Forestry investment involves the long-term growth and management of timber assets, offering sustainable returns through both wood production and carbon credit opportunities. Commodity trading, by contrast, focuses on the short-term buying and selling of raw materials such as oil, metals, and agricultural products, driven by market volatility and price speculation. Discover the distinct benefits and risks of forestry investment compared to commodity trading to make informed financial decisions.
Why it is important
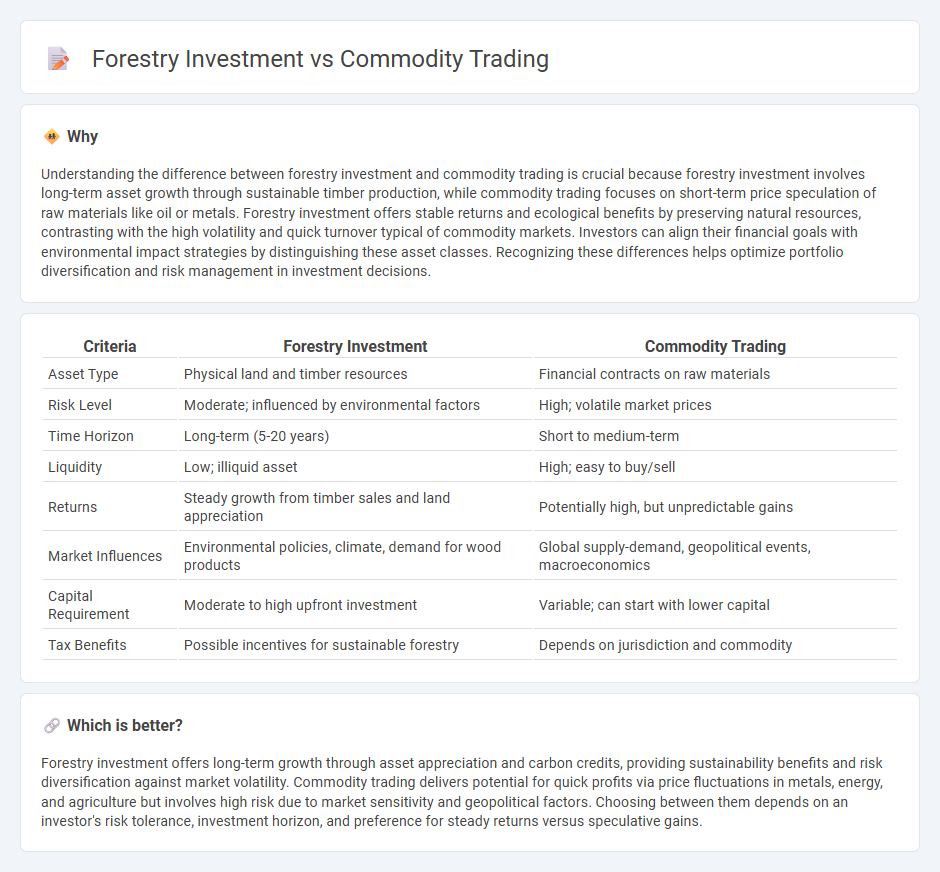
Understanding the difference between forestry investment and commodity trading is crucial because forestry investment involves long-term asset growth through sustainable timber production, while commodity trading focuses on short-term price speculation of raw materials like oil or metals. Forestry investment offers stable returns and ecological benefits by preserving natural resources, contrasting with the high volatility and quick turnover typical of commodity markets. Investors can align their financial goals with environmental impact strategies by distinguishing these asset classes. Recognizing these differences helps optimize portfolio diversification and risk management in investment decisions.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Forestry Investment | Commodity Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Physical land and timber resources | Financial contracts on raw materials |
| Risk Level | Moderate; influenced by environmental factors | High; volatile market prices |
| Time Horizon | Long-term (5-20 years) | Short to medium-term |
| Liquidity | Low; illiquid asset | High; easy to buy/sell |
| Returns | Steady growth from timber sales and land appreciation | Potentially high, but unpredictable gains |
| Market Influences | Environmental policies, climate, demand for wood products | Global supply-demand, geopolitical events, macroeconomics |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate to high upfront investment | Variable; can start with lower capital |
| Tax Benefits | Possible incentives for sustainable forestry | Depends on jurisdiction and commodity |
Which is better?
Forestry investment offers long-term growth through asset appreciation and carbon credits, providing sustainability benefits and risk diversification against market volatility. Commodity trading delivers potential for quick profits via price fluctuations in metals, energy, and agriculture but involves high risk due to market sensitivity and geopolitical factors. Choosing between them depends on an investor's risk tolerance, investment horizon, and preference for steady returns versus speculative gains.
Connection
Forestry investment and commodity trading are interconnected through the financial markets where timber and related products serve as tradable commodities, reflecting supply and demand fluctuations. Investments in sustainable forestry generate raw materials like lumber and pulp, which directly influence commodity prices on exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Market dynamics in commodity trading affect the profitability and valuation of forestry assets, linking ecological resource management with global trade and investment strategies.
Key Terms
Asset Liquidity
Commodity trading offers high asset liquidity with the ability to quickly buy and sell futures contracts on agriculture, energy, or metal markets, ensuring rapid capital turnover. Forestry investment, by contrast, involves long-term asset holding where liquidity is limited due to the growth cycle of timber and market access constraints. Explore deeper insights into liquidity differences between these two asset classes to optimize your investment strategy.
Market Volatility
Commodity trading experiences high market volatility driven by factors such as geopolitical events, weather conditions, and supply-demand fluctuations, leading to rapid price shifts. Forestry investment generally offers lower volatility due to the long growth cycles of timber and stable demand in construction and paper industries. Explore in-depth analyses to understand how market volatility differentially impacts these two asset classes.
Sustainability
Commodity trading often involves fluctuating markets for raw materials like oil, metals, and agricultural products, with sustainability gains dependent on supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing. Forestry investment focuses on long-term ecological and economic benefits, promoting carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and sustainable timber production. Explore how integrating sustainability principles in these sectors can drive responsible investment and environmental impact.
Source and External Links
Commodity Market - A market where primary goods such as agricultural products and raw materials are traded.
The Critical Role of Commodity Trading in Times of Uncertainty - The article discusses the resilience of commodity trading despite market volatility and global uncertainties.
Commodity Trading Report 2024 - Highlights the evolution of the commodity trading industry, including rebalancing and strategic investments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com