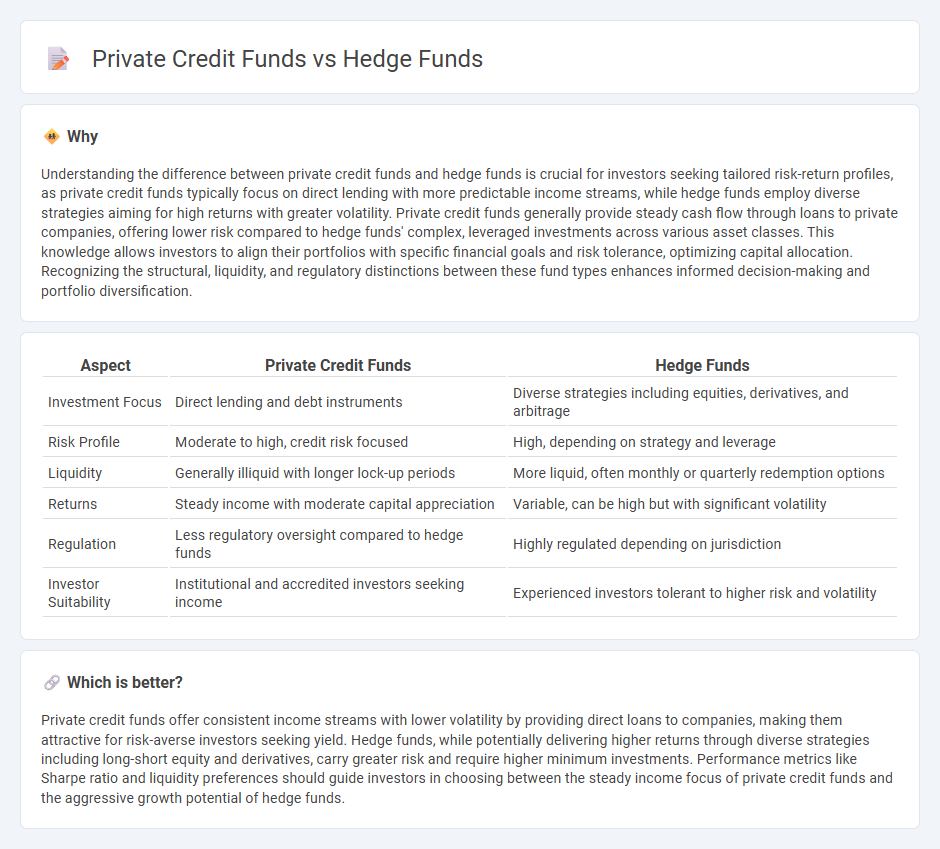
| Aspect | Private Credit Funds | Hedge Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Focus | Direct lending and debt instruments | Diverse strategies including equities, derivatives, and arbitrage |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high, credit risk focused | High, depending on strategy and leverage |
| Liquidity | Generally illiquid with longer lock-up periods | More liquid, often monthly or quarterly redemption options |
| Returns | Steady income with moderate capital appreciation | Variable, can be high but with significant volatility |
| Regulation | Less regulatory oversight compared to hedge funds | Highly regulated depending on jurisdiction |
| Investor Suitability | Institutional and accredited investors seeking income | Experienced investors tolerant to higher risk and volatility |
Which is better?
Private credit funds offer consistent income streams with lower volatility by providing direct loans to companies, making them attractive for risk-averse investors seeking yield. Hedge funds, while potentially delivering higher returns through diverse strategies including long-short equity and derivatives, carry greater risk and require higher minimum investments. Performance metrics like Sharpe ratio and liquidity preferences should guide investors in choosing between the steady income focus of private credit funds and the aggressive growth potential of hedge funds.
Connection
Private credit funds and hedge funds are connected through their mutual involvement in alternative investment strategies aimed at generating higher returns and diversifying portfolios. Both fund types often co-invest in debt instruments and distressed assets, leveraging flexible capital structures to capitalize on market inefficiencies. Collaboration between private credit and hedge funds enhances liquidity and risk management, benefiting investors seeking non-traditional sources of yield.
Key Terms
Leverage
Hedge funds typically employ higher leverage, with ratios often ranging from 2:1 to 6:1, to amplify returns through diverse strategies such as long-short equity and global macro. Private credit funds use modest leverage, generally between 1:1 and 2:1, focusing on direct lending and generating steady income with lower risk exposure. Explore the nuanced leverage strategies that differentiate hedge funds and private credit funds to better understand their risk-return profiles.
Liquidity
Hedge funds typically offer higher liquidity with daily or weekly redemptions, allowing investors to access capital quickly, whereas private credit funds often impose longer lock-up periods ranging from several months to years due to the illiquid nature of their underlying loans. The liquidity profile of hedge funds suits investors seeking flexibility, while private credit funds appeal to those targeting stable, income-generating investments with lower volatility. Discover more about how liquidity considerations impact investment strategies in alternative asset classes.
Underlying assets
Hedge funds primarily invest in liquid securities such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and currencies to exploit market inefficiencies and achieve high returns. Private credit funds focus on direct lending to private companies, often targeting illiquid debt instruments like mezzanine loans, senior secured loans, and distressed debt that provide steady income streams. Explore further to understand how asset allocation shapes risk and return in these distinct investment vehicles.
Source and External Links
Hedge Funds: Overview, Recruitment, Careers & Salaries - A hedge fund is an investment firm that raises capital from institutional and accredited investors to invest in various financial assets using diverse strategies to achieve absolute returns and reduce risks, differing from mutual funds by targeting absolute rather than relative returns.
Hedge Funds - Hedge funds are private, unregistered investment funds that pool money from qualified investors and pursue flexible, often riskier investment strategies not available to mutual funds, and are not subject to the same regulations or marketed to retail investors.
Hedge fund - Hedge funds are pooled investment funds using complex trading and risk management techniques, charging management and performance fees, historically intended to hedge risk but now employing diverse strategies, and pose systemic risks due to leverage and liquidity concerns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com