Patent monetization transforms intellectual property into a revenue-generating asset, providing companies with non-dilutive funding without increasing liabilities. Debt financing involves borrowing capital that requires repayment with interest, impacting cash flow but preserving ownership equity. Explore the strategic advantages and challenges of patent monetization compared to debt financing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between patent monetization and debt financing is crucial for optimizing investment strategies, as patent monetization leverages intellectual property to generate revenue without increasing liabilities, while debt financing involves borrowing funds that must be repaid with interest. Patent monetization can provide cash flow through licensing or selling patents, enhancing a company's asset base and innovation potential. Debt financing impacts a company's credit profile and financial risk, influencing long-term capital structure and cost of capital. Investors benefit from knowing these distinctions to make informed decisions about risk, returns, and growth potential.
Comparison Table
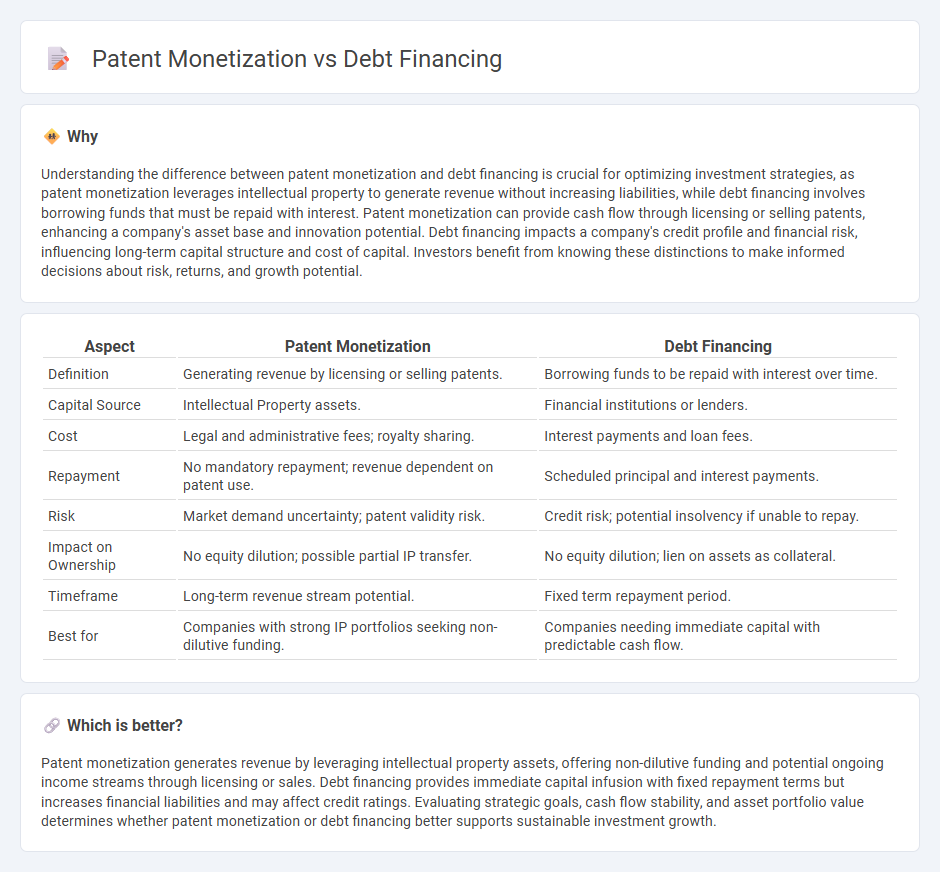
| Aspect | Patent Monetization | Debt Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generating revenue by licensing or selling patents. | Borrowing funds to be repaid with interest over time. |
| Capital Source | Intellectual Property assets. | Financial institutions or lenders. |
| Cost | Legal and administrative fees; royalty sharing. | Interest payments and loan fees. |
| Repayment | No mandatory repayment; revenue dependent on patent use. | Scheduled principal and interest payments. |
| Risk | Market demand uncertainty; patent validity risk. | Credit risk; potential insolvency if unable to repay. |
| Impact on Ownership | No equity dilution; possible partial IP transfer. | No equity dilution; lien on assets as collateral. |
| Timeframe | Long-term revenue stream potential. | Fixed term repayment period. |
| Best for | Companies with strong IP portfolios seeking non-dilutive funding. | Companies needing immediate capital with predictable cash flow. |
Which is better?
Patent monetization generates revenue by leveraging intellectual property assets, offering non-dilutive funding and potential ongoing income streams through licensing or sales. Debt financing provides immediate capital infusion with fixed repayment terms but increases financial liabilities and may affect credit ratings. Evaluating strategic goals, cash flow stability, and asset portfolio value determines whether patent monetization or debt financing better supports sustainable investment growth.
Connection
Patent monetization generates revenue by licensing or selling intellectual property, which can enhance a company's balance sheet and creditworthiness. This improved financial position enables easier access to debt financing with favorable terms, as lenders perceive lower risk. Consequently, leveraging patents as assets supports strategic borrowing to fuel further investment and growth.
Key Terms
Interest Rate
Debt financing typically involves borrowing funds with fixed or variable interest rates determined by market conditions and creditworthiness, often leading to predictable repayment schedules. Patent monetization, through licensing or selling intellectual property, can generate income without interest charges but may entail complex valuation and negotiation processes. Explore strategies to optimize your capital cost by understanding the differences in interest impact between debt and patent monetization.
Intellectual Property Valuation
Debt financing leverages borrowed capital that must be repaid with interest, often requiring tangible assets or solid credit for approval. Patent monetization involves unlocking the value of intellectual property through licensing, sales, or securitization, relying heavily on accurate intellectual property valuation techniques such as income, market, and cost approaches. Explore comprehensive methods to assess intellectual property valuation for optimized financing strategies.
Collateral
Debt financing relies heavily on collateral, often requiring tangible assets like property or equipment to secure loans and minimize lender risk. Patent monetization transforms intellectual property into revenue streams, using patents themselves as innovative collateral to attract investment without traditional physical assets. Explore how leveraging patent collateral can diversify your financing strategy and unlock new capital opportunities.
Source and External Links
Debt Financing - Overview, Options, Pros and Cons - Debt financing is when a company raises money by selling debt instruments like bank loans or bonds, promising to repay with interest, often used by established businesses for capital expenditures or working capital.
Debt Financing: Definition & How It Works - Debt financing involves borrowing money through various forms such as bank loans, credit lines, bonds, or private credit, with repayment typically scheduled along with interest, suitable for different business stages including startups with venture debt.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Debt Financing - Debt financing allows businesses to secure funds without diluting ownership, with fixed repayment obligations and the possibility of collateral requirements, offering financial flexibility but obligating regular payments regardless of business performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com