Fractional ownership allows investors to buy partial shares of high-value assets, enabling diversified portfolios with relatively low capital. Crowdfunding pools funds from a large number of investors to finance projects or startups, often via specialized online platforms. Discover how these innovative investment strategies can fit your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership and crowd investing is crucial for informed investment decisions, as fractional ownership entails holding a legally recognized share of an asset, while crowd investing involves pooling funds to support projects without direct ownership rights. Fractional ownership allows investors to gain tangible equity in real estate, art, or other high-value assets, offering potential for asset appreciation and voting rights. Crowd investing typically targets startups or small businesses, providing returns through profit sharing or equity stakes but carries higher risk due to market volatility and business uncertainty. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize portfolio diversification and risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
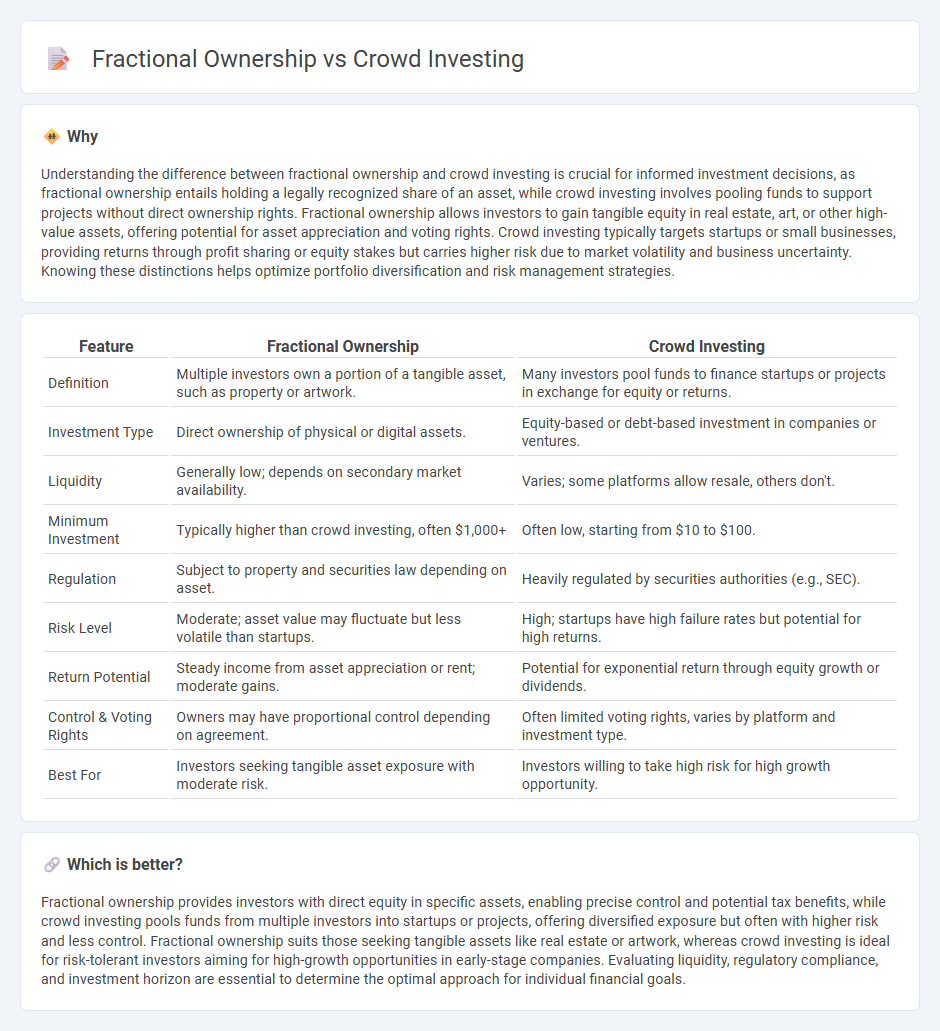
| Feature | Fractional Ownership | Crowd Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple investors own a portion of a tangible asset, such as property or artwork. | Many investors pool funds to finance startups or projects in exchange for equity or returns. |
| Investment Type | Direct ownership of physical or digital assets. | Equity-based or debt-based investment in companies or ventures. |
| Liquidity | Generally low; depends on secondary market availability. | Varies; some platforms allow resale, others don't. |
| Minimum Investment | Typically higher than crowd investing, often $1,000+ | Often low, starting from $10 to $100. |
| Regulation | Subject to property and securities law depending on asset. | Heavily regulated by securities authorities (e.g., SEC). |
| Risk Level | Moderate; asset value may fluctuate but less volatile than startups. | High; startups have high failure rates but potential for high returns. |
| Return Potential | Steady income from asset appreciation or rent; moderate gains. | Potential for exponential return through equity growth or dividends. |
| Control & Voting Rights | Owners may have proportional control depending on agreement. | Often limited voting rights, varies by platform and investment type. |
| Best For | Investors seeking tangible asset exposure with moderate risk. | Investors willing to take high risk for high growth opportunity. |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership provides investors with direct equity in specific assets, enabling precise control and potential tax benefits, while crowd investing pools funds from multiple investors into startups or projects, offering diversified exposure but often with higher risk and less control. Fractional ownership suits those seeking tangible assets like real estate or artwork, whereas crowd investing is ideal for risk-tolerant investors aiming for high-growth opportunities in early-stage companies. Evaluating liquidity, regulatory compliance, and investment horizon are essential to determine the optimal approach for individual financial goals.
Connection
Fractional ownership and crowd investing both democratize access to high-value assets by allowing multiple investors to own a portion of property or securities. These models utilize online platforms to pool funds, reducing individual capital requirements while diversifying investment portfolios. Together, fractional ownership and crowd investing enhance liquidity and create new opportunities in real estate, startups, and alternative asset classes.
Key Terms
**Crowd Investing:**
Crowd investing allows multiple investors to pool their capital into startups or projects, gaining equity stakes and potential returns based on company performance. This model provides access to diverse investment opportunities with relatively low minimum contributions compared to traditional venture capital. Explore further to understand how crowd investing can diversify your portfolio and support innovative enterprises.
Equity Crowdfunding
Equity crowdfunding enables investors to acquire shares in a startup or growing company, offering potential financial returns based on the company's success. Crowd investing involves pooling funds from multiple investors, while fractional ownership divides a specific asset into shares for collective possession, often related to physical assets like real estate. Explore how equity crowdfunding distinctively balances risk and return by combining elements of both models.
Pooled Capital
Pooled capital in crowd investing combines funds from multiple investors to finance projects or startups, enabling access to larger-scale opportunities and diversified risk. Fractional ownership divides a single asset, such as real estate or art, into shares that investors buy, granting partial ownership and proportional benefits from the asset's appreciation or income. Discover how pooled capital strategies in crowd investing can maximize your investment potential.
Source and External Links
5 Best Crowdfunding Platforms For Investing In Startups | Bankrate - Crowd investing, also known as equity crowdfunding, allows individuals to invest in startups in exchange for ownership shares, making startup investing accessible beyond just accredited investors and venture capital firms.
Crowdfunding Offerings and Investments - Crowd investing involves raising capital through many small investments from individuals, often conducted via intermediary portals, with SEC rules limiting raises to $5 million and setting investment caps for non-accredited investors.
Invest in founders building the future | Wefunder - Platforms like Wefunder enable crowd investing by allowing investors to browse startups, invest money for equity, and participate in long-term angel investing with access to company updates and community support.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com